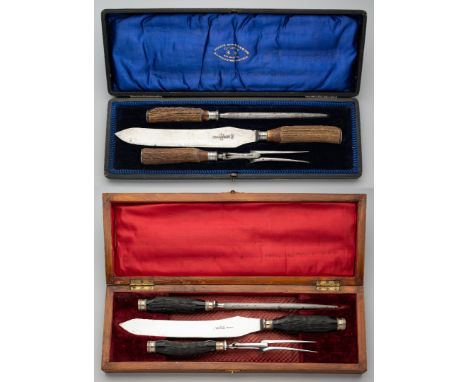
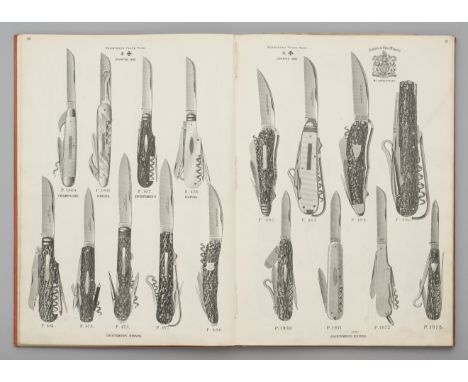
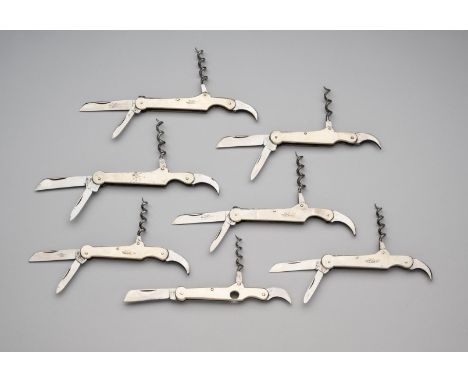
A LARGE DISPLAY BOWIE KNIFE, JOSEPH RODGERS & SONS, 6 NORFOLK STREET, SHEFFIELD, LATE 19TH CENTURY with heavy blade formed with a spear point, chevron fluted back-edge of V-section and a long slender fuller on each face, stamped with the maker’s details and star and cross mark on one face, rectangular ricasso, nickel silver cross-piece cast and chased with foliage in low relief, comprising a pair of slightly curved quillons enclosing an elliptical guard beneath, natural staghorn angular grip, and gadrooned pommel (flattened for display), 36.0 cm blade LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 103. In the nineteenth century, Rodgers had an unsurpassed reputation and history that was synonymous with the cutlery trade. The family's first cutler, John Rodgers (1701-85), is recorded around 1724, with a workshop near the present cathedral. In the same year the Company of Cutlers 'let' him a mark, a Star and Maltese Cross, which became world famous in later years. John Rodgers had three sons, John (1731-1811), Joseph (1743-1821), and Maurice (c.1747-1824) who joined the business and succeeded him. They are recorded with more workshops by 1780 and the business soon extended to occupy a nearby block of buildings at 6 Norfolk Street, an address that became as famous as Rodgers’ trade mark. By the early 19th century their trade had expanded from pen and pocket knives to include table cutlery and scissors. By 1817 the General Sheffield Directory lists the firm as ‘merchants, factors, table and pocket knife, and razor manufacturers’. In 1821 John’s son Joseph died and his sons continued the business under the leadership of the younger John (grandson of the founder). John was described as ‘unobtrusive in his manner’ but was ambitious and one of the founding partners of the Sheffield Banking Co. He had a flair for marketing and travelled the country taking orders. Not only was his firm’s output and range greater than any other Sheffield firm, but its quality was superior. The company’s manifesto states: ‘The principle on which the manufacture of cutlery is carried on by this firm is – quality first … [and] … price comes second’. He began making exhibitions knives and presented George IV with a minute specimen of cutlery with 57 blades, which occupied only an inch [25mm] when closed. In 1822, Rodgers’ was awarded its first Royal Warrant. Another fourteen royal appointments, from British and overseas royal dignitaries, followed over the next eighty years, and its company history was duly titled: Under Five Sovereigns. John Rodgers next commissioned the Year Knife, with a blade for every year (1821) and opened his sensational cutlery showroom in Norfolk Street where visitors came to marvel at Rodgers’ creations. Perhaps the greatest highlight shown there was the Norfolk Knife, an over 30 inch long sportsman’s knife with 75 blades and tools, that Rodgers’ produced for the Great Exhibition in 1851. The showroom proved particularly popular with Americans whose trade played a significant role in the firm’s expansion. Additionally, they looked East, with agents in Calcutta, Bombay, and Hong Kong by the mid-19th century. These markets enabled Rodgers to become the largest cutlery factory in Sheffield. The number of workmen appears to have grown from about 300 in the late 1820s, to over 500 in the 1840s. In 1871 the business became a limited company with Joseph Rodgers (1828-1883), grandson of the Joseph Rodgers who had died in 1821 and Robert Newbold as managing directors. Joseph died on 12 May 1883 and Newbold became the chairman and managing director. The firm continued to expand with offices in London, New York, New Orleans, Montreal, Toronto, Calcutta, Bombay and Havana. Their work force in 1871 was around 1,200 and accounted for one-seventh of all Sheffield’s American cutlery trade. In 1876 the American market was stagnating and Rodgers’ began looking elsewhere with a focus on trade in the Middle East, India and Australia. Notably the name ‘Rujjus’ or ‘Rojers’ was said to have entered the language as an adjective expressing superb quality in Persia, India and Ceylon. By 1888, the value of Rodgers’ shares had more than doubled and, in 1889, a silver and electro-plate showroom was opened in London. At this time, Rodgers acquired the scissors business of Joseph Hobson & Son. Rodgers’ produced catalogues that were packed with every type of knife imaginable. Pocket knives were made in scores of different styles. Ornate daggers and Bowie knives and complicated horseman’s knives were made routinely. Some patterns, such as the Congress knife and Wharncliffe knife, were Rodgers’ own design. The Wharncliffe – with its serpentine handle and beaked master blade – was apparently designed after a dinner attended by Rodgers’ patron Lord Wharncliffe. The firm’s workmanship was usually backed by the best materials. Rodgers’ ivory cellar in Norfolk Street was crammed with giant tusks and was regarded as one of the hidden sights of the town. Four or five men were constantly employed in sawing the tusks, and around twenty four tons of ivory were used a year around 1882. Rodgers’ appetite for stag was no less insatiable: deer horns and antlers filled another cellar and pearl from the Philippines and was also cut there. Around 1890, Rodgers’ began forging its own shear steel and in 1894 they began melting crucible steel. Newbold retired in 1890 and the grandsons of Maurice Rodgers, Maurice George Rodgers (1855-1898) and John Rodgers (1856-1919), became joint-managing directors. The McKinley Tariff Act of 1890 halved their American business and consequently they toured South Africa. Despite increasing foreign competition and the decline of the American market, Rodgers’ prospered before the First World War. However, workers’ wages were cut while the partners continued to take significant dividend which culminated in a prolonged and bitter strike. The First World War saw a decline in the business which continued steadily until the 1975 when it was absorbed by Richards and ceased trading in 1983. Joseph Rodgers & Sons left an enduring legacy in its knives. Its dazzling exhibition pieces and other fine cutlery show that the company’s reputation as Sheffield’s foremost knife maker was well founded. Abbreviated from Geoffrey Tweedale 2019. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
We found 596780 price guide item(s) matching your search
There are 596780 lots that match your search criteria. Subscribe now to get instant access to the full price guide service.
Click here to subscribe- List
- Grid
-
596780 item(s)/page
A LARGE DISPLAY BOWIE KNIFE IN THE EASTERN STYLE, JOSEPH RODGERS, SHEFFIELD, EARLY 20TH CENTURY with strongly curved ‘scimitar’ blade with a double-edged point, fullered and elaborately filed over the lower back-edge, engraved with the maker’s details including star and cross mark, and a crown dividing the royal initials GR (rubbed), silver plated cross-piece and pommel each engraved with flowers and foliage and chequered grip (the inner face flattened for display), framed, the knife 48.7 cm overall LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 100. In the nineteenth century, Rodgers had an unsurpassed reputation and history that was synonymous with the cutlery trade. The family's first cutler, John Rodgers (1701-85), is recorded around 1724, with a workshop near the present cathedral. In the same year the Company of Cutlers 'let' him a mark, a Star and Maltese Cross, which became world famous in later years. John Rodgers had three sons, John (1731-1811), Joseph (1743-1821), and Maurice (c.1747-1824) who joined the business and succeeded him. They are recorded with more workshops by 1780 and the business soon extended to occupy a nearby block of buildings at 6 Norfolk Street, an address that became as famous as Rodgers’ trade mark. By the early 19th century their trade had expanded from pen and pocket knives to include table cutlery and scissors. By 1817 the General Sheffield Directory lists the firm as ‘merchants, factors, table and pocket knife, and razor manufacturers’. In 1821 John’s son Joseph died and his sons continued the business under the leadership of the younger John (grandson of the founder). John was described as ‘unobtrusive in his manner’ but was ambitious and one of the founding partners of the Sheffield Banking Co. He had a flair for marketing and travelled the country taking orders. Not only was his firm’s output and range greater than any other Sheffield firm, but its quality was superior. The company’s manifesto states: ‘The principle on which the manufacture of cutlery is carried on by this firm is – quality first … [and] … price comes second’. He began making exhibitions knives and presented George IV with a minute specimen of cutlery with 57 blades, which occupied only an inch [25mm] when closed. In 1822, Rodgers’ was awarded its first Royal Warrant. Another fourteen royal appointments, from British and overseas royal dignitaries, followed over the next eighty years, and its company history was duly titled: Under Five Sovereigns. John Rodgers next commissioned the Year Knife, with a blade for every year (1821) and opened his sensational cutlery showroom in Norfolk Street where visitors came to marvel at Rodgers’ creations. Perhaps the greatest highlight shown there was the Norfolk Knife, an over 30 inch long sportsman’s knife with 75 blades and tools, that Rodgers’ produced for the Great Exhibition in 1851. The showroom proved particularly popular with Americans whose trade played a significant role in the firm’s expansion. Additionally, they looked East, with agents in Calcutta, Bombay, and Hong Kong by the mid-19th century. These markets enabled Rodgers to become the largest cutlery factory in Sheffield. The number of workmen appears to have grown from about 300 in the late 1820s, to over 500 in the 1840s. In 1871 the business became a limited company with Joseph Rodgers (1828-1883), grandson of the Joseph Rodgers who had died in 1821 and Robert Newbold as managing directors. Joseph died on 12 May 1883 and Newbold became the chairman and managing director. The firm continued to expand with offices in London, New York, New Orleans, Montreal, Toronto, Calcutta, Bombay and Havana. Their work force in 1871 was around 1,200 and accounted for one-seventh of all Sheffield’s American cutlery trade. In 1876 the American market was stagnating and Rodgers’ began looking elsewhere with a focus on trade in the Middle East, India and Australia. Notably the name ‘Rujjus’ or ‘Rojers’ was said to have entered the language as an adjective expressing superb quality in Persia, India and Ceylon. By 1888, the value of Rodgers’ shares had more than doubled and, in 1889, a silver and electro-plate showroom was opened in London. At this time, Rodgers acquired the scissors business of Joseph Hobson & Son. Rodgers’ produced catalogues that were packed with every type of knife imaginable. Pocket knives were made in scores of different styles. Ornate daggers and Bowie knives and complicated horseman’s knives were made routinely. Some patterns, such as the Congress knife and Wharncliffe knife, were Rodgers’ own design. The Wharncliffe – with its serpentine handle and beaked master blade – was apparently designed after a dinner attended by Rodgers’ patron Lord Wharncliffe. The firm’s workmanship was usually backed by the best materials. Rodgers’ ivory cellar in Norfolk Street was crammed with giant tusks and was regarded as one of the hidden sights of the town. Four or five men were constantly employed in sawing the tusks, and around twenty four tons of ivory were used a year around 1882. Rodgers’ appetite for stag was no less insatiable: deer horns and antlers filled another cellar and pearl from the Philippines and was also cut there. Around 1890, Rodgers’ began forging its own shear steel and in 1894 they began melting crucible steel. Newbold retired in 1890 and the grandsons of Maurice Rodgers, Maurice George Rodgers (1855-1898) and John Rodgers (1856-1919), became joint-managing directors. The McKinley Tariff Act of 1890 halved their American business and consequently they toured South Africa. Despite increasing foreign competition and the decline of the American market, Rodgers’ prospered before the First World War. However, workers’ wages were cut while the partners continued to take significant dividend which culminated in a prolonged and bitter strike. The First World War saw a decline in the business which continued steadily until the 1975 when it was absorbed by Richards and ceased trading in 1983. Joseph Rodgers & Sons left an enduring legacy in its knives. Its dazzling exhibition pieces and other fine cutlery show that the company’s reputation as Sheffield’s foremost knife maker was well founded. Abbreviated from Geoffrey Tweedale 2019. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A LARGE BOWIE KNIFE, JOSEPH RODGERS & SONS, 6 NORFOLK STREET, SHEFFIELD, LATE 19TH CENTURY with strongly curved ‘scimitar’ blade double-edged over its upper half and elaborately filed over the lower back-edge, struck with the maker’s details, and cross and star mark at the ricasso on one face and ‘double sheer steel’ and ‘hand forged’ on the other, thick burnished cross-piece with filed edges, gilt copper alloy cylindrical grip cast and chased with an elaborate frieze of vine fruit and foliage against a finely matted ground, and the top with the owners monogramed initials, 45.7 cm overall LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 101. In the nineteenth century, Rodgers had an unsurpassed reputation and history that was synonymous with the cutlery trade. The family's first cutler, John Rodgers (1701-85), is recorded around 1724, with a workshop near the present cathedral. In the same year the Company of Cutlers 'let' him a mark, a Star and Maltese Cross, which became world famous in later years. John Rodgers had three sons, John (1731-1811), Joseph (1743-1821), and Maurice (c.1747-1824) who joined the business and succeeded him. They are recorded with more workshops by 1780 and the business soon extended to occupy a nearby block of buildings at 6 Norfolk Street, an address that became as famous as Rodgers’ trade mark. By the early 19th century their trade had expanded from pen and pocket knives to include table cutlery and scissors. By 1817 the General Sheffield Directory lists the firm as ‘merchants, factors, table and pocket knife, and razor manufacturers’. In 1821 John’s son Joseph died and his sons continued the business under the leadership of the younger John (grandson of the founder). John was described as ‘unobtrusive in his manner’ but was ambitious and one of the founding partners of the Sheffield Banking Co. He had a flair for marketing and travelled the country taking orders. Not only was his firm’s output and range greater than any other Sheffield firm, but its quality was superior. The company’s manifesto states: ‘The principle on which the manufacture of cutlery is carried on by this firm is – quality first … [and] … price comes second’. He began making exhibitions knives and presented George IV with a minute specimen of cutlery with 57 blades, which occupied only an inch [25mm] when closed. In 1822, Rodgers’ was awarded its first Royal Warrant. Another fourteen royal appointments, from British and overseas royal dignitaries, followed over the next eighty years, and its company history was duly titled: Under Five Sovereigns. John Rodgers next commissioned the Year Knife, with a blade for every year (1821) and opened his sensational cutlery showroom in Norfolk Street where visitors came to marvel at Rodgers’ creations. Perhaps the greatest highlight shown there was the Norfolk Knife, an over 30 inch long sportsman’s knife with 75 blades and tools, that Rodgers’ produced for the Great Exhibition in 1851. The showroom proved particularly popular with Americans whose trade played a significant role in the firm’s expansion. Additionally, they looked East, with agents in Calcutta, Bombay, and Hong Kong by the mid-19th century. These markets enabled Rodgers to become the largest cutlery factory in Sheffield. The number of workmen appears to have grown from about 300 in the late 1820s, to over 500 in the 1840s. In 1871 the business became a limited company with Joseph Rodgers (1828-1883), grandson of the Joseph Rodgers who had died in 1821 and Robert Newbold as managing directors. Joseph died on 12 May 1883 and Newbold became the chairman and managing director. The firm continued to expand with offices in London, New York, New Orleans, Montreal, Toronto, Calcutta, Bombay and Havana. Their work force in 1871 was around 1,200 and accounted for one-seventh of all Sheffield’s American cutlery trade. In 1876 the American market was stagnating and Rodgers’ began looking elsewhere with a focus on trade in the Middle East, India and Australia. Notably the name ‘Rujjus’ or ‘Rojers’ was said to have entered the language as an adjective expressing superb quality in Persia, India and Ceylon. By 1888, the value of Rodgers’ shares had more than doubled and, in 1889, a silver and electro-plate showroom was opened in London. At this time, Rodgers acquired the scissors business of Joseph Hobson & Son. Rodgers’ produced catalogues that were packed with every type of knife imaginable. Pocket knives were made in scores of different styles. Ornate daggers and Bowie knives and complicated horseman’s knives were made routinely. Some patterns, such as the Congress knife and Wharncliffe knife, were Rodgers’ own design. The Wharncliffe – with its serpentine handle and beaked master blade – was apparently designed after a dinner attended by Rodgers’ patron Lord Wharncliffe. The firm’s workmanship was usually backed by the best materials. Rodgers’ ivory cellar in Norfolk Street was crammed with giant tusks and was regarded as one of the hidden sights of the town. Four or five men were constantly employed in sawing the tusks, and around twenty four tons of ivory were used a year around 1882. Rodgers’ appetite for stag was no less insatiable: deer horns and antlers filled another cellar and pearl from the Philippines and was also cut there. Around 1890, Rodgers’ began forging its own shear steel and in 1894 they began melting crucible steel. Newbold retired in 1890 and the grandsons of Maurice Rodgers, Maurice George Rodgers (1855-1898) and John Rodgers (1856-1919), became joint-managing directors. The McKinley Tariff Act of 1890 halved their American business and consequently they toured South Africa. Despite increasing foreign competition and the decline of the American market, Rodgers’ prospered before the First World War. However, workers’ wages were cut while the partners continued to take significant dividend which culminated in a prolonged and bitter strike. The First World War saw a decline in the business which continued steadily until the 1975 when it was absorbed by Richards and ceased trading in 1983. Joseph Rodgers & Sons left an enduring legacy in its knives. Its dazzling exhibition pieces and other fine cutlery show that the company’s reputation as Sheffield’s foremost knife maker was well founded. Abbreviated from Geoffrey Tweedale 2019. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A BOWIE KNIFE, JOSEPH RODGERS & SONS, CUTLERS TO THEIR MAJESTIES, NO. 6 NORFOLK STREET, SHEFFIELD, CIRCA 1880 with single-edged blade formed with a false swage and stamped with the maker’s details including cross and star mark on one face, German silver hilt comprising shaped guard with integral ferrule, back-strap shaped for the fingers and domed pommel, and chequered horn grips retained by four rivets, in its leather scabbard with large shaped German silver mounts and later belt loop, 22.5 cm blade LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 259. In the nineteenth century, Rodgers had an unsurpassed reputation and history that was synonymous with the cutlery trade. The family's first cutler, John Rodgers (1701-85), is recorded around 1724, with a workshop near the present cathedral. In the same year the Company of Cutlers 'let' him a mark, a Star and Maltese Cross, which became world famous in later years. John Rodgers had three sons, John (1731-1811), Joseph (1743-1821), and Maurice (c.1747-1824) who joined the business and succeeded him. They are recorded with more workshops by 1780 and the business soon extended to occupy a nearby block of buildings at 6 Norfolk Street, an address that became as famous as Rodgers’ trade mark. By the early 19th century their trade had expanded from pen and pocket knives to include table cutlery and scissors. By 1817 the General Sheffield Directory lists the firm as ‘merchants, factors, table and pocket knife, and razor manufacturers’. In 1821 John’s son Joseph died and his sons continued the business under the leadership of the younger John (grandson of the founder). John was described as ‘unobtrusive in his manner’ but was ambitious and one of the founding partners of the Sheffield Banking Co. He had a flair for marketing and travelled the country taking orders. Not only was his firm’s output and range greater than any other Sheffield firm, but its quality was superior. The company’s manifesto states: ‘The principle on which the manufacture of cutlery is carried on by this firm is – quality first … [and] … price comes second’. He began making exhibitions knives and presented George IV with a minute specimen of cutlery with 57 blades, which occupied only an inch [25mm] when closed. In 1822, Rodgers’ was awarded its first Royal Warrant. Another fourteen royal appointments, from British and overseas royal dignitaries, followed over the next eighty years, and its company history was duly titled: Under Five Sovereigns. John Rodgers next commissioned the Year Knife, with a blade for every year (1821) and opened his sensational cutlery showroom in Norfolk Street where visitors came to marvel at Rodgers’ creations. Perhaps the greatest highlight shown there was the Norfolk Knife, an over 30 inch long sportsman’s knife with 75 blades and tools, that Rodgers’ produced for the Great Exhibition in 1851. The showroom proved particularly popular with Americans whose trade played a significant role in the firm’s expansion. Additionally, they looked East, with agents in Calcutta, Bombay, and Hong Kong by the mid-19th century. These markets enabled Rodgers to become the largest cutlery factory in Sheffield. The number of workmen appears to have grown from about 300 in the late 1820s, to over 500 in the 1840s. In 1871 the business became a limited company with Joseph Rodgers (1828-1883), grandson of the Joseph Rodgers who had died in 1821 and Robert Newbold as managing directors. Joseph died on 12 May 1883 and Newbold became the chairman and managing director. The firm continued to expand with offices in London, New York, New Orleans, Montreal, Toronto, Calcutta, Bombay and Havana. Their work force in 1871 was around 1,200 and accounted for one-seventh of all Sheffield’s American cutlery trade. In 1876 the American market was stagnating and Rodgers’ began looking elsewhere with a focus on trade in the Middle East, India and Australia. Notably the name ‘Rujjus’ or ‘Rojers’ was said to have entered the language as an adjective expressing superb quality in Persia, India and Ceylon. By 1888, the value of Rodgers’ shares had more than doubled and, in 1889, a silver and electro-plate showroom was opened in London. At this time, Rodgers acquired the scissors business of Joseph Hobson & Son. Rodgers’ produced catalogues that were packed with every type of knife imaginable. Pocket knives were made in scores of different styles. Ornate daggers and Bowie knives and complicated horseman’s knives were made routinely. Some patterns, such as the Congress knife and Wharncliffe knife, were Rodgers’ own design. The Wharncliffe – with its serpentine handle and beaked master blade – was apparently designed after a dinner attended by Rodgers’ patron Lord Wharncliffe. The firm’s workmanship was usually backed by the best materials. Rodgers’ ivory cellar in Norfolk Street was crammed with giant tusks and was regarded as one of the hidden sights of the town. Four or five men were constantly employed in sawing the tusks, and around twenty four tons of ivory were used a year around 1882. Rodgers’ appetite for stag was no less insatiable: deer horns and antlers filled another cellar and pearl from the Philippines and was also cut there. Around 1890, Rodgers’ began forging its own shear steel and in 1894 they began melting crucible steel. Newbold retired in 1890 and the grandsons of Maurice Rodgers, Maurice George Rodgers (1855-1898) and John Rodgers (1856-1919), became joint-managing directors. The McKinley Tariff Act of 1890 halved their American business and consequently they toured South Africa. Despite increasing foreign competition and the decline of the American market, Rodgers’ prospered before the First World War. However, workers’ wages were cut while the partners continued to take significant dividend which culminated in a prolonged and bitter strike. The First World War saw a decline in the business which continued steadily until the 1975 when it was absorbed by Richards and ceased trading in 1983. Joseph Rodgers & Sons left an enduring legacy in its knives. Its dazzling exhibition pieces and other fine cutlery show that the company’s reputation as Sheffield’s foremost knife maker was well founded. Abbreviated from Geoffrey Tweedale 2019. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A BOWIE KNIFE, JOSEPH RODGERS & SONS, MAKERS TO HER MAJESTY, LATE 19TH CENTURY with robust blade formed with a clipped-back point and false swage, filed back-edge and stamped by the maker along with star and cross mark on one face (light pitting, later blued finish in places), recessed ricasso, engraved gilt brass hilt comprising scrolling quillons and integral ferrule decorated with a neo rococo flower on a punched group, low domed pommel and natural staghorn grip, 25.2 cm blade LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 256 In the nineteenth century, Rodgers had an unsurpassed reputation and history that was synonymous with the cutlery trade. The family's first cutler, John Rodgers (1701-85), is recorded around 1724, with a workshop near the present cathedral. In the same year the Company of Cutlers 'let' him a mark, a Star and Maltese Cross, which became world famous in later years. John Rodgers had three sons, John (1731-1811), Joseph (1743-1821), and Maurice (c.1747-1824) who joined the business and succeeded him. They are recorded with more workshops by 1780 and the business soon extended to occupy a nearby block of buildings at 6 Norfolk Street, an address that became as famous as Rodgers’ trade mark. By the early 19th century their trade had expanded from pen and pocket knives to include table cutlery and scissors. By 1817 the General Sheffield Directory lists the firm as ‘merchants, factors, table and pocket knife, and razor manufacturers’. In 1821 John’s son Joseph died and his sons continued the business under the leadership of the younger John (grandson of the founder). John was described as ‘unobtrusive in his manner’ but was ambitious and one of the founding partners of the Sheffield Banking Co. He had a flair for marketing and travelled the country taking orders. Not only was his firm’s output and range greater than any other Sheffield firm, but its quality was superior. The company’s manifesto states: ‘The principle on which the manufacture of cutlery is carried on by this firm is – quality first … [and] … price comes second’. He began making exhibitions knives and presented George IV with a minute specimen of cutlery with 57 blades, which occupied only an inch [25mm] when closed. In 1822, Rodgers’ was awarded its first Royal Warrant. Another fourteen royal appointments, from British and overseas royal dignitaries, followed over the next eighty years, and its company history was duly titled: Under Five Sovereigns. John Rodgers next commissioned the Year Knife, with a blade for every year (1821) and opened his sensational cutlery showroom in Norfolk Street where visitors came to marvel at Rodgers’ creations. Perhaps the greatest highlight shown there was the Norfolk Knife, an over 30 inch long sportsman’s knife with 75 blades and tools, that Rodgers’ produced for the Great Exhibition in 1851. The showroom proved particularly popular with Americans whose trade played a significant role in the firm’s expansion. Additionally, they looked East, with agents in Calcutta, Bombay, and Hong Kong by the mid-19th century. These markets enabled Rodgers to become the largest cutlery factory in Sheffield. The number of workmen appears to have grown from about 300 in the late 1820s, to over 500 in the 1840s. In 1871 the business became a limited company with Joseph Rodgers (1828-1883), grandson of the Joseph Rodgers who had died in 1821 and Robert Newbold as managing directors. Joseph died on 12 May 1883 and Newbold became the chairman and managing director. The firm continued to expand with offices in London, New York, New Orleans, Montreal, Toronto, Calcutta, Bombay and Havana. Their work force in 1871 was around 1,200 and accounted for one-seventh of all Sheffield’s American cutlery trade. In 1876 the American market was stagnating and Rodgers’ began looking elsewhere with a focus on trade in the Middle East, India and Australia. Notably the name ‘Rujjus’ or ‘Rojers’ was said to have entered the language as an adjective expressing superb quality in Persia, India and Ceylon. By 1888, the value of Rodgers’ shares had more than doubled and, in 1889, a silver and electro-plate showroom was opened in London. At this time, Rodgers acquired the scissors business of Joseph Hobson & Son. Rodgers’ produced catalogues that were packed with every type of knife imaginable. Pocket knives were made in scores of different styles. Ornate daggers and Bowie knives and complicated horseman’s knives were made routinely. Some patterns, such as the Congress knife and Wharncliffe knife, were Rodgers’ own design. The Wharncliffe – with its serpentine handle and beaked master blade – was apparently designed after a dinner attended by Rodgers’ patron Lord Wharncliffe. The firm’s workmanship was usually backed by the best materials. Rodgers’ ivory cellar in Norfolk Street was crammed with giant tusks and was regarded as one of the hidden sights of the town. Four or five men were constantly employed in sawing the tusks, and around twenty four tons of ivory were used a year around 1882. Rodgers’ appetite for stag was no less insatiable: deer horns and antlers filled another cellar and pearl from the Philippines and was also cut there. Around 1890, Rodgers’ began forging its own shear steel and in 1894 they began melting crucible steel. Newbold retired in 1890 and the grandsons of Maurice Rodgers, Maurice George Rodgers (1855-1898) and John Rodgers (1856-1919), became joint-managing directors. The McKinley Tariff Act of 1890 halved their American business and consequently they toured South Africa. Despite increasing foreign competition and the decline of the American market, Rodgers’ prospered before the First World War. However, workers’ wages were cut while the partners continued to take significant dividend which culminated in a prolonged and bitter strike. The First World War saw a decline in the business which continued steadily until the 1975 when it was absorbed by Richards and ceased trading in 1983. Joseph Rodgers & Sons left an enduring legacy in its knives. Its dazzling exhibition pieces and other fine cutlery show that the company’s reputation as Sheffield’s foremost knife maker was well founded. Abbreviated from Geoffrey Tweedale 2019. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A FINE BOWIE KNIFE, JOSEPH RODGERS & SONS, NO. 6 NORFOLK STREET, SHEFFIELD, LATE 19TH CENTURY with tapering blade formed with a swaged clipped-back point, finely chevron-milled back edge with a fuller beneath on each face, stamped with the maker’s details and star and cross mark, German silver hilt comprising cross-piece with short recurved quillons with globular terminals and gadrooned cap pommel and natural staghorn grip, in its leather-covered wooden scabbard with German silver chape with moulded terminals, and locket with flower-shaped belt stud, 20.5 cm blade LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 264. In the nineteenth century, Rodgers had an unsurpassed reputation and history that was synonymous with the cutlery trade. The family's first cutler, John Rodgers (1701-85), is recorded around 1724, with a workshop near the present cathedral. In the same year the Company of Cutlers 'let' him a mark, a Star and Maltese Cross, which became world famous in later years. John Rodgers had three sons, John (1731-1811), Joseph (1743-1821), and Maurice (c.1747-1824) who joined the business and succeeded him. They are recorded with more workshops by 1780 and the business soon extended to occupy a nearby block of buildings at 6 Norfolk Street, an address that became as famous as Rodgers’ trade mark. By the early 19th century their trade had expanded from pen and pocket knives to include table cutlery and scissors. By 1817 the General Sheffield Directory lists the firm as ‘merchants, factors, table and pocket knife, and razor manufacturers’. In 1821 John’s son Joseph died and his sons continued the business under the leadership of the younger John (grandson of the founder). John was described as ‘unobtrusive in his manner’ but was ambitious and one of the founding partners of the Sheffield Banking Co. He had a flair for marketing and travelled the country taking orders. Not only was his firm’s output and range greater than any other Sheffield firm, but its quality was superior. The company’s manifesto states: ‘The principle on which the manufacture of cutlery is carried on by this firm is – quality first … [and] … price comes second’. He began making exhibitions knives and presented George IV with a minute specimen of cutlery with 57 blades, which occupied only an inch [25mm] when closed. In 1822, Rodgers’ was awarded its first Royal Warrant. Another fourteen royal appointments, from British and overseas royal dignitaries, followed over the next eighty years, and its company history was duly titled: Under Five Sovereigns. John Rodgers next commissioned the Year Knife, with a blade for every year (1821) and opened his sensational cutlery showroom in Norfolk Street where visitors came to marvel at Rodgers’ creations. Perhaps the greatest highlight shown there was the Norfolk Knife, an over 30 inch long sportsman’s knife with 75 blades and tools, that Rodgers’ produced for the Great Exhibition in 1851. The showroom proved particularly popular with Americans whose trade played a significant role in the firm’s expansion. Additionally, they looked East, with agents in Calcutta, Bombay, and Hong Kong by the mid-19th century. These markets enabled Rodgers to become the largest cutlery factory in Sheffield. The number of workmen appears to have grown from about 300 in the late 1820s, to over 500 in the 1840s. In 1871 the business became a limited company with Joseph Rodgers (1828-1883), grandson of the Joseph Rodgers who had died in 1821 and Robert Newbold as managing directors. Joseph died on 12 May 1883 and Newbold became the chairman and managing director. The firm continued to expand with offices in London, New York, New Orleans, Montreal, Toronto, Calcutta, Bombay and Havana. Their work force in 1871 was around 1,200 and accounted for one-seventh of all Sheffield’s American cutlery trade. In 1876 the American market was stagnating and Rodgers’ began looking elsewhere with a focus on trade in the Middle East, India and Australia. Notably the name ‘Rujjus’ or ‘Rojers’ was said to have entered the language as an adjective expressing superb quality in Persia, India and Ceylon. By 1888, the value of Rodgers’ shares had more than doubled and, in 1889, a silver and electro-plate showroom was opened in London. At this time, Rodgers acquired the scissors business of Joseph Hobson & Son. Rodgers’ produced catalogues that were packed with every type of knife imaginable. Pocket knives were made in scores of different styles. Ornate daggers and Bowie knives and complicated horseman’s knives were made routinely. Some patterns, such as the Congress knife and Wharncliffe knife, were Rodgers’ own design. The Wharncliffe – with its serpentine handle and beaked master blade – was apparently designed after a dinner attended by Rodgers’ patron Lord Wharncliffe. The firm’s workmanship was usually backed by the best materials. Rodgers’ ivory cellar in Norfolk Street was crammed with giant tusks and was regarded as one of the hidden sights of the town. Four or five men were constantly employed in sawing the tusks, and around twenty four tons of ivory were used a year around 1882. Rodgers’ appetite for stag was no less insatiable: deer horns and antlers filled another cellar and pearl from the Philippines and was also cut there. Around 1890, Rodgers’ began forging its own shear steel and in 1894 they began melting crucible steel. Newbold retired in 1890 and the grandsons of Maurice Rodgers, Maurice George Rodgers (1855-1898) and John Rodgers (1856-1919), became joint-managing directors. The McKinley Tariff Act of 1890 halved their American business and consequently they toured South Africa. Despite increasing foreign competition and the decline of the American market, Rodgers’ prospered before the First World War. However, workers’ wages were cut while the partners continued to take significant dividend which culminated in a prolonged and bitter strike. The First World War saw a decline in the business which continued steadily until the 1975 when it was absorbed by Richards and ceased trading in 1983. Joseph Rodgers & Sons left an enduring legacy in its knives. Its dazzling exhibition pieces and other fine cutlery show that the company’s reputation as Sheffield’s foremost knife maker was well founded. Abbreviated from Geoffrey Tweedale 2019. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A BOWIE KNIFE, JOSEPH RODGERS & SONS, CUTLERS TO THEIR MAJESTIES, NO. 6 NORFOLK STREET SHEFFIELD MADE FOR MANTON & CO. CALCUTTA, LAST QUARTER OF THE 19TH CENTURY with single-edged blade formed with a spear point, struck with the maker’s and retailer’s details on one face, recessed rectangular ricasso, German silver oval guard, natural staghorn grip and German silver cap pommel (one rivet missing), in its leather scabbard with belt loop, 20.5 cm blade LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 270. In the nineteenth century, Rodgers had an unsurpassed reputation and history that was synonymous with the cutlery trade. The family's first cutler, John Rodgers (1701-85), is recorded around 1724, with a workshop near the present cathedral. In the same year the Company of Cutlers 'let' him a mark, a Star and Maltese Cross, which became world famous in later years. John Rodgers had three sons, John (1731-1811), Joseph (1743-1821), and Maurice (c.1747-1824) who joined the business and succeeded him. They are recorded with more workshops by 1780 and the business soon extended to occupy a nearby block of buildings at 6 Norfolk Street, an address that became as famous as Rodgers’ trade mark. By the early 19th century their trade had expanded from pen and pocket knives to include table cutlery and scissors. By 1817 the General Sheffield Directory lists the firm as ‘merchants, factors, table and pocket knife, and razor manufacturers’. In 1821 John’s son Joseph died and his sons continued the business under the leadership of the younger John (grandson of the founder). John was described as ‘unobtrusive in his manner’ but was ambitious and one of the founding partners of the Sheffield Banking Co. He had a flair for marketing and travelled the country taking orders. Not only was his firm’s output and range greater than any other Sheffield firm, but its quality was superior. The company’s manifesto states: ‘The principle on which the manufacture of cutlery is carried on by this firm is – quality first … [and] … price comes second’. He began making exhibitions knives and presented George IV with a minute specimen of cutlery with 57 blades, which occupied only an inch [25mm] when closed. In 1822, Rodgers’ was awarded its first Royal Warrant. Another fourteen royal appointments, from British and overseas royal dignitaries, followed over the next eighty years, and its company history was duly titled: Under Five Sovereigns. John Rodgers next commissioned the Year Knife, with a blade for every year (1821) and opened his sensational cutlery showroom in Norfolk Street where visitors came to marvel at Rodgers’ creations. Perhaps the greatest highlight shown there was the Norfolk Knife, an over 30 inch long sportsman’s knife with 75 blades and tools, that Rodgers’ produced for the Great Exhibition in 1851. The showroom proved particularly popular with Americans whose trade played a significant role in the firm’s expansion. Additionally, they looked East, with agents in Calcutta, Bombay, and Hong Kong by the mid-19th century. These markets enabled Rodgers to become the largest cutlery factory in Sheffield. The number of workmen appears to have grown from about 300 in the late 1820s, to over 500 in the 1840s. In 1871 the business became a limited company with Joseph Rodgers (1828-1883), grandson of the Joseph Rodgers who had died in 1821 and Robert Newbold as managing directors. Joseph died on 12 May 1883 and Newbold became the chairman and managing director. The firm continued to expand with offices in London, New York, New Orleans, Montreal, Toronto, Calcutta, Bombay and Havana. Their work force in 1871 was around 1,200 and accounted for one-seventh of all Sheffield’s American cutlery trade. In 1876 the American market was stagnating and Rodgers’ began looking elsewhere with a focus on trade in the Middle East, India and Australia. Notably the name ‘Rujjus’ or ‘Rojers’ was said to have entered the language as an adjective expressing superb quality in Persia, India and Ceylon. By 1888, the value of Rodgers’ shares had more than doubled and, in 1889, a silver and electro-plate showroom was opened in London. At this time, Rodgers acquired the scissors business of Joseph Hobson & Son. Rodgers’ produced catalogues that were packed with every type of knife imaginable. Pocket knives were made in scores of different styles. Ornate daggers and Bowie knives and complicated horseman’s knives were made routinely. Some patterns, such as the Congress knife and Wharncliffe knife, were Rodgers’ own design. The Wharncliffe – with its serpentine handle and beaked master blade – was apparently designed after a dinner attended by Rodgers’ patron Lord Wharncliffe. The firm’s workmanship was usually backed by the best materials. Rodgers’ ivory cellar in Norfolk Street was crammed with giant tusks and was regarded as one of the hidden sights of the town. Four or five men were constantly employed in sawing the tusks, and around twenty four tons of ivory were used a year around 1882. Rodgers’ appetite for stag was no less insatiable: deer horns and antlers filled another cellar and pearl from the Philippines and was also cut there. Around 1890, Rodgers’ began forging its own shear steel and in 1894 they began melting crucible steel. Newbold retired in 1890 and the grandsons of Maurice Rodgers, Maurice George Rodgers (1855-1898) and John Rodgers (1856-1919), became joint-managing directors. The McKinley Tariff Act of 1890 halved their American business and consequently they toured South Africa. Despite increasing foreign competition and the decline of the American market, Rodgers’ prospered before the First World War. However, workers’ wages were cut while the partners continued to take significant dividend which culminated in a prolonged and bitter strike. The First World War saw a decline in the business which continued steadily until the 1975 when it was absorbed by Richards and ceased trading in 1983. Joseph Rodgers & Sons left an enduring legacy in its knives. Its dazzling exhibition pieces and other fine cutlery show that the company’s reputation as Sheffield’s foremost knife maker was well founded. Abbreviated from Geoffrey Tweedale 2019. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A BOWIE KNIFE, JOSEPH RODGERS & SONS, NO. 6 NORFOLK ST., SHEFFIELD, LATE 19TH CENTURY with straight blade formed with a clipped-back point and writhen back-edge accompanied by a long slender fuller on each face, signed on one face and with cross and star mark, rectangular ricasso, German silver hilt comprising recurved guard with globular terminals and gadrooned cap pommel, and natural staghorn grip, in its leather scabbard with belt loop, 18.2 cm blade LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 296. In the nineteenth century, Rodgers had an unsurpassed reputation and history that was synonymous with the cutlery trade. The family's first cutler, John Rodgers (1701-85), is recorded around 1724, with a workshop near the present cathedral. In the same year the Company of Cutlers 'let' him a mark, a Star and Maltese Cross, which became world famous in later years. John Rodgers had three sons, John (1731-1811), Joseph (1743-1821), and Maurice (c.1747-1824) who joined the business and succeeded him. They are recorded with more workshops by 1780 and the business soon extended to occupy a nearby block of buildings at 6 Norfolk Street, an address that became as famous as Rodgers’ trade mark. By the early 19th century their trade had expanded from pen and pocket knives to include table cutlery and scissors. By 1817 the General Sheffield Directory lists the firm as ‘merchants, factors, table and pocket knife, and razor manufacturers’. In 1821 John’s son Joseph died and his sons continued the business under the leadership of the younger John (grandson of the founder). John was described as ‘unobtrusive in his manner’ but was ambitious and one of the founding partners of the Sheffield Banking Co. He had a flair for marketing and travelled the country taking orders. Not only was his firm’s output and range greater than any other Sheffield firm, but its quality was superior. The company’s manifesto states: ‘The principle on which the manufacture of cutlery is carried on by this firm is – quality first … [and] … price comes second’. He began making exhibitions knives and presented George IV with a minute specimen of cutlery with 57 blades, which occupied only an inch [25mm] when closed. In 1822, Rodgers’ was awarded its first Royal Warrant. Another fourteen royal appointments, from British and overseas royal dignitaries, followed over the next eighty years, and its company history was duly titled: Under Five Sovereigns. John Rodgers next commissioned the Year Knife, with a blade for every year (1821) and opened his sensational cutlery showroom in Norfolk Street where visitors came to marvel at Rodgers’ creations. Perhaps the greatest highlight shown there was the Norfolk Knife, an over 30 inch long sportsman’s knife with 75 blades and tools, that Rodgers’ produced for the Great Exhibition in 1851. The showroom proved particularly popular with Americans whose trade played a significant role in the firm’s expansion. Additionally, they looked East, with agents in Calcutta, Bombay, and Hong Kong by the mid-19th century. These markets enabled Rodgers to become the largest cutlery factory in Sheffield. The number of workmen appears to have grown from about 300 in the late 1820s, to over 500 in the 1840s. In 1871 the business became a limited company with Joseph Rodgers (1828-1883), grandson of the Joseph Rodgers who had died in 1821 and Robert Newbold as managing directors. Joseph died on 12 May 1883 and Newbold became the chairman and managing director. The firm continued to expand with offices in London, New York, New Orleans, Montreal, Toronto, Calcutta, Bombay and Havana. Their work force in 1871 was around 1,200 and accounted for one-seventh of all Sheffield’s American cutlery trade. In 1876 the American market was stagnating and Rodgers’ began looking elsewhere with a focus on trade in the Middle East, India and Australia. Notably the name ‘Rujjus’ or ‘Rojers’ was said to have entered the language as an adjective expressing superb quality in Persia, India and Ceylon. By 1888, the value of Rodgers’ shares had more than doubled and, in 1889, a silver and electro-plate showroom was opened in London. At this time, Rodgers acquired the scissors business of Joseph Hobson & Son. Rodgers’ produced catalogues that were packed with every type of knife imaginable. Pocket knives were made in scores of different styles. Ornate daggers and Bowie knives and complicated horseman’s knives were made routinely. Some patterns, such as the Congress knife and Wharncliffe knife, were Rodgers’ own design. The Wharncliffe – with its serpentine handle and beaked master blade – was apparently designed after a dinner attended by Rodgers’ patron Lord Wharncliffe. The firm’s workmanship was usually backed by the best materials. Rodgers’ ivory cellar in Norfolk Street was crammed with giant tusks and was regarded as one of the hidden sights of the town. Four or five men were constantly employed in sawing the tusks, and around twenty four tons of ivory were used a year around 1882. Rodgers’ appetite for stag was no less insatiable: deer horns and antlers filled another cellar and pearl from the Philippines and was also cut there. Around 1890, Rodgers’ began forging its own shear steel and in 1894 they began melting crucible steel. Newbold retired in 1890 and the grandsons of Maurice Rodgers, Maurice George Rodgers (1855-1898) and John Rodgers (1856-1919), became joint-managing directors. The McKinley Tariff Act of 1890 halved their American business and consequently they toured South Africa. Despite increasing foreign competition and the decline of the American market, Rodgers’ prospered before the First World War. However, workers’ wages were cut while the partners continued to take significant dividend which culminated in a prolonged and bitter strike. The First World War saw a decline in the business which continued steadily until the 1975 when it was absorbed by Richards and ceased trading in 1983. Joseph Rodgers & Sons left an enduring legacy in its knives. Its dazzling exhibition pieces and other fine cutlery show that the company’s reputation as Sheffield’s foremost knife maker was well founded. Abbreviated from Geoffrey Tweedale 2019. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A FINE BOWIE KNIFE, JOSEPH RODGERS & SONS, CUTLERS TO HER MAJESTY, LAST QUARTER OF THE 19TH CENTURY with broad double-edged blade of flattened-diamond section, formed with a spear point and three small elliptical indents on each face along the median, rectangular ricasso of flattened-hexagonal action struck with the maker’s details, the Royal letters ‘VR’ divided by a crown, and star and cross mark, German silver hilt comprising straight guard with integral ferrule and cap pommel, and natural staghorn grip, in its leather-covered wooden scabbard with German silver chape and locket, the latter with a button for a frog, 21.0 cm blade LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 264. In the nineteenth century, Rodgers had an unsurpassed reputation and history that was synonymous with the cutlery trade. The family's first cutler, John Rodgers (1701-85), is recorded around 1724, with a workshop near the present cathedral. In the same year the Company of Cutlers 'let' him a mark, a Star and Maltese Cross, which became world famous in later years. John Rodgers had three sons, John (1731-1811), Joseph (1743-1821), and Maurice (c.1747-1824) who joined the business and succeeded him. They are recorded with more workshops by 1780 and the business soon extended to occupy a nearby block of buildings at 6 Norfolk Street, an address that became as famous as Rodgers’ trade mark. By the early 19th century their trade had expanded from pen and pocket knives to include table cutlery and scissors. By 1817 the General Sheffield Directory lists the firm as ‘merchants, factors, table and pocket knife, and razor manufacturers’. In 1821 John’s son Joseph died and his sons continued the business under the leadership of the younger John (grandson of the founder). John was described as ‘unobtrusive in his manner’ but was ambitious and one of the founding partners of the Sheffield Banking Co. He had a flair for marketing and travelled the country taking orders. Not only was his firm’s output and range greater than any other Sheffield firm, but its quality was superior. The company’s manifesto states: ‘The principle on which the manufacture of cutlery is carried on by this firm is – quality first … [and] … price comes second’. He began making exhibitions knives and presented George IV with a minute specimen of cutlery with 57 blades, which occupied only an inch [25mm] when closed. In 1822, Rodgers’ was awarded its first Royal Warrant. Another fourteen royal appointments, from British and overseas royal dignitaries, followed over the next eighty years, and its company history was duly titled: Under Five Sovereigns. John Rodgers next commissioned the Year Knife, with a blade for every year (1821) and opened his sensational cutlery showroom in Norfolk Street where visitors came to marvel at Rodgers’ creations. Perhaps the greatest highlight shown there was the Norfolk Knife, an over 30 inch long sportsman’s knife with 75 blades and tools, that Rodgers’ produced for the Great Exhibition in 1851. The showroom proved particularly popular with Americans whose trade played a significant role in the firm’s expansion. Additionally, they looked East, with agents in Calcutta, Bombay, and Hong Kong by the mid-19th century. These markets enabled Rodgers to become the largest cutlery factory in Sheffield. The number of workmen appears to have grown from about 300 in the late 1820s, to over 500 in the 1840s. In 1871 the business became a limited company with Joseph Rodgers (1828-1883), grandson of the Joseph Rodgers who had died in 1821 and Robert Newbold as managing directors. Joseph died on 12 May 1883 and Newbold became the chairman and managing director. The firm continued to expand with offices in London, New York, New Orleans, Montreal, Toronto, Calcutta, Bombay and Havana. Their work force in 1871 was around 1,200 and accounted for one-seventh of all Sheffield’s American cutlery trade. In 1876 the American market was stagnating and Rodgers’ began looking elsewhere with a focus on trade in the Middle East, India and Australia. Notably the name ‘Rujjus’ or ‘Rojers’ was said to have entered the language as an adjective expressing superb quality in Persia, India and Ceylon. By 1888, the value of Rodgers’ shares had more than doubled and, in 1889, a silver and electro-plate showroom was opened in London. At this time, Rodgers acquired the scissors business of Joseph Hobson & Son. Rodgers’ produced catalogues that were packed with every type of knife imaginable. Pocket knives were made in scores of different styles. Ornate daggers and Bowie knives and complicated horseman’s knives were made routinely. Some patterns, such as the Congress knife and Wharncliffe knife, were Rodgers’ own design. The Wharncliffe – with its serpentine handle and beaked master blade – was apparently designed after a dinner attended by Rodgers’ patron Lord Wharncliffe. The firm’s workmanship was usually backed by the best materials. Rodgers’ ivory cellar in Norfolk Street was crammed with giant tusks and was regarded as one of the hidden sights of the town. Four or five men were constantly employed in sawing the tusks, and around twenty four tons of ivory were used a year around 1882. Rodgers’ appetite for stag was no less insatiable: deer horns and antlers filled another cellar and pearl from the Philippines and was also cut there. Around 1890, Rodgers’ began forging its own shear steel and in 1894 they began melting crucible steel. Newbold retired in 1890 and the grandsons of Maurice Rodgers, Maurice George Rodgers (1855-1898) and John Rodgers (1856-1919), became joint-managing directors. The McKinley Tariff Act of 1890 halved their American business and consequently they toured South Africa. Despite increasing foreign competition and the decline of the American market, Rodgers’ prospered before the First World War. However, workers’ wages were cut while the partners continued to take significant dividend which culminated in a prolonged and bitter strike. The First World War saw a decline in the business which continued steadily until the 1975 when it was absorbed by Richards and ceased trading in 1983. Joseph Rodgers & Sons left an enduring legacy in its knives. Its dazzling exhibition pieces and other fine cutlery show that the company’s reputation as Sheffield’s foremost knife maker was well founded. Abbreviated from Geoffrey Tweedale 2019. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A FINE BOWIE KNIFE, JOSEPH RODGERS & SONS, CUTLERS TO THEIR MAJESTIES, NO. 6 NORFOLK STREET, SHEFFIELD, LAST QUARTER OF THE 19TH CENTURY with broad blade formed with a clipped-back point, struck with the maker’s details and star and cross mark on one face, German silver hilt shaped for grip and formed in one piece, including straight guard with integral ferrule and cap pommel, and a pair of mother-of-pearl scales retained by five rivets, in its leather scabbard with German silver locket and chape and belt loop with vacant German silver escutcheon, 15.3 cm blade LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 264. In the nineteenth century, Rodgers had an unsurpassed reputation and history that was synonymous with the cutlery trade. The family's first cutler, John Rodgers (1701-85), is recorded around 1724, with a workshop near the present cathedral. In the same year the Company of Cutlers 'let' him a mark, a Star and Maltese Cross, which became world famous in later years. John Rodgers had three sons, John (1731-1811), Joseph (1743-1821), and Maurice (c.1747-1824) who joined the business and succeeded him. They are recorded with more workshops by 1780 and the business soon extended to occupy a nearby block of buildings at 6 Norfolk Street, an address that became as famous as Rodgers’ trade mark. By the early 19th century their trade had expanded from pen and pocket knives to include table cutlery and scissors. By 1817 the General Sheffield Directory lists the firm as ‘merchants, factors, table and pocket knife, and razor manufacturers’. In 1821 John’s son Joseph died and his sons continued the business under the leadership of the younger John (grandson of the founder). John was described as ‘unobtrusive in his manner’ but was ambitious and one of the founding partners of the Sheffield Banking Co. He had a flair for marketing and travelled the country taking orders. Not only was his firm’s output and range greater than any other Sheffield firm, but its quality was superior. The company’s manifesto states: ‘The principle on which the manufacture of cutlery is carried on by this firm is – quality first … [and] … price comes second’. He began making exhibitions knives and presented George IV with a minute specimen of cutlery with 57 blades, which occupied only an inch [25mm] when closed. In 1822, Rodgers’ was awarded its first Royal Warrant. Another fourteen royal appointments, from British and overseas royal dignitaries, followed over the next eighty years, and its company history was duly titled: Under Five Sovereigns. John Rodgers next commissioned the Year Knife, with a blade for every year (1821) and opened his sensational cutlery showroom in Norfolk Street where visitors came to marvel at Rodgers’ creations. Perhaps the greatest highlight shown there was the Norfolk Knife, an over 30 inch long sportsman’s knife with 75 blades and tools, that Rodgers’ produced for the Great Exhibition in 1851. The showroom proved particularly popular with Americans whose trade played a significant role in the firm’s expansion. Additionally, they looked East, with agents in Calcutta, Bombay, and Hong Kong by the mid-19th century. These markets enabled Rodgers to become the largest cutlery factory in Sheffield. The number of workmen appears to have grown from about 300 in the late 1820s, to over 500 in the 1840s. In 1871 the business became a limited company with Joseph Rodgers (1828-1883), grandson of the Joseph Rodgers who had died in 1821 and Robert Newbold as managing directors. Joseph died on 12 May 1883 and Newbold became the chairman and managing director. The firm continued to expand with offices in London, New York, New Orleans, Montreal, Toronto, Calcutta, Bombay and Havana. Their work force in 1871 was around 1,200 and accounted for one-seventh of all Sheffield’s American cutlery trade. In 1876 the American market was stagnating and Rodgers’ began looking elsewhere with a focus on trade in the Middle East, India and Australia. Notably the name ‘Rujjus’ or ‘Rojers’ was said to have entered the language as an adjective expressing superb quality in Persia, India and Ceylon. By 1888, the value of Rodgers’ shares had more than doubled and, in 1889, a silver and electro-plate showroom was opened in London. At this time, Rodgers acquired the scissors business of Joseph Hobson & Son. Rodgers’ produced catalogues that were packed with every type of knife imaginable. Pocket knives were made in scores of different styles. Ornate daggers and Bowie knives and complicated horseman’s knives were made routinely. Some patterns, such as the Congress knife and Wharncliffe knife, were Rodgers’ own design. The Wharncliffe – with its serpentine handle and beaked master blade – was apparently designed after a dinner attended by Rodgers’ patron Lord Wharncliffe. The firm’s workmanship was usually backed by the best materials. Rodgers’ ivory cellar in Norfolk Street was crammed with giant tusks and was regarded as one of the hidden sights of the town. Four or five men were constantly employed in sawing the tusks, and around twenty four tons of ivory were used a year around 1882. Rodgers’ appetite for stag was no less insatiable: deer horns and antlers filled another cellar and pearl from the Philippines and was also cut there. Around 1890, Rodgers’ began forging its own shear steel and in 1894 they began melting crucible steel. Newbold retired in 1890 and the grandsons of Maurice Rodgers, Maurice George Rodgers (1855-1898) and John Rodgers (1856-1919), became joint-managing directors. The McKinley Tariff Act of 1890 halved their American business and consequently they toured South Africa. Despite increasing foreign competition and the decline of the American market, Rodgers’ prospered before the First World War. However, workers’ wages were cut while the partners continued to take significant dividend which culminated in a prolonged and bitter strike. The First World War saw a decline in the business which continued steadily until the 1975 when it was absorbed by Richards and ceased trading in 1983. Joseph Rodgers & Sons left an enduring legacy in its knives. Its dazzling exhibition pieces and other fine cutlery show that the company’s reputation as Sheffield’s foremost knife maker was well founded. Abbreviated from Geoffrey Tweedale 2019. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A BOWIE KNIFE BY JOSEPH RODGERS & SONS, 6 NORFOLK STREET, SHEFFIELD, LAST QUARTER OF THE 19TH CENTURY with broad single-edged blade formed with a spear point, recessed rectangular ricasso struck with the maker’s details, the royal letters ‘VR’ divided by a crown, and cross and star mark, German silver hilt comprising two-piece ‘split’ guard and pommel each decorated with a design of raised dots and stylised foliage in low relief, and chequered horn scales retained by two rivets, in associated leather scabbard with German silver locket and chape, 20.5 cm blade LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 265. In the nineteenth century, Rodgers had an unsurpassed reputation and history that was synonymous with the cutlery trade. The family's first cutler, John Rodgers (1701-85), is recorded around 1724, with a workshop near the present cathedral. In the same year the Company of Cutlers 'let' him a mark, a Star and Maltese Cross, which became world famous in later years. John Rodgers had three sons, John (1731-1811), Joseph (1743-1821), and Maurice (c.1747-1824) who joined the business and succeeded him. They are recorded with more workshops by 1780 and the business soon extended to occupy a nearby block of buildings at 6 Norfolk Street, an address that became as famous as Rodgers’ trade mark. By the early 19th century their trade had expanded from pen and pocket knives to include table cutlery and scissors. By 1817 the General Sheffield Directory lists the firm as ‘merchants, factors, table and pocket knife, and razor manufacturers’. In 1821 John’s son Joseph died and his sons continued the business under the leadership of the younger John (grandson of the founder). John was described as ‘unobtrusive in his manner’ but was ambitious and one of the founding partners of the Sheffield Banking Co. He had a flair for marketing and travelled the country taking orders. Not only was his firm’s output and range greater than any other Sheffield firm, but its quality was superior. The company’s manifesto states: ‘The principle on which the manufacture of cutlery is carried on by this firm is – quality first … [and] … price comes second’. He began making exhibitions knives and presented George IV with a minute specimen of cutlery with 57 blades, which occupied only an inch [25mm] when closed. In 1822, Rodgers’ was awarded its first Royal Warrant. Another fourteen royal appointments, from British and overseas royal dignitaries, followed over the next eighty years, and its company history was duly titled: Under Five Sovereigns. John Rodgers next commissioned the Year Knife, with a blade for every year (1821) and opened his sensational cutlery showroom in Norfolk Street where visitors came to marvel at Rodgers’ creations. Perhaps the greatest highlight shown there was the Norfolk Knife, an over 30 inch long sportsman’s knife with 75 blades and tools, that Rodgers’ produced for the Great Exhibition in 1851. The showroom proved particularly popular with Americans whose trade played a significant role in the firm’s expansion. Additionally, they looked East, with agents in Calcutta, Bombay, and Hong Kong by the mid-19th century. These markets enabled Rodgers to become the largest cutlery factory in Sheffield. The number of workmen appears to have grown from about 300 in the late 1820s, to over 500 in the 1840s. In 1871 the business became a limited company with Joseph Rodgers (1828-1883), grandson of the Joseph Rodgers who had died in 1821 and Robert Newbold as managing directors. Joseph died on 12 May 1883 and Newbold became the chairman and managing director. The firm continued to expand with offices in London, New York, New Orleans, Montreal, Toronto, Calcutta, Bombay and Havana. Their work force in 1871 was around 1,200 and accounted for one-seventh of all Sheffield’s American cutlery trade. In 1876 the American market was stagnating and Rodgers’ began looking elsewhere with a focus on trade in the Middle East, India and Australia. Notably the name ‘Rujjus’ or ‘Rojers’ was said to have entered the language as an adjective expressing superb quality in Persia, India and Ceylon. By 1888, the value of Rodgers’ shares had more than doubled and, in 1889, a silver and electro-plate showroom was opened in London. At this time, Rodgers acquired the scissors business of Joseph Hobson & Son. Rodgers’ produced catalogues that were packed with every type of knife imaginable. Pocket knives were made in scores of different styles. Ornate daggers and Bowie knives and complicated horseman’s knives were made routinely. Some patterns, such as the Congress knife and Wharncliffe knife, were Rodgers’ own design. The Wharncliffe – with its serpentine handle and beaked master blade – was apparently designed after a dinner attended by Rodgers’ patron Lord Wharncliffe. The firm’s workmanship was usually backed by the best materials. Rodgers’ ivory cellar in Norfolk Street was crammed with giant tusks and was regarded as one of the hidden sights of the town. Four or five men were constantly employed in sawing the tusks, and around twenty four tons of ivory were used a year around 1882. Rodgers’ appetite for stag was no less insatiable: deer horns and antlers filled another cellar and pearl from the Philippines and was also cut there. Around 1890, Rodgers’ began forging its own shear steel and in 1894 they began melting crucible steel. Newbold retired in 1890 and the grandsons of Maurice Rodgers, Maurice George Rodgers (1855-1898) and John Rodgers (1856-1919), became joint-managing directors. The McKinley Tariff Act of 1890 halved their American business and consequently they toured South Africa. Despite increasing foreign competition and the decline of the American market, Rodgers’ prospered before the First World War. However, workers’ wages were cut while the partners continued to take significant dividend which culminated in a prolonged and bitter strike. The First World War saw a decline in the business which continued steadily until the 1975 when it was absorbed by Richards and ceased trading in 1983. Joseph Rodgers & Sons left an enduring legacy in its knives. Its dazzling exhibition pieces and other fine cutlery show that the company’s reputation as Sheffield’s foremost knife maker was well founded. Abbreviated from Geoffrey Tweedale 2019. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A BOWIE KNIFE, JOSEPH RODGERS & SONS, CUTLERS TO THEIR MAJESTIES, NO. 6 NORFOLK STREET, SHEFFIELD, LAST QUARTER OF THE 19TH CENTURY with broad blade formed with a clipped-back point, struck with the maker’s details and star and cross mark on one face (small areas of light pitting), oval German silver guard, and natural staghorn scales retained by five rivets, in its leather scabbard with large German silver locket and chape, 20.8 cm blade LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 265. In the nineteenth century, Rodgers had an unsurpassed reputation and history that was synonymous with the cutlery trade. The family's first cutler, John Rodgers (1701-85), is recorded around 1724, with a workshop near the present cathedral. In the same year the Company of Cutlers 'let' him a mark, a Star and Maltese Cross, which became world famous in later years. John Rodgers had three sons, John (1731-1811), Joseph (1743-1821), and Maurice (c.1747-1824) who joined the business and succeeded him. They are recorded with more workshops by 1780 and the business soon extended to occupy a nearby block of buildings at 6 Norfolk Street, an address that became as famous as Rodgers’ trade mark. By the early 19th century their trade had expanded from pen and pocket knives to include table cutlery and scissors. By 1817 the General Sheffield Directory lists the firm as ‘merchants, factors, table and pocket knife, and razor manufacturers’. In 1821 John’s son Joseph died and his sons continued the business under the leadership of the younger John (grandson of the founder). John was described as ‘unobtrusive in his manner’ but was ambitious and one of the founding partners of the Sheffield Banking Co. He had a flair for marketing and travelled the country taking orders. Not only was his firm’s output and range greater than any other Sheffield firm, but its quality was superior. The company’s manifesto states: ‘The principle on which the manufacture of cutlery is carried on by this firm is – quality first … [and] … price comes second’. He began making exhibitions knives and presented George IV with a minute specimen of cutlery with 57 blades, which occupied only an inch [25mm] when closed. In 1822, Rodgers’ was awarded its first Royal Warrant. Another fourteen royal appointments, from British and overseas royal dignitaries, followed over the next eighty years, and its company history was duly titled: Under Five Sovereigns. John Rodgers next commissioned the Year Knife, with a blade for every year (1821) and opened his sensational cutlery showroom in Norfolk Street where visitors came to marvel at Rodgers’ creations. Perhaps the greatest highlight shown there was the Norfolk Knife, an over 30 inch long sportsman’s knife with 75 blades and tools, that Rodgers’ produced for the Great Exhibition in 1851. The showroom proved particularly popular with Americans whose trade played a significant role in the firm’s expansion. Additionally, they looked East, with agents in Calcutta, Bombay, and Hong Kong by the mid-19th century. These markets enabled Rodgers to become the largest cutlery factory in Sheffield. The number of workmen appears to have grown from about 300 in the late 1820s, to over 500 in the 1840s. In 1871 the business became a limited company with Joseph Rodgers (1828-1883), grandson of the Joseph Rodgers who had died in 1821 and Robert Newbold as managing directors. Joseph died on 12 May 1883 and Newbold became the chairman and managing director. The firm continued to expand with offices in London, New York, New Orleans, Montreal, Toronto, Calcutta, Bombay and Havana. Their work force in 1871 was around 1,200 and accounted for one-seventh of all Sheffield’s American cutlery trade. In 1876 the American market was stagnating and Rodgers’ began looking elsewhere with a focus on trade in the Middle East, India and Australia. Notably the name ‘Rujjus’ or ‘Rojers’ was said to have entered the language as an adjective expressing superb quality in Persia, India and Ceylon. By 1888, the value of Rodgers’ shares had more than doubled and, in 1889, a silver and electro-plate showroom was opened in London. At this time, Rodgers acquired the scissors business of Joseph Hobson & Son. Rodgers’ produced catalogues that were packed with every type of knife imaginable. Pocket knives were made in scores of different styles. Ornate daggers and Bowie knives and complicated horseman’s knives were made routinely. Some patterns, such as the Congress knife and Wharncliffe knife, were Rodgers’ own design. The Wharncliffe – with its serpentine handle and beaked master blade – was apparently designed after a dinner attended by Rodgers’ patron Lord Wharncliffe. The firm’s workmanship was usually backed by the best materials. Rodgers’ ivory cellar in Norfolk Street was crammed with giant tusks and was regarded as one of the hidden sights of the town. Four or five men were constantly employed in sawing the tusks, and around twenty four tons of ivory were used a year around 1882. Rodgers’ appetite for stag was no less insatiable: deer horns and antlers filled another cellar and pearl from the Philippines and was also cut there. Around 1890, Rodgers’ began forging its own shear steel and in 1894 they began melting crucible steel. Newbold retired in 1890 and the grandsons of Maurice Rodgers, Maurice George Rodgers (1855-1898) and John Rodgers (1856-1919), became joint-managing directors. The McKinley Tariff Act of 1890 halved their American business and consequently they toured South Africa. Despite increasing foreign competition and the decline of the American market, Rodgers’ prospered before the First World War. However, workers’ wages were cut while the partners continued to take significant dividend which culminated in a prolonged and bitter strike. The First World War saw a decline in the business which continued steadily until the 1975 when it was absorbed by Richards and ceased trading in 1983. Joseph Rodgers & Sons left an enduring legacy in its knives. Its dazzling exhibition pieces and other fine cutlery show that the company’s reputation as Sheffield’s foremost knife maker was well founded. Abbreviated from Geoffrey Tweedale 2019. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A BOWIE KNIFE, JOSEPH RODGERS & SONS, CUTLERS TO THEIR MAJESTIES, NO. 6 NORFOLK STREET, SHEFFIELD, LATE 19TH CENTURY with straight blade formed with a clipped-back point, signed on one face and with star and cross mark (worn), German silver hilt shaped for the fingers, including oval guard and pommel, and a pair of natural staghorn scales retained by four rivets, in its pigskin scabbard with German silver locket, 21.5 cm blade LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 303. In the nineteenth century, Rodgers had an unsurpassed reputation and history that was synonymous with the cutlery trade. The family's first cutler, John Rodgers (1701-85), is recorded around 1724, with a workshop near the present cathedral. In the same year the Company of Cutlers 'let' him a mark, a Star and Maltese Cross, which became world famous in later years. John Rodgers had three sons, John (1731-1811), Joseph (1743-1821), and Maurice (c.1747-1824) who joined the business and succeeded him. They are recorded with more workshops by 1780 and the business soon extended to occupy a nearby block of buildings at 6 Norfolk Street, an address that became as famous as Rodgers’ trade mark. By the early 19th century their trade had expanded from pen and pocket knives to include table cutlery and scissors. By 1817 the General Sheffield Directory lists the firm as ‘merchants, factors, table and pocket knife, and razor manufacturers’. In 1821 John’s son Joseph died and his sons continued the business under the leadership of the younger John (grandson of the founder). John was described as ‘unobtrusive in his manner’ but was ambitious and one of the founding partners of the Sheffield Banking Co. He had a flair for marketing and travelled the country taking orders. Not only was his firm’s output and range greater than any other Sheffield firm, but its quality was superior. The company’s manifesto states: ‘The principle on which the manufacture of cutlery is carried on by this firm is – quality first … [and] … price comes second’. He began making exhibitions knives and presented George IV with a minute specimen of cutlery with 57 blades, which occupied only an inch [25mm] when closed. In 1822, Rodgers’ was awarded its first Royal Warrant. Another fourteen royal appointments, from British and overseas royal dignitaries, followed over the next eighty years, and its company history was duly titled: Under Five Sovereigns. John Rodgers next commissioned the Year Knife, with a blade for every year (1821) and opened his sensational cutlery showroom in Norfolk Street where visitors came to marvel at Rodgers’ creations. Perhaps the greatest highlight shown there was the Norfolk Knife, an over 30 inch long sportsman’s knife with 75 blades and tools, that Rodgers’ produced for the Great Exhibition in 1851. The showroom proved particularly popular with Americans whose trade played a significant role in the firm’s expansion. Additionally, they looked East, with agents in Calcutta, Bombay, and Hong Kong by the mid-19th century. These markets enabled Rodgers to become the largest cutlery factory in Sheffield. The number of workmen appears to have grown from about 300 in the late 1820s, to over 500 in the 1840s. In 1871 the business became a limited company with Joseph Rodgers (1828-1883), grandson of the Joseph Rodgers who had died in 1821 and Robert Newbold as managing directors. Joseph died on 12 May 1883 and Newbold became the chairman and managing director. The firm continued to expand with offices in London, New York, New Orleans, Montreal, Toronto, Calcutta, Bombay and Havana. Their work force in 1871 was around 1,200 and accounted for one-seventh of all Sheffield’s American cutlery trade. In 1876 the American market was stagnating and Rodgers’ began looking elsewhere with a focus on trade in the Middle East, India and Australia. Notably the name ‘Rujjus’ or ‘Rojers’ was said to have entered the language as an adjective expressing superb quality in Persia, India and Ceylon. By 1888, the value of Rodgers’ shares had more than doubled and, in 1889, a silver and electro-plate showroom was opened in London. At this time, Rodgers acquired the scissors business of Joseph Hobson & Son. Rodgers’ produced catalogues that were packed with every type of knife imaginable. Pocket knives were made in scores of different styles. Ornate daggers and Bowie knives and complicated horseman’s knives were made routinely. Some patterns, such as the Congress knife and Wharncliffe knife, were Rodgers’ own design. The Wharncliffe – with its serpentine handle and beaked master blade – was apparently designed after a dinner attended by Rodgers’ patron Lord Wharncliffe. The firm’s workmanship was usually backed by the best materials. Rodgers’ ivory cellar in Norfolk Street was crammed with giant tusks and was regarded as one of the hidden sights of the town. Four or five men were constantly employed in sawing the tusks, and around twenty four tons of ivory were used a year around 1882. Rodgers’ appetite for stag was no less insatiable: deer horns and antlers filled another cellar and pearl from the Philippines and was also cut there. Around 1890, Rodgers’ began forging its own shear steel and in 1894 they began melting crucible steel. Newbold retired in 1890 and the grandsons of Maurice Rodgers, Maurice George Rodgers (1855-1898) and John Rodgers (1856-1919), became joint-managing directors. The McKinley Tariff Act of 1890 halved their American business and consequently they toured South Africa. Despite increasing foreign competition and the decline of the American market, Rodgers’ prospered before the First World War. However, workers’ wages were cut while the partners continued to take significant dividend which culminated in a prolonged and bitter strike. The First World War saw a decline in the business which continued steadily until the 1975 when it was absorbed by Richards and ceased trading in 1983. Joseph Rodgers & Sons left an enduring legacy in its knives. Its dazzling exhibition pieces and other fine cutlery show that the company’s reputation as Sheffield’s foremost knife maker was well founded. Abbreviated from Geoffrey Tweedale 2019. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A FINE BOWIE KNIFE, JOSEPH RODGERS & SONS, NO. 6 NORFOLK STREET, SHEFFIELD, LATE 19TH CENTURY with tapering blade formed with a swaged clipped-back point, finely scallop-milled back edge with a fuller beneath on each face, stamped with the maker’s details in small letters and with star and cross mark, German silver hilt comprising shaped cross-piece and flattened globular pommel and natural staghorn grip carved with a leaf on one face, in its leather scabbard and with a belt loop, 18.5 cm blade LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 264. Described by the author as his favourite Bowie knife. In the nineteenth century, Rodgers had an unsurpassed reputation and history that was synonymous with the cutlery trade. The family's first cutler, John Rodgers (1701-85), is recorded around 1724, with a workshop near the present cathedral. In the same year the Company of Cutlers 'let' him a mark, a Star and Maltese Cross, which became world famous in later years. John Rodgers had three sons, John (1731-1811), Joseph (1743-1821), and Maurice (c.1747-1824) who joined the business and succeeded him. They are recorded with more workshops by 1780 and the business soon extended to occupy a nearby block of buildings at 6 Norfolk Street, an address that became as famous as Rodgers’ trade mark. By the early 19th century their trade had expanded from pen and pocket knives to include table cutlery and scissors. By 1817 the General Sheffield Directory lists the firm as ‘merchants, factors, table and pocket knife, and razor manufacturers’. In 1821 John’s son Joseph died and his sons continued the business under the leadership of the younger John (grandson of the founder). John was described as ‘unobtrusive in his manner’ but was ambitious and one of the founding partners of the Sheffield Banking Co. He had a flair for marketing and travelled the country taking orders. Not only was his firm’s output and range greater than any other Sheffield firm, but its quality was superior. The company’s manifesto states: ‘The principle on which the manufacture of cutlery is carried on by this firm is – quality first … [and] … price comes second’. He began making exhibitions knives and presented George IV with a minute specimen of cutlery with 57 blades, which occupied only an inch [25mm] when closed. In 1822, Rodgers’ was awarded its first Royal Warrant. Another fourteen royal appointments, from British and overseas royal dignitaries, followed over the next eighty years, and its company history was duly titled: Under Five Sovereigns. John Rodgers next commissioned the Year Knife, with a blade for every year (1821) and opened his sensational cutlery showroom in Norfolk Street where visitors came to marvel at Rodgers’ creations. Perhaps the greatest highlight shown there was the Norfolk Knife, an over 30 inch long sportsman’s knife with 75 blades and tools, that Rodgers’ produced for the Great Exhibition in 1851. The showroom proved particularly popular with Americans whose trade played a significant role in the firm’s expansion. Additionally, they looked East, with agents in Calcutta, Bombay, and Hong Kong by the mid-19th century. These markets enabled Rodgers to become the largest cutlery factory in Sheffield. The number of workmen appears to have grown from about 300 in the late 1820s, to over 500 in the 1840s. In 1871 the business became a limited company with Joseph Rodgers (1828-1883), grandson of the Joseph Rodgers who had died in 1821 and Robert Newbold as managing directors. Joseph died on 12 May 1883 and Newbold became the chairman and managing director. The firm continued to expand with offices in London, New York, New Orleans, Montreal, Toronto, Calcutta, Bombay and Havana. Their work force in 1871 was around 1,200 and accounted for one-seventh of all Sheffield’s American cutlery trade. In 1876 the American market was stagnating and Rodgers’ began looking elsewhere with a focus on trade in the Middle East, India and Australia. Notably the name ‘Rujjus’ or ‘Rojers’ was said to have entered the language as an adjective expressing superb quality in Persia, India and Ceylon. By 1888, the value of Rodgers’ shares had more than doubled and, in 1889, a silver and electro-plate showroom was opened in London. At this time, Rodgers acquired the scissors business of Joseph Hobson & Son. Rodgers’ produced catalogues that were packed with every type of knife imaginable. Pocket knives were made in scores of different styles. Ornate daggers and Bowie knives and complicated horseman’s knives were made routinely. Some patterns, such as the Congress knife and Wharncliffe knife, were Rodgers’ own design. The Wharncliffe – with its serpentine handle and beaked master blade – was apparently designed after a dinner attended by Rodgers’ patron Lord Wharncliffe. The firm’s workmanship was usually backed by the best materials. Rodgers’ ivory cellar in Norfolk Street was crammed with giant tusks and was regarded as one of the hidden sights of the town. Four or five men were constantly employed in sawing the tusks, and around twenty four tons of ivory were used a year around 1882. Rodgers’ appetite for stag was no less insatiable: deer horns and antlers filled another cellar and pearl from the Philippines and was also cut there. Around 1890, Rodgers’ began forging its own shear steel and in 1894 they began melting crucible steel. Newbold retired in 1890 and the grandsons of Maurice Rodgers, Maurice George Rodgers (1855-1898) and John Rodgers (1856-1919), became joint-managing directors. The McKinley Tariff Act of 1890 halved their American business and consequently they toured South Africa. Despite increasing foreign competition and the decline of the American market, Rodgers’ prospered before the First World War. However, workers’ wages were cut while the partners continued to take significant dividend which culminated in a prolonged and bitter strike. The First World War saw a decline in the business which continued steadily until the 1975 when it was absorbed by Richards and ceased trading in 1983. Joseph Rodgers & Sons left an enduring legacy in its knives. Its dazzling exhibition pieces and other fine cutlery show that the company’s reputation as Sheffield’s foremost knife maker was well founded. Abbreviated from Geoffrey Tweedale 2019. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A BOWIE KNIFE, JOSEPH RODGERS & SONS, NO. 6 NORFOLK STREET, SHEFFIELD, LATE 19TH CENTURY with single-edged fullered blade formed with a false swage, rectangular ricasso stamped with the maker’s details including cross and star mark, iron guard, German silver pommel and natural staghorn grip, in leather scabbard, 25.0 cm blade LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 261. In the nineteenth century, Rodgers had an unsurpassed reputation and history that was synonymous with the cutlery trade. The family's first cutler, John Rodgers (1701-85), is recorded around 1724, with a workshop near the present cathedral. In the same year the Company of Cutlers 'let' him a mark, a Star and Maltese Cross, which became world famous in later years. John Rodgers had three sons, John (1731-1811), Joseph (1743-1821), and Maurice (c.1747-1824) who joined the business and succeeded him. They are recorded with more workshops by 1780 and the business soon extended to occupy a nearby block of buildings at 6 Norfolk Street, an address that became as famous as Rodgers’ trade mark. By the early 19th century their trade had expanded from pen and pocket knives to include table cutlery and scissors. By 1817 the General Sheffield Directory lists the firm as ‘merchants, factors, table and pocket knife, and razor manufacturers’. In 1821 John’s son Joseph died and his sons continued the business under the leadership of the younger John (grandson of the founder). John was described as ‘unobtrusive in his manner’ but was ambitious and one of the founding partners of the Sheffield Banking Co. He had a flair for marketing and travelled the country taking orders. Not only was his firm’s output and range greater than any other Sheffield firm, but its quality was superior. The company’s manifesto states: ‘The principle on which the manufacture of cutlery is carried on by this firm is – quality first … [and] … price comes second’. He began making exhibitions knives and presented George IV with a minute specimen of cutlery with 57 blades, which occupied only an inch [25mm] when closed. In 1822, Rodgers’ was awarded its first Royal Warrant. Another fourteen royal appointments, from British and overseas royal dignitaries, followed over the next eighty years, and its company history was duly titled: Under Five Sovereigns. John Rodgers next commissioned the Year Knife, with a blade for every year (1821) and opened his sensational cutlery showroom in Norfolk Street where visitors came to marvel at Rodgers’ creations. Perhaps the greatest highlight shown there was the Norfolk Knife, an over 30 inch long sportsman’s knife with 75 blades and tools, that Rodgers’ produced for the Great Exhibition in 1851. The showroom proved particularly popular with Americans whose trade played a significant role in the firm’s expansion. Additionally, they looked East, with agents in Calcutta, Bombay, and Hong Kong by the mid-19th century. These markets enabled Rodgers to become the largest cutlery factory in Sheffield. The number of workmen appears to have grown from about 300 in the late 1820s, to over 500 in the 1840s. In 1871 the business became a limited company with Joseph Rodgers (1828-1883), grandson of the Joseph Rodgers who had died in 1821 and Robert Newbold as managing directors. Joseph died on 12 May 1883 and Newbold became the chairman and managing director. The firm continued to expand with offices in London, New York, New Orleans, Montreal, Toronto, Calcutta, Bombay and Havana. Their work force in 1871 was around 1,200 and accounted for one-seventh of all Sheffield’s American cutlery trade. In 1876 the American market was stagnating and Rodgers’ began looking elsewhere with a focus on trade in the Middle East, India and Australia. Notably the name ‘Rujjus’ or ‘Rojers’ was said to have entered the language as an adjective expressing superb quality in Persia, India and Ceylon. By 1888, the value of Rodgers’ shares had more than doubled and, in 1889, a silver and electro-plate showroom was opened in London. At this time, Rodgers acquired the scissors business of Joseph Hobson & Son. Rodgers’ produced catalogues that were packed with every type of knife imaginable. Pocket knives were made in scores of different styles. Ornate daggers and Bowie knives and complicated horseman’s knives were made routinely. Some patterns, such as the Congress knife and Wharncliffe knife, were Rodgers’ own design. The Wharncliffe – with its serpentine handle and beaked master blade – was apparently designed after a dinner attended by Rodgers’ patron Lord Wharncliffe. The firm’s workmanship was usually backed by the best materials. Rodgers’ ivory cellar in Norfolk Street was crammed with giant tusks and was regarded as one of the hidden sights of the town. Four or five men were constantly employed in sawing the tusks, and around twenty four tons of ivory were used a year around 1882. Rodgers’ appetite for stag was no less insatiable: deer horns and antlers filled another cellar and pearl from the Philippines and was also cut there. Around 1890, Rodgers’ began forging its own shear steel and in 1894 they began melting crucible steel. Newbold retired in 1890 and the grandsons of Maurice Rodgers, Maurice George Rodgers (1855-1898) and John Rodgers (1856-1919), became joint-managing directors. The McKinley Tariff Act of 1890 halved their American business and consequently they toured South Africa. Despite increasing foreign competition and the decline of the American market, Rodgers’ prospered before the First World War. However, workers’ wages were cut while the partners continued to take significant dividend which culminated in a prolonged and bitter strike. The First World War saw a decline in the business which continued steadily until the 1975 when it was absorbed by Richards and ceased trading in 1983. Joseph Rodgers & Sons left an enduring legacy in its knives. Its dazzling exhibition pieces and other fine cutlery show that the company’s reputation as Sheffield’s foremost knife maker was well founded. Abbreviated from Geoffrey Tweedale 2019. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A FINE BOWIE KNIFE, JOSEPH RODGERS & SONS, CUTLERS TO HER MAJESTY, LAST QUARTER OF THE 19TH CENTURY with broad blade formed with a clipped-back point, struck with the maker’s details, the royal letters ‘VR’ divided by a crown and star and cross mark on one face, the reverse etched ‘Never draw me without reason’ and ‘nor sheath me without honour’ (faint in places), oval German silver guard, and chequered horn scales retained by three rivets, in its leather scabbard with German silver locket and chape and belt loop with vacant German silver escutcheon, 15.3 cm blade LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 265. In the nineteenth century, Rodgers had an unsurpassed reputation and history that was synonymous with the cutlery trade. The family's first cutler, John Rodgers (1701-85), is recorded around 1724, with a workshop near the present cathedral. In the same year the Company of Cutlers 'let' him a mark, a Star and Maltese Cross, which became world famous in later years. John Rodgers had three sons, John (1731-1811), Joseph (1743-1821), and Maurice (c.1747-1824) who joined the business and succeeded him. They are recorded with more workshops by 1780 and the business soon extended to occupy a nearby block of buildings at 6 Norfolk Street, an address that became as famous as Rodgers’ trade mark. By the early 19th century their trade had expanded from pen and pocket knives to include table cutlery and scissors. By 1817 the General Sheffield Directory lists the firm as ‘merchants, factors, table and pocket knife, and razor manufacturers’. In 1821 John’s son Joseph died and his sons continued the business under the leadership of the younger John (grandson of the founder). John was described as ‘unobtrusive in his manner’ but was ambitious and one of the founding partners of the Sheffield Banking Co. He had a flair for marketing and travelled the country taking orders. Not only was his firm’s output and range greater than any other Sheffield firm, but its quality was superior. The company’s manifesto states: ‘The principle on which the manufacture of cutlery is carried on by this firm is – quality first … [and] … price comes second’. He began making exhibitions knives and presented George IV with a minute specimen of cutlery with 57 blades, which occupied only an inch [25mm] when closed. In 1822, Rodgers’ was awarded its first Royal Warrant. Another fourteen royal appointments, from British and overseas royal dignitaries, followed over the next eighty years, and its company history was duly titled: Under Five Sovereigns. John Rodgers next commissioned the Year Knife, with a blade for every year (1821) and opened his sensational cutlery showroom in Norfolk Street where visitors came to marvel at Rodgers’ creations. Perhaps the greatest highlight shown there was the Norfolk Knife, an over 30 inch long sportsman’s knife with 75 blades and tools, that Rodgers’ produced for the Great Exhibition in 1851. The showroom proved particularly popular with Americans whose trade played a significant role in the firm’s expansion. Additionally, they looked East, with agents in Calcutta, Bombay, and Hong Kong by the mid-19th century. These markets enabled Rodgers to become the largest cutlery factory in Sheffield. The number of workmen appears to have grown from about 300 in the late 1820s, to over 500 in the 1840s. In 1871 the business became a limited company with Joseph Rodgers (1828-1883), grandson of the Joseph Rodgers who had died in 1821 and Robert Newbold as managing directors. Joseph died on 12 May 1883 and Newbold became the chairman and managing director. The firm continued to expand with offices in London, New York, New Orleans, Montreal, Toronto, Calcutta, Bombay and Havana. Their work force in 1871 was around 1,200 and accounted for one-seventh of all Sheffield’s American cutlery trade. In 1876 the American market was stagnating and Rodgers’ began looking elsewhere with a focus on trade in the Middle East, India and Australia. Notably the name ‘Rujjus’ or ‘Rojers’ was said to have entered the language as an adjective expressing superb quality in Persia, India and Ceylon. By 1888, the value of Rodgers’ shares had more than doubled and, in 1889, a silver and electro-plate showroom was opened in London. At this time, Rodgers acquired the scissors business of Joseph Hobson & Son. Rodgers’ produced catalogues that were packed with every type of knife imaginable. Pocket knives were made in scores of different styles. Ornate daggers and Bowie knives and complicated horseman’s knives were made routinely. Some patterns, such as the Congress knife and Wharncliffe knife, were Rodgers’ own design. The Wharncliffe – with its serpentine handle and beaked master blade – was apparently designed after a dinner attended by Rodgers’ patron Lord Wharncliffe. The firm’s workmanship was usually backed by the best materials. Rodgers’ ivory cellar in Norfolk Street was crammed with giant tusks and was regarded as one of the hidden sights of the town. Four or five men were constantly employed in sawing the tusks, and around twenty four tons of ivory were used a year around 1882. Rodgers’ appetite for stag was no less insatiable: deer horns and antlers filled another cellar and pearl from the Philippines and was also cut there. Around 1890, Rodgers’ began forging its own shear steel and in 1894 they began melting crucible steel. Newbold retired in 1890 and the grandsons of Maurice Rodgers, Maurice George Rodgers (1855-1898) and John Rodgers (1856-1919), became joint-managing directors. The McKinley Tariff Act of 1890 halved their American business and consequently they toured South Africa. Despite increasing foreign competition and the decline of the American market, Rodgers’ prospered before the First World War. However, workers’ wages were cut while the partners continued to take significant dividend which culminated in a prolonged and bitter strike. The First World War saw a decline in the business which continued steadily until the 1975 when it was absorbed by Richards and ceased trading in 1983. Joseph Rodgers & Sons left an enduring legacy in its knives. Its dazzling exhibition pieces and other fine cutlery show that the company’s reputation as Sheffield’s foremost knife maker was well founded. Abbreviated from Geoffrey Tweedale 2019. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A BOWIE KNIFE, JOSEPH RODGERS & SONS, NO. 6 NORFOLK STREET, SHEFFIELD, EARLY 20TH CENTURY with tapering blade formed with a clipped-back point, rectangular ricasso stamped with the maker’s details including cross and star mark and the Royal letters ‘ER’ divided by a crown, German silver guard with globular terminals, natural staghorn scales, vacant German silver escutcheon in its German silver-mounted leather scabbard with belt loop, 20.2 cm blade LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 261. In the nineteenth century, Rodgers had an unsurpassed reputation and history that was synonymous with the cutlery trade. The family's first cutler, John Rodgers (1701-85), is recorded around 1724, with a workshop near the present cathedral. In the same year the Company of Cutlers 'let' him a mark, a Star and Maltese Cross, which became world famous in later years. John Rodgers had three sons, John (1731-1811), Joseph (1743-1821), and Maurice (c.1747-1824) who joined the business and succeeded him. They are recorded with more workshops by 1780 and the business soon extended to occupy a nearby block of buildings at 6 Norfolk Street, an address that became as famous as Rodgers’ trade mark. By the early 19th century their trade had expanded from pen and pocket knives to include table cutlery and scissors. By 1817 the General Sheffield Directory lists the firm as ‘merchants, factors, table and pocket knife, and razor manufacturers’. In 1821 John’s son Joseph died and his sons continued the business under the leadership of the younger John (grandson of the founder). John was described as ‘unobtrusive in his manner’ but was ambitious and one of the founding partners of the Sheffield Banking Co. He had a flair for marketing and travelled the country taking orders. Not only was his firm’s output and range greater than any other Sheffield firm, but its quality was superior. The company’s manifesto states: ‘The principle on which the manufacture of cutlery is carried on by this firm is – quality first … [and] … price comes second’. He began making exhibitions knives and presented George IV with a minute specimen of cutlery with 57 blades, which occupied only an inch [25mm] when closed. In 1822, Rodgers’ was awarded its first Royal Warrant. Another fourteen royal appointments, from British and overseas royal dignitaries, followed over the next eighty years, and its company history was duly titled: Under Five Sovereigns. John Rodgers next commissioned the Year Knife, with a blade for every year (1821) and opened his sensational cutlery showroom in Norfolk Street where visitors came to marvel at Rodgers’ creations. Perhaps the greatest highlight shown there was the Norfolk Knife, an over 30 inch long sportsman’s knife with 75 blades and tools, that Rodgers’ produced for the Great Exhibition in 1851. The showroom proved particularly popular with Americans whose trade played a significant role in the firm’s expansion. Additionally, they looked East, with agents in Calcutta, Bombay, and Hong Kong by the mid-19th century. These markets enabled Rodgers to become the largest cutlery factory in Sheffield. The number of workmen appears to have grown from about 300 in the late 1820s, to over 500 in the 1840s. In 1871 the business became a limited company with Joseph Rodgers (1828-1883), grandson of the Joseph Rodgers who had died in 1821 and Robert Newbold as managing directors. Joseph died on 12 May 1883 and Newbold became the chairman and managing director. The firm continued to expand with offices in London, New York, New Orleans, Montreal, Toronto, Calcutta, Bombay and Havana. Their work force in 1871 was around 1,200 and accounted for one-seventh of all Sheffield’s American cutlery trade. In 1876 the American market was stagnating and Rodgers’ began looking elsewhere with a focus on trade in the Middle East, India and Australia. Notably the name ‘Rujjus’ or ‘Rojers’ was said to have entered the language as an adjective expressing superb quality in Persia, India and Ceylon. By 1888, the value of Rodgers’ shares had more than doubled and, in 1889, a silver and electro-plate showroom was opened in London. At this time, Rodgers acquired the scissors business of Joseph Hobson & Son. Rodgers’ produced catalogues that were packed with every type of knife imaginable. Pocket knives were made in scores of different styles. Ornate daggers and Bowie knives and complicated horseman’s knives were made routinely. Some patterns, such as the Congress knife and Wharncliffe knife, were Rodgers’ own design. The Wharncliffe – with its serpentine handle and beaked master blade – was apparently designed after a dinner attended by Rodgers’ patron Lord Wharncliffe. The firm’s workmanship was usually backed by the best materials. Rodgers’ ivory cellar in Norfolk Street was crammed with giant tusks and was regarded as one of the hidden sights of the town. Four or five men were constantly employed in sawing the tusks, and around twenty four tons of ivory were used a year around 1882. Rodgers’ appetite for stag was no less insatiable: deer horns and antlers filled another cellar and pearl from the Philippines and was also cut there. Around 1890, Rodgers’ began forging its own shear steel and in 1894 they began melting crucible steel. Newbold retired in 1890 and the grandsons of Maurice Rodgers, Maurice George Rodgers (1855-1898) and John Rodgers (1856-1919), became joint-managing directors. The McKinley Tariff Act of 1890 halved their American business and consequently they toured South Africa. Despite increasing foreign competition and the decline of the American market, Rodgers’ prospered before the First World War. However, workers’ wages were cut while the partners continued to take significant dividend which culminated in a prolonged and bitter strike. The First World War saw a decline in the business which continued steadily until the 1975 when it was absorbed by Richards and ceased trading in 1983. Joseph Rodgers & Sons left an enduring legacy in its knives. Its dazzling exhibition pieces and other fine cutlery show that the company’s reputation as Sheffield’s foremost knife maker was well founded. Abbreviated from Geoffrey Tweedale 2019. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A BOWIE KNIFE, JOSEPH RODGERS & SONS, NO. 6 NORFOLK STREET, SHEFFIELD, EARLY 20TH CENTURY with tapering blade formed with a spear point, rectangular ricasso stamped with the maker’s details including cross and star mark and the Royal letters ‘GR’ divided by a crown, German silver oval guard, natural staghorn scales, in its leather scabbard with belt loop, embossed ‘H. Hidden’, 17.5 cm blade LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 261. In the nineteenth century, Rodgers had an unsurpassed reputation and history that was synonymous with the cutlery trade. The family's first cutler, John Rodgers (1701-85), is recorded around 1724, with a workshop near the present cathedral. In the same year the Company of Cutlers 'let' him a mark, a Star and Maltese Cross, which became world famous in later years. John Rodgers had three sons, John (1731-1811), Joseph (1743-1821), and Maurice (c.1747-1824) who joined the business and succeeded him. They are recorded with more workshops by 1780 and the business soon extended to occupy a nearby block of buildings at 6 Norfolk Street, an address that became as famous as Rodgers’ trade mark. By the early 19th century their trade had expanded from pen and pocket knives to include table cutlery and scissors. By 1817 the General Sheffield Directory lists the firm as ‘merchants, factors, table and pocket knife, and razor manufacturers’. In 1821 John’s son Joseph died and his sons continued the business under the leadership of the younger John (grandson of the founder). John was described as ‘unobtrusive in his manner’ but was ambitious and one of the founding partners of the Sheffield Banking Co. He had a flair for marketing and travelled the country taking orders. Not only was his firm’s output and range greater than any other Sheffield firm, but its quality was superior. The company’s manifesto states: ‘The principle on which the manufacture of cutlery is carried on by this firm is – quality first … [and] … price comes second’. He began making exhibitions knives and presented George IV with a minute specimen of cutlery with 57 blades, which occupied only an inch [25mm] when closed. In 1822, Rodgers’ was awarded its first Royal Warrant. Another fourteen royal appointments, from British and overseas royal dignitaries, followed over the next eighty years, and its company history was duly titled: Under Five Sovereigns. John Rodgers next commissioned the Year Knife, with a blade for every year (1821) and opened his sensational cutlery showroom in Norfolk Street where visitors came to marvel at Rodgers’ creations. Perhaps the greatest highlight shown there was the Norfolk Knife, an over 30 inch long sportsman’s knife with 75 blades and tools, that Rodgers’ produced for the Great Exhibition in 1851. The showroom proved particularly popular with Americans whose trade played a significant role in the firm’s expansion. Additionally, they looked East, with agents in Calcutta, Bombay, and Hong Kong by the mid-19th century. These markets enabled Rodgers to become the largest cutlery factory in Sheffield. The number of workmen appears to have grown from about 300 in the late 1820s, to over 500 in the 1840s. In 1871 the business became a limited company with Joseph Rodgers (1828-1883), grandson of the Joseph Rodgers who had died in 1821 and Robert Newbold as managing directors. Joseph died on 12 May 1883 and Newbold became the chairman and managing director. The firm continued to expand with offices in London, New York, New Orleans, Montreal, Toronto, Calcutta, Bombay and Havana. Their work force in 1871 was around 1,200 and accounted for one-seventh of all Sheffield’s American cutlery trade. In 1876 the American market was stagnating and Rodgers’ began looking elsewhere with a focus on trade in the Middle East, India and Australia. Notably the name ‘Rujjus’ or ‘Rojers’ was said to have entered the language as an adjective expressing superb quality in Persia, India and Ceylon. By 1888, the value of Rodgers’ shares had more than doubled and, in 1889, a silver and electro-plate showroom was opened in London. At this time, Rodgers acquired the scissors business of Joseph Hobson & Son. Rodgers’ produced catalogues that were packed with every type of knife imaginable. Pocket knives were made in scores of different styles. Ornate daggers and Bowie knives and complicated horseman’s knives were made routinely. Some patterns, such as the Congress knife and Wharncliffe knife, were Rodgers’ own design. The Wharncliffe – with its serpentine handle and beaked master blade – was apparently designed after a dinner attended by Rodgers’ patron Lord Wharncliffe. The firm’s workmanship was usually backed by the best materials. Rodgers’ ivory cellar in Norfolk Street was crammed with giant tusks and was regarded as one of the hidden sights of the town. Four or five men were constantly employed in sawing the tusks, and around twenty four tons of ivory were used a year around 1882. Rodgers’ appetite for stag was no less insatiable: deer horns and antlers filled another cellar and pearl from the Philippines and was also cut there. Around 1890, Rodgers’ began forging its own shear steel and in 1894 they began melting crucible steel. Newbold retired in 1890 and the grandsons of Maurice Rodgers, Maurice George Rodgers (1855-1898) and John Rodgers (1856-1919), became joint-managing directors. The McKinley Tariff Act of 1890 halved their American business and consequently they toured South Africa. Despite increasing foreign competition and the decline of the American market, Rodgers’ prospered before the First World War. However, workers’ wages were cut while the partners continued to take significant dividend which culminated in a prolonged and bitter strike. The First World War saw a decline in the business which continued steadily until the 1975 when it was absorbed by Richards and ceased trading in 1983. Joseph Rodgers & Sons left an enduring legacy in its knives. Its dazzling exhibition pieces and other fine cutlery show that the company’s reputation as Sheffield’s foremost knife maker was well founded. Abbreviated from Geoffrey Tweedale 2019. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A MASSIVE KNIFE FOR EXHBITION, JOSEPH RODGERS & SONS, NO. 6 NORFOLK STREET, SHEFFIELD, LATE 19TH CENTURY with strongly tapering blade engraved ‘The Camp Knife’ in capitals, signed in full and with star and cross mark on one face, formed with a scrolled fluted back-edge and recessed at the ricasso, engraved silver-plated hilt of derived scimitar form decorated with flowers and foliage (losses) and gutta percha grips, 64.5 cm overall LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 102. In the nineteenth century, Rodgers had an unsurpassed reputation and history that was synonymous with the cutlery trade. The family's first cutler, John Rodgers (1701-85), is recorded around 1724, with a workshop near the present cathedral. In the same year the Company of Cutlers 'let' him a mark, a Star and Maltese Cross, which became world famous in later years. John Rodgers had three sons, John (1731-1811), Joseph (1743-1821), and Maurice (c.1747-1824) who joined the business and succeeded him. They are recorded with more workshops by 1780 and the business soon extended to occupy a nearby block of buildings at 6 Norfolk Street, an address that became as famous as Rodgers’ trade mark. By the early 19th century their trade had expanded from pen and pocket knives to include table cutlery and scissors. By 1817 the General Sheffield Directory lists the firm as ‘merchants, factors, table and pocket knife, and razor manufacturers’. In 1821 John’s son Joseph died and his sons continued the business under the leadership of the younger John (grandson of the founder). John was described as ‘unobtrusive in his manner’ but was ambitious and one of the founding partners of the Sheffield Banking Co. He had a flair for marketing and travelled the country taking orders. Not only was his firm’s output and range greater than any other Sheffield firm, but its quality was superior. The company’s manifesto states: ‘The principle on which the manufacture of cutlery is carried on by this firm is – quality first … [and] … price comes second’. He began making exhibitions knives and presented George IV with a minute specimen of cutlery with 57 blades, which occupied only an inch [25mm] when closed. In 1822, Rodgers’ was awarded its first Royal Warrant. Another fourteen royal appointments, from British and overseas royal dignitaries, followed over the next eighty years, and its company history was duly titled: Under Five Sovereigns. John Rodgers next commissioned the Year Knife, with a blade for every year (1821) and opened his sensational cutlery showroom in Norfolk Street where visitors came to marvel at Rodgers’ creations. Perhaps the greatest highlight shown there was the Norfolk Knife, an over 30 inch long sportsman’s knife with 75 blades and tools, that Rodgers’ produced for the Great Exhibition in 1851. The showroom proved particularly popular with Americans whose trade played a significant role in the firm’s expansion. Additionally, they looked East, with agents in Calcutta, Bombay, and Hong Kong by the mid-19th century. These markets enabled Rodgers to become the largest cutlery factory in Sheffield. The number of workmen appears to have grown from about 300 in the late 1820s, to over 500 in the 1840s. In 1871 the business became a limited company with Joseph Rodgers (1828-1883), grandson of the Joseph Rodgers who had died in 1821 and Robert Newbold as managing directors. Joseph died on 12 May 1883 and Newbold became the chairman and managing director. The firm continued to expand with offices in London, New York, New Orleans, Montreal, Toronto, Calcutta, Bombay and Havana. Their work force in 1871 was around 1,200 and accounted for one-seventh of all Sheffield’s American cutlery trade. In 1876 the American market was stagnating and Rodgers’ began looking elsewhere with a focus on trade in the Middle East, India and Australia. Notably the name ‘Rujjus’ or ‘Rojers’ was said to have entered the language as an adjective expressing superb quality in Persia, India and Ceylon. By 1888, the value of Rodgers’ shares had more than doubled and, in 1889, a silver and electro-plate showroom was opened in London. At this time, Rodgers acquired the scissors business of Joseph Hobson & Son. Rodgers’ produced catalogues that were packed with every type of knife imaginable. Pocket knives were made in scores of different styles. Ornate daggers and Bowie knives and complicated horseman’s knives were made routinely. Some patterns, such as the Congress knife and Wharncliffe knife, were Rodgers’ own design. The Wharncliffe – with its serpentine handle and beaked master blade – was apparently designed after a dinner attended by Rodgers’ patron Lord Wharncliffe. The firm’s workmanship was usually backed by the best materials. Rodgers’ ivory cellar in Norfolk Street was crammed with giant tusks and was regarded as one of the hidden sights of the town. Four or five men were constantly employed in sawing the tusks, and around twenty four tons of ivory were used a year around 1882. Rodgers’ appetite for stag was no less insatiable: deer horns and antlers filled another cellar and pearl from the Philippines and was also cut there. Around 1890, Rodgers’ began forging its own shear steel and in 1894 they began melting crucible steel. Newbold retired in 1890 and the grandsons of Maurice Rodgers, Maurice George Rodgers (1855-1898) and John Rodgers (1856-1919), became joint-managing directors. The McKinley Tariff Act of 1890 halved their American business and consequently they toured South Africa. Despite increasing foreign competition and the decline of the American market, Rodgers’ prospered before the First World War. However, workers’ wages were cut while the partners continued to take significant dividend which culminated in a prolonged and bitter strike. The First World War saw a decline in the business which continued steadily until the 1975 when it was absorbed by Richards and ceased trading in 1983. Joseph Rodgers & Sons left an enduring legacy in its knives. Its dazzling exhibition pieces and other fine cutlery show that the company’s reputation as Sheffield’s foremost knife maker was well founded. Abbreviated from Geoffrey Tweedale 2019. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A FIXED-BLADE CAMPAIGN KNIFE, JOSEPH RODGERS & SONS, CUTLERS TO HER MAJESTY, LATE 19TH CENTURY, POSSIBLY MADE FOR PRESENTATION BY ALBERT EDWARD, PRINCE OF WALES AND LATER KING EDWARD VII (1841-1910) with fixed blade with clipped-back point and filed back-edge, struck with the maker’s details, ‘VR’ divided by a crown, and star and cross, with four folding elements including corkscrew, button hook and awl, further accessories including tweezers, pincers, scissors and pricker concealed in the German silver pommel, the latter engraved ‘1875’ and ‘AE’, chequered horn scales, in its German silver-mounted leather scabbard engraved ‘AE’ ‘1875’ and with the crowned Most Noble Order of the Garter on the locket, with a loop for suspension, 22.0 cm overall (the knife) LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 97. In the nineteenth century, Rodgers had an unsurpassed reputation and history that was synonymous with the cutlery trade. The family's first cutler, John Rodgers (1701-85), is recorded around 1724, with a workshop near the present cathedral. In the same year the Company of Cutlers 'let' him a mark, a Star and Maltese Cross, which became world famous in later years. John Rodgers had three sons, John (1731-1811), Joseph (1743-1821), and Maurice (c.1747-1824) who joined the business and succeeded him. They are recorded with more workshops by 1780 and the business soon extended to occupy a nearby block of buildings at 6 Norfolk Street, an address that became as famous as Rodgers’ trade mark. By the early 19th century their trade had expanded from pen and pocket knives to include table cutlery and scissors. By 1817 the General Sheffield Directory lists the firm as ‘merchants, factors, table and pocket knife, and razor manufacturers’. In 1821 John’s son Joseph died and his sons continued the business under the leadership of the younger John (grandson of the founder). John was described as ‘unobtrusive in his manner’ but was ambitious and one of the founding partners of the Sheffield Banking Co. He had a flair for marketing and travelled the country taking orders. Not only was his firm’s output and range greater than any other Sheffield firm, but its quality was superior. The company’s manifesto states: ‘The principle on which the manufacture of cutlery is carried on by this firm is – quality first … [and] … price comes second’. He began making exhibitions knives and presented George IV with a minute specimen of cutlery with 57 blades, which occupied only an inch [25mm] when closed. In 1822, Rodgers’ was awarded its first Royal Warrant. Another fourteen royal appointments, from British and overseas royal dignitaries, followed over the next eighty years, and its company history was duly titled: Under Five Sovereigns. John Rodgers next commissioned the Year Knife, with a blade for every year (1821) and opened his sensational cutlery showroom in Norfolk Street where visitors came to marvel at Rodgers’ creations. Perhaps the greatest highlight shown there was the Norfolk Knife, an over 30 inch long sportsman’s knife with 75 blades and tools, that Rodgers’ produced for the Great Exhibition in 1851. The showroom proved particularly popular with Americans whose trade played a significant role in the firm’s expansion. Additionally, they looked East, with agents in Calcutta, Bombay, and Hong Kong by the mid-19th century. These markets enabled Rodgers to become the largest cutlery factory in Sheffield. The number of workmen appears to have grown from about 300 in the late 1820s, to over 500 in the 1840s. In 1871 the business became a limited company with Joseph Rodgers (1828-1883), grandson of the Joseph Rodgers who had died in 1821 and Robert Newbold as managing directors. Joseph died on 12 May 1883 and Newbold became the chairman and managing director. The firm continued to expand with offices in London, New York, New Orleans, Montreal, Toronto, Calcutta, Bombay and Havana. Their work force in 1871 was around 1,200 and accounted for one-seventh of all Sheffield’s American cutlery trade. In 1876 the American market was stagnating and Rodgers’ began looking elsewhere with a focus on trade in the Middle East, India and Australia. Notably the name ‘Rujjus’ or ‘Rojers’ was said to have entered the language as an adjective expressing superb quality in Persia, India and Ceylon. By 1888, the value of Rodgers’ shares had more than doubled and, in 1889, a silver and electro-plate showroom was opened in London. At this time, Rodgers acquired the scissors business of Joseph Hobson & Son. Rodgers’ produced catalogues that were packed with every type of knife imaginable. Pocket knives were made in scores of different styles. Ornate daggers and Bowie knives and complicated horseman’s knives were made routinely. Some patterns, such as the Congress knife and Wharncliffe knife, were Rodgers’ own design. The Wharncliffe – with its serpentine handle and beaked master blade – was apparently designed after a dinner attended by Rodgers’ patron Lord Wharncliffe. The firm’s workmanship was usually backed by the best materials. Rodgers’ ivory cellar in Norfolk Street was crammed with giant tusks and was regarded as one of the hidden sights of the town. Four or five men were constantly employed in sawing the tusks, and around twenty four tons of ivory were used a year around 1882. Rodgers’ appetite for stag was no less insatiable: deer horns and antlers filled another cellar and pearl from the Philippines and was also cut there. Around 1890, Rodgers’ began forging its own shear steel and in 1894 they began melting crucible steel. Newbold retired in 1890 and the grandsons of Maurice Rodgers, Maurice George Rodgers (1855-1898) and John Rodgers (1856-1919), became joint-managing directors. The McKinley Tariff Act of 1890 halved their American business and consequently they toured South Africa. Despite increasing foreign competition and the decline of the American market, Rodgers’ prospered before the First World War. However, workers’ wages were cut while the partners continued to take significant dividend which culminated in a prolonged and bitter strike. The First World War saw a decline in the business which continued steadily until the 1975 when it was absorbed by Richards and ceased trading in 1983. Joseph Rodgers & Sons left an enduring legacy in its knives. Its dazzling exhibition pieces and other fine cutlery show that the company’s reputation as Sheffield’s foremost knife maker was well founded. Abbreviated from Geoffrey Tweedale 2019. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A HUNTING KNIFE, JOSEPH RODGERS & SONS CUTLERS TO HER MAJESTY, SHEFFIELD, CIRCA 1860 with tapering blade formed with a spear point, stamped with the maker’s details on one face, and ‘The Hunter’s Companion’ in script, rectangular ricasso struck with star and cross mark, German silver hilt comprising recurved quillons with flattened scrolling terminals, cap pommel (fitted with later copper alloy oval), and spirally-bound fishskin-covered grip, in its leather scabbard with German silver chape and locket, the latter with a belt hook, 23.5 cm blade LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 262. In the nineteenth century, Rodgers had an unsurpassed reputation and history that was synonymous with the cutlery trade. The family's first cutler, John Rodgers (1701-85), is recorded around 1724, with a workshop near the present cathedral. In the same year the Company of Cutlers 'let' him a mark, a Star and Maltese Cross, which became world famous in later years. John Rodgers had three sons, John (1731-1811), Joseph (1743-1821), and Maurice (c.1747-1824) who joined the business and succeeded him. They are recorded with more workshops by 1780 and the business soon extended to occupy a nearby block of buildings at 6 Norfolk Street, an address that became as famous as Rodgers’ trade mark. By the early 19th century their trade had expanded from pen and pocket knives to include table cutlery and scissors. By 1817 the General Sheffield Directory lists the firm as ‘merchants, factors, table and pocket knife, and razor manufacturers’. In 1821 John’s son Joseph died and his sons continued the business under the leadership of the younger John (grandson of the founder). John was described as ‘unobtrusive in his manner’ but was ambitious and one of the founding partners of the Sheffield Banking Co. He had a flair for marketing and travelled the country taking orders. Not only was his firm’s output and range greater than any other Sheffield firm, but its quality was superior. The company’s manifesto states: ‘The principle on which the manufacture of cutlery is carried on by this firm is – quality first … [and] … price comes second’. He began making exhibitions knives and presented George IV with a minute specimen of cutlery with 57 blades, which occupied only an inch [25mm] when closed. In 1822, Rodgers’ was awarded its first Royal Warrant. Another fourteen royal appointments, from British and overseas royal dignitaries, followed over the next eighty years, and its company history was duly titled: Under Five Sovereigns. John Rodgers next commissioned the Year Knife, with a blade for every year (1821) and opened his sensational cutlery showroom in Norfolk Street where visitors came to marvel at Rodgers’ creations. Perhaps the greatest highlight shown there was the Norfolk Knife, an over 30 inch long sportsman’s knife with 75 blades and tools, that Rodgers’ produced for the Great Exhibition in 1851. The showroom proved particularly popular with Americans whose trade played a significant role in the firm’s expansion. Additionally, they looked East, with agents in Calcutta, Bombay, and Hong Kong by the mid-19th century. These markets enabled Rodgers to become the largest cutlery factory in Sheffield. The number of workmen appears to have grown from about 300 in the late 1820s, to over 500 in the 1840s. In 1871 the business became a limited company with Joseph Rodgers (1828-1883), grandson of the Joseph Rodgers who had died in 1821 and Robert Newbold as managing directors. Joseph died on 12 May 1883 and Newbold became the chairman and managing director. The firm continued to expand with offices in London, New York, New Orleans, Montreal, Toronto, Calcutta, Bombay and Havana. Their work force in 1871 was around 1,200 and accounted for one-seventh of all Sheffield’s American cutlery trade. In 1876 the American market was stagnating and Rodgers’ began looking elsewhere with a focus on trade in the Middle East, India and Australia. Notably the name ‘Rujjus’ or ‘Rojers’ was said to have entered the language as an adjective expressing superb quality in Persia, India and Ceylon. By 1888, the value of Rodgers’ shares had more than doubled and, in 1889, a silver and electro-plate showroom was opened in London. At this time, Rodgers acquired the scissors business of Joseph Hobson & Son. Rodgers’ produced catalogues that were packed with every type of knife imaginable. Pocket knives were made in scores of different styles. Ornate daggers and Bowie knives and complicated horseman’s knives were made routinely. Some patterns, such as the Congress knife and Wharncliffe knife, were Rodgers’ own design. The Wharncliffe – with its serpentine handle and beaked master blade – was apparently designed after a dinner attended by Rodgers’ patron Lord Wharncliffe. The firm’s workmanship was usually backed by the best materials. Rodgers’ ivory cellar in Norfolk Street was crammed with giant tusks and was regarded as one of the hidden sights of the town. Four or five men were constantly employed in sawing the tusks, and around twenty four tons of ivory were used a year around 1882. Rodgers’ appetite for stag was no less insatiable: deer horns and antlers filled another cellar and pearl from the Philippines and was also cut there. Around 1890, Rodgers’ began forging its own shear steel and in 1894 they began melting crucible steel. Newbold retired in 1890 and the grandsons of Maurice Rodgers, Maurice George Rodgers (1855-1898) and John Rodgers (1856-1919), became joint-managing directors. The McKinley Tariff Act of 1890 halved their American business and consequently they toured South Africa. Despite increasing foreign competition and the decline of the American market, Rodgers’ prospered before the First World War. However, workers’ wages were cut while the partners continued to take significant dividend which culminated in a prolonged and bitter strike. The First World War saw a decline in the business which continued steadily until the 1975 when it was absorbed by Richards and ceased trading in 1983. Joseph Rodgers & Sons left an enduring legacy in its knives. Its dazzling exhibition pieces and other fine cutlery show that the company’s reputation as Sheffield’s foremost knife maker was well founded. Abbreviated from Geoffrey Tweedale 2019. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A HUNTING KNIFE, JOSEPH RODGERS & SONS CUTLERS TO HER MAJESTY, SHEFFIELD, CIRCA 1860 with tapering blade formed with a false swage, engraved ‘The Hunter’s Companion’ in script, rectangular ricasso stamped with the maker’s details and star and cross mark, iron cross-guard, German silver small ferule, and shaped chequered grip, in its leather scabbard with German silver locket and chape, the former with an iron spring catch, 20.4 cm blade LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 262. In the nineteenth century, Rodgers had an unsurpassed reputation and history that was synonymous with the cutlery trade. The family's first cutler, John Rodgers (1701-85), is recorded around 1724, with a workshop near the present cathedral. In the same year the Company of Cutlers 'let' him a mark, a Star and Maltese Cross, which became world famous in later years. John Rodgers had three sons, John (1731-1811), Joseph (1743-1821), and Maurice (c.1747-1824) who joined the business and succeeded him. They are recorded with more workshops by 1780 and the business soon extended to occupy a nearby block of buildings at 6 Norfolk Street, an address that became as famous as Rodgers’ trade mark. By the early 19th century their trade had expanded from pen and pocket knives to include table cutlery and scissors. By 1817 the General Sheffield Directory lists the firm as ‘merchants, factors, table and pocket knife, and razor manufacturers’. In 1821 John’s son Joseph died and his sons continued the business under the leadership of the younger John (grandson of the founder). John was described as ‘unobtrusive in his manner’ but was ambitious and one of the founding partners of the Sheffield Banking Co. He had a flair for marketing and travelled the country taking orders. Not only was his firm’s output and range greater than any other Sheffield firm, but its quality was superior. The company’s manifesto states: ‘The principle on which the manufacture of cutlery is carried on by this firm is – quality first … [and] … price comes second’. He began making exhibitions knives and presented George IV with a minute specimen of cutlery with 57 blades, which occupied only an inch [25mm] when closed. In 1822, Rodgers’ was awarded its first Royal Warrant. Another fourteen royal appointments, from British and overseas royal dignitaries, followed over the next eighty years, and its company history was duly titled: Under Five Sovereigns. John Rodgers next commissioned the Year Knife, with a blade for every year (1821) and opened his sensational cutlery showroom in Norfolk Street where visitors came to marvel at Rodgers’ creations. Perhaps the greatest highlight shown there was the Norfolk Knife, an over 30 inch long sportsman’s knife with 75 blades and tools, that Rodgers’ produced for the Great Exhibition in 1851. The showroom proved particularly popular with Americans whose trade played a significant role in the firm’s expansion. Additionally, they looked East, with agents in Calcutta, Bombay, and Hong Kong by the mid-19th century. These markets enabled Rodgers to become the largest cutlery factory in Sheffield. The number of workmen appears to have grown from about 300 in the late 1820s, to over 500 in the 1840s. In 1871 the business became a limited company with Joseph Rodgers (1828-1883), grandson of the Joseph Rodgers who had died in 1821 and Robert Newbold as managing directors. Joseph died on 12 May 1883 and Newbold became the chairman and managing director. The firm continued to expand with offices in London, New York, New Orleans, Montreal, Toronto, Calcutta, Bombay and Havana. Their work force in 1871 was around 1,200 and accounted for one-seventh of all Sheffield’s American cutlery trade. In 1876 the American market was stagnating and Rodgers’ began looking elsewhere with a focus on trade in the Middle East, India and Australia. Notably the name ‘Rujjus’ or ‘Rojers’ was said to have entered the language as an adjective expressing superb quality in Persia, India and Ceylon. By 1888, the value of Rodgers’ shares had more than doubled and, in 1889, a silver and electro-plate showroom was opened in London. At this time, Rodgers acquired the scissors business of Joseph Hobson & Son. Rodgers’ produced catalogues that were packed with every type of knife imaginable. Pocket knives were made in scores of different styles. Ornate daggers and Bowie knives and complicated horseman’s knives were made routinely. Some patterns, such as the Congress knife and Wharncliffe knife, were Rodgers’ own design. The Wharncliffe – with its serpentine handle and beaked master blade – was apparently designed after a dinner attended by Rodgers’ patron Lord Wharncliffe. The firm’s workmanship was usually backed by the best materials. Rodgers’ ivory cellar in Norfolk Street was crammed with giant tusks and was regarded as one of the hidden sights of the town. Four or five men were constantly employed in sawing the tusks, and around twenty four tons of ivory were used a year around 1882. Rodgers’ appetite for stag was no less insatiable: deer horns and antlers filled another cellar and pearl from the Philippines and was also cut there. Around 1890, Rodgers’ began forging its own shear steel and in 1894 they began melting crucible steel. Newbold retired in 1890 and the grandsons of Maurice Rodgers, Maurice George Rodgers (1855-1898) and John Rodgers (1856-1919), became joint-managing directors. The McKinley Tariff Act of 1890 halved their American business and consequently they toured South Africa. Despite increasing foreign competition and the decline of the American market, Rodgers’ prospered before the First World War. However, workers’ wages were cut while the partners continued to take significant dividend which culminated in a prolonged and bitter strike. The First World War saw a decline in the business which continued steadily until the 1975 when it was absorbed by Richards and ceased trading in 1983. Joseph Rodgers & Sons left an enduring legacy in its knives. Its dazzling exhibition pieces and other fine cutlery show that the company’s reputation as Sheffield’s foremost knife maker was well founded. Abbreviated from Geoffrey Tweedale 2019. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A SMALL DIRK, JOSEPH RODGERS & SONS, CUTLERS TO THEIR MAJESTIES, NO. 6 NORFOLK STREET, SHEFFIELD, CIRCA 1880 with double-edged polished blade of diamond section swelling towards the point, stamped with the maker’s details including cross and star mark on one face, German silver recurved guard, mother-of-pearl grip. In its German silver-mounted leather scabbard and in fine condition throughout, 13.0 cm blade LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 259. In the nineteenth century, Rodgers had an unsurpassed reputation and history that was synonymous with the cutlery trade. The family's first cutler, John Rodgers (1701-85), is recorded around 1724, with a workshop near the present cathedral. In the same year the Company of Cutlers 'let' him a mark, a Star and Maltese Cross, which became world famous in later years. John Rodgers had three sons, John (1731-1811), Joseph (1743-1821), and Maurice (c.1747-1824) who joined the business and succeeded him. They are recorded with more workshops by 1780 and the business soon extended to occupy a nearby block of buildings at 6 Norfolk Street, an address that became as famous as Rodgers’ trade mark. By the early 19th century their trade had expanded from pen and pocket knives to include table cutlery and scissors. By 1817 the General Sheffield Directory lists the firm as ‘merchants, factors, table and pocket knife, and razor manufacturers’. In 1821 John’s son Joseph died and his sons continued the business under the leadership of the younger John (grandson of the founder). John was described as ‘unobtrusive in his manner’ but was ambitious and one of the founding partners of the Sheffield Banking Co. He had a flair for marketing and travelled the country taking orders. Not only was his firm’s output and range greater than any other Sheffield firm, but its quality was superior. The company’s manifesto states: ‘The principle on which the manufacture of cutlery is carried on by this firm is – quality first … [and] … price comes second’. He began making exhibitions knives and presented George IV with a minute specimen of cutlery with 57 blades, which occupied only an inch [25mm] when closed. In 1822, Rodgers’ was awarded its first Royal Warrant. Another fourteen royal appointments, from British and overseas royal dignitaries, followed over the next eighty years, and its company history was duly titled: Under Five Sovereigns. John Rodgers next commissioned the Year Knife, with a blade for every year (1821) and opened his sensational cutlery showroom in Norfolk Street where visitors came to marvel at Rodgers’ creations. Perhaps the greatest highlight shown there was the Norfolk Knife, an over 30 inch long sportsman’s knife with 75 blades and tools, that Rodgers’ produced for the Great Exhibition in 1851. The showroom proved particularly popular with Americans whose trade played a significant role in the firm’s expansion. Additionally, they looked East, with agents in Calcutta, Bombay, and Hong Kong by the mid-19th century. These markets enabled Rodgers to become the largest cutlery factory in Sheffield. The number of workmen appears to have grown from about 300 in the late 1820s, to over 500 in the 1840s. In 1871 the business became a limited company with Joseph Rodgers (1828-1883), grandson of the Joseph Rodgers who had died in 1821 and Robert Newbold as managing directors. Joseph died on 12 May 1883 and Newbold became the chairman and managing director. The firm continued to expand with offices in London, New York, New Orleans, Montreal, Toronto, Calcutta, Bombay and Havana. Their work force in 1871 was around 1,200 and accounted for one-seventh of all Sheffield’s American cutlery trade. In 1876 the American market was stagnating and Rodgers’ began looking elsewhere with a focus on trade in the Middle East, India and Australia. Notably the name ‘Rujjus’ or ‘Rojers’ was said to have entered the language as an adjective expressing superb quality in Persia, India and Ceylon. By 1888, the value of Rodgers’ shares had more than doubled and, in 1889, a silver and electro-plate showroom was opened in London. At this time, Rodgers acquired the scissors business of Joseph Hobson & Son. Rodgers’ produced catalogues that were packed with every type of knife imaginable. Pocket knives were made in scores of different styles. Ornate daggers and Bowie knives and complicated horseman’s knives were made routinely. Some patterns, such as the Congress knife and Wharncliffe knife, were Rodgers’ own design. The Wharncliffe – with its serpentine handle and beaked master blade – was apparently designed after a dinner attended by Rodgers’ patron Lord Wharncliffe. The firm’s workmanship was usually backed by the best materials. Rodgers’ ivory cellar in Norfolk Street was crammed with giant tusks and was regarded as one of the hidden sights of the town. Four or five men were constantly employed in sawing the tusks, and around twenty four tons of ivory were used a year around 1882. Rodgers’ appetite for stag was no less insatiable: deer horns and antlers filled another cellar and pearl from the Philippines and was also cut there. Around 1890, Rodgers’ began forging its own shear steel and in 1894 they began melting crucible steel. Newbold retired in 1890 and the grandsons of Maurice Rodgers, Maurice George Rodgers (1855-1898) and John Rodgers (1856-1919), became joint-managing directors. The McKinley Tariff Act of 1890 halved their American business and consequently they toured South Africa. Despite increasing foreign competition and the decline of the American market, Rodgers’ prospered before the First World War. However, workers’ wages were cut while the partners continued to take significant dividend which culminated in a prolonged and bitter strike. The First World War saw a decline in the business which continued steadily until the 1975 when it was absorbed by Richards and ceased trading in 1983. Joseph Rodgers & Sons left an enduring legacy in its knives. Its dazzling exhibition pieces and other fine cutlery show that the company’s reputation as Sheffield’s foremost knife maker was well founded. Abbreviated from Geoffrey Tweedale 2019. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A SMALL DAGGER, RODGERS, CUTLERS TO HER MAJESTY AND ANOTHER, UNSIGNED, LATE 19TH CENTURY the first with tapering double-edged blade, signed ricasso with star and cross mark, German silver hilt comprising straight guard with globular terminals, and beadwork grip, in associated scabbard; the second with tapering double-edged blade German silver beadwork hilt, and a pair of staghorn scales, in its leather scabbard, the first: 13.5 cm (2) LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, pp. 298 and 303. In the nineteenth century, Rodgers had an unsurpassed reputation and history that was synonymous with the cutlery trade. The family's first cutler, John Rodgers (1701-85), is recorded around 1724, with a workshop near the present cathedral. In the same year the Company of Cutlers 'let' him a mark, a Star and Maltese Cross, which became world famous in later years. John Rodgers had three sons, John (1731-1811), Joseph (1743-1821), and Maurice (c.1747-1824) who joined the business and succeeded him. They are recorded with more workshops by 1780 and the business soon extended to occupy a nearby block of buildings at 6 Norfolk Street, an address that became as famous as Rodgers’ trade mark. By the early 19th century their trade had expanded from pen and pocket knives to include table cutlery and scissors. By 1817 the General Sheffield Directory lists the firm as ‘merchants, factors, table and pocket knife, and razor manufacturers’. In 1821 John’s son Joseph died and his sons continued the business under the leadership of the younger John (grandson of the founder). John was described as ‘unobtrusive in his manner’ but was ambitious and one of the founding partners of the Sheffield Banking Co. He had a flair for marketing and travelled the country taking orders. Not only was his firm’s output and range greater than any other Sheffield firm, but its quality was superior. The company’s manifesto states: ‘The principle on which the manufacture of cutlery is carried on by this firm is – quality first … [and] … price comes second’. He began making exhibitions knives and presented George IV with a minute specimen of cutlery with 57 blades, which occupied only an inch [25mm] when closed. In 1822, Rodgers’ was awarded its first Royal Warrant. Another fourteen royal appointments, from British and overseas royal dignitaries, followed over the next eighty years, and its company history was duly titled: Under Five Sovereigns. John Rodgers next commissioned the Year Knife, with a blade for every year (1821) and opened his sensational cutlery showroom in Norfolk Street where visitors came to marvel at Rodgers’ creations. Perhaps the greatest highlight shown there was the Norfolk Knife, an over 30 inch long sportsman’s knife with 75 blades and tools, that Rodgers’ produced for the Great Exhibition in 1851. The showroom proved particularly popular with Americans whose trade played a significant role in the firm’s expansion. Additionally, they looked East, with agents in Calcutta, Bombay, and Hong Kong by the mid-19th century. These markets enabled Rodgers to become the largest cutlery factory in Sheffield. The number of workmen appears to have grown from about 300 in the late 1820s, to over 500 in the 1840s. In 1871 the business became a limited company with Joseph Rodgers (1828-1883), grandson of the Joseph Rodgers who had died in 1821 and Robert Newbold as managing directors. Joseph died on 12 May 1883 and Newbold became the chairman and managing director. The firm continued to expand with offices in London, New York, New Orleans, Montreal, Toronto, Calcutta, Bombay and Havana. Their work force in 1871 was around 1,200 and accounted for one-seventh of all Sheffield’s American cutlery trade. In 1876 the American market was stagnating and Rodgers’ began looking elsewhere with a focus on trade in the Middle East, India and Australia. Notably the name ‘Rujjus’ or ‘Rojers’ was said to have entered the language as an adjective expressing superb quality in Persia, India and Ceylon. By 1888, the value of Rodgers’ shares had more than doubled and, in 1889, a silver and electro-plate showroom was opened in London. At this time, Rodgers acquired the scissors business of Joseph Hobson & Son. Rodgers’ produced catalogues that were packed with every type of knife imaginable. Pocket knives were made in scores of different styles. Ornate daggers and Bowie knives and complicated horseman’s knives were made routinely. Some patterns, such as the Congress knife and Wharncliffe knife, were Rodgers’ own design. The Wharncliffe – with its serpentine handle and beaked master blade – was apparently designed after a dinner attended by Rodgers’ patron Lord Wharncliffe. The firm’s workmanship was usually backed by the best materials. Rodgers’ ivory cellar in Norfolk Street was crammed with giant tusks and was regarded as one of the hidden sights of the town. Four or five men were constantly employed in sawing the tusks, and around twenty four tons of ivory were used a year around 1882. Rodgers’ appetite for stag was no less insatiable: deer horns and antlers filled another cellar and pearl from the Philippines and was also cut there. Around 1890, Rodgers’ began forging its own shear steel and in 1894 they began melting crucible steel. Newbold retired in 1890 and the grandsons of Maurice Rodgers, Maurice George Rodgers (1855-1898) and John Rodgers (1856-1919), became joint-managing directors. The McKinley Tariff Act of 1890 halved their American business and consequently they toured South Africa. Despite increasing foreign competition and the decline of the American market, Rodgers’ prospered before the First World War. However, workers’ wages were cut while the partners continued to take significant dividend which culminated in a prolonged and bitter strike. The First World War saw a decline in the business which continued steadily until the 1975 when it was absorbed by Richards and ceased trading in 1983. Joseph Rodgers & Sons left an enduring legacy in its knives. Its dazzling exhibition pieces and other fine cutlery show that the company’s reputation as Sheffield’s foremost knife maker was well founded. Abbreviated from Geoffrey Tweedale 2019. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A DIRK BY JOSEPH RODGERS & SONS, CUTLERS TO THEIR MAJESTIES, NO. 6 NORFOLK STREET, SHEFFIELD, LAST QUARTER OF THE 19TH CENTURY with tapering blade formed with a false swage point and struck with the maker’s details including cross and star mark on one face, rectangular ricasso formed with two pairs of small notches, moulded ferrule, German silver pommel, spirally carved horn grip bound with plaited copper alloy wire, leather scabbard with large German silver chape and locket, the latter with belt hook, 15.5 cm blade LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 265. In the nineteenth century, Rodgers had an unsurpassed reputation and history that was synonymous with the cutlery trade. The family's first cutler, John Rodgers (1701-85), is recorded around 1724, with a workshop near the present cathedral. In the same year the Company of Cutlers 'let' him a mark, a Star and Maltese Cross, which became world famous in later years. John Rodgers had three sons, John (1731-1811), Joseph (1743-1821), and Maurice (c.1747-1824) who joined the business and succeeded him. They are recorded with more workshops by 1780 and the business soon extended to occupy a nearby block of buildings at 6 Norfolk Street, an address that became as famous as Rodgers’ trade mark. By the early 19th century their trade had expanded from pen and pocket knives to include table cutlery and scissors. By 1817 the General Sheffield Directory lists the firm as ‘merchants, factors, table and pocket knife, and razor manufacturers’. In 1821 John’s son Joseph died and his sons continued the business under the leadership of the younger John (grandson of the founder). John was described as ‘unobtrusive in his manner’ but was ambitious and one of the founding partners of the Sheffield Banking Co. He had a flair for marketing and travelled the country taking orders. Not only was his firm’s output and range greater than any other Sheffield firm, but its quality was superior. The company’s manifesto states: ‘The principle on which the manufacture of cutlery is carried on by this firm is – quality first … [and] … price comes second’. He began making exhibitions knives and presented George IV with a minute specimen of cutlery with 57 blades, which occupied only an inch [25mm] when closed. In 1822, Rodgers’ was awarded its first Royal Warrant. Another fourteen royal appointments, from British and overseas royal dignitaries, followed over the next eighty years, and its company history was duly titled: Under Five Sovereigns. John Rodgers next commissioned the Year Knife, with a blade for every year (1821) and opened his sensational cutlery showroom in Norfolk Street where visitors came to marvel at Rodgers’ creations. Perhaps the greatest highlight shown there was the Norfolk Knife, an over 30 inch long sportsman’s knife with 75 blades and tools, that Rodgers’ produced for the Great Exhibition in 1851. The showroom proved particularly popular with Americans whose trade played a significant role in the firm’s expansion. Additionally, they looked East, with agents in Calcutta, Bombay, and Hong Kong by the mid-19th century. These markets enabled Rodgers to become the largest cutlery factory in Sheffield. The number of workmen appears to have grown from about 300 in the late 1820s, to over 500 in the 1840s. In 1871 the business became a limited company with Joseph Rodgers (1828-1883), grandson of the Joseph Rodgers who had died in 1821 and Robert Newbold as managing directors. Joseph died on 12 May 1883 and Newbold became the chairman and managing director. The firm continued to expand with offices in London, New York, New Orleans, Montreal, Toronto, Calcutta, Bombay and Havana. Their work force in 1871 was around 1,200 and accounted for one-seventh of all Sheffield’s American cutlery trade. In 1876 the American market was stagnating and Rodgers’ began looking elsewhere with a focus on trade in the Middle East, India and Australia. Notably the name ‘Rujjus’ or ‘Rojers’ was said to have entered the language as an adjective expressing superb quality in Persia, India and Ceylon. By 1888, the value of Rodgers’ shares had more than doubled and, in 1889, a silver and electro-plate showroom was opened in London. At this time, Rodgers acquired the scissors business of Joseph Hobson & Son. Rodgers’ produced catalogues that were packed with every type of knife imaginable. Pocket knives were made in scores of different styles. Ornate daggers and Bowie knives and complicated horseman’s knives were made routinely. Some patterns, such as the Congress knife and Wharncliffe knife, were Rodgers’ own design. The Wharncliffe – with its serpentine handle and beaked master blade – was apparently designed after a dinner attended by Rodgers’ patron Lord Wharncliffe. The firm’s workmanship was usually backed by the best materials. Rodgers’ ivory cellar in Norfolk Street was crammed with giant tusks and was regarded as one of the hidden sights of the town. Four or five men were constantly employed in sawing the tusks, and around twenty four tons of ivory were used a year around 1882. Rodgers’ appetite for stag was no less insatiable: deer horns and antlers filled another cellar and pearl from the Philippines and was also cut there. Around 1890, Rodgers’ began forging its own shear steel and in 1894 they began melting crucible steel. Newbold retired in 1890 and the grandsons of Maurice Rodgers, Maurice George Rodgers (1855-1898) and John Rodgers (1856-1919), became joint-managing directors. The McKinley Tariff Act of 1890 halved their American business and consequently they toured South Africa. Despite increasing foreign competition and the decline of the American market, Rodgers’ prospered before the First World War. However, workers’ wages were cut while the partners continued to take significant dividend which culminated in a prolonged and bitter strike. The First World War saw a decline in the business which continued steadily until the 1975 when it was absorbed by Richards and ceased trading in 1983. Joseph Rodgers & Sons left an enduring legacy in its knives. Its dazzling exhibition pieces and other fine cutlery show that the company’s reputation as Sheffield’s foremost knife maker was well founded. Abbreviated from Geoffrey Tweedale 2019. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A CASED SET OF CARVING KNIVES, JOSEPH RODGERS & SONS, CUTLERS TO HIS MAJESTY, SHEFFIELD, EARLY 20TH CENTURY AND ANOTHER comprising knife struck with maker’s details, crown dividing the royal initials ‘GR’, and ‘Shear steel', natural staghorn grip, and nickel silver pommel, fork and steel en suite in its leatherette case lined in blue with the maker’s detail inside the lid in gilt letters; the second, T. Glossop, Sheffield, similar, in its mahogany case, the first case 41.5 cm (2) LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 192. In the nineteenth century, Rodgers had an unsurpassed reputation and history that was synonymous with the cutlery trade. The family's first cutler, John Rodgers (1701-85), is recorded around 1724, with a workshop near the present cathedral. In the same year the Company of Cutlers 'let' him a mark, a Star and Maltese Cross, which became world famous in later years. John Rodgers had three sons, John (1731-1811), Joseph (1743-1821), and Maurice (c.1747-1824) who joined the business and succeeded him. They are recorded with more workshops by 1780 and the business soon extended to occupy a nearby block of buildings at 6 Norfolk Street, an address that became as famous as Rodgers’ trade mark. By the early 19th century their trade had expanded from pen and pocket knives to include table cutlery and scissors. By 1817 the General Sheffield Directory lists the firm as ‘merchants, factors, table and pocket knife, and razor manufacturers’. In 1821 John’s son Joseph died and his sons continued the business under the leadership of the younger John (grandson of the founder). John was described as ‘unobtrusive in his manner’ but was ambitious and one of the founding partners of the Sheffield Banking Co. He had a flair for marketing and travelled the country taking orders. Not only was his firm’s output and range greater than any other Sheffield firm, but its quality was superior. The company’s manifesto states: ‘The principle on which the manufacture of cutlery is carried on by this firm is – quality first … [and] … price comes second’. He began making exhibitions knives and presented George IV with a minute specimen of cutlery with 57 blades, which occupied only an inch [25mm] when closed. In 1822, Rodgers’ was awarded its first Royal Warrant. Another fourteen royal appointments, from British and overseas royal dignitaries, followed over the next eighty years, and its company history was duly titled: Under Five Sovereigns. John Rodgers next commissioned the Year Knife, with a blade for every year (1821) and opened his sensational cutlery showroom in Norfolk Street where visitors came to marvel at Rodgers’ creations. Perhaps the greatest highlight shown there was the Norfolk Knife, an over 30 inch long sportsman’s knife with 75 blades and tools, that Rodgers’ produced for the Great Exhibition in 1851. The showroom proved particularly popular with Americans whose trade played a significant role in the firm’s expansion. Additionally, they looked East, with agents in Calcutta, Bombay, and Hong Kong by the mid-19th century. These markets enabled Rodgers to become the largest cutlery factory in Sheffield. The number of workmen appears to have grown from about 300 in the late 1820s, to over 500 in the 1840s. In 1871 the business became a limited company with Joseph Rodgers (1828-1883), grandson of the Joseph Rodgers who had died in 1821 and Robert Newbold as managing directors. Joseph died on 12 May 1883 and Newbold became the chairman and managing director. The firm continued to expand with offices in London, New York, New Orleans, Montreal, Toronto, Calcutta, Bombay and Havana. Their work force in 1871 was around 1,200 and accounted for one-seventh of all Sheffield’s American cutlery trade. In 1876 the American market was stagnating and Rodgers’ began looking elsewhere with a focus on trade in the Middle East, India and Australia. Notably the name ‘Rujjus’ or ‘Rojers’ was said to have entered the language as an adjective expressing superb quality in Persia, India and Ceylon. By 1888, the value of Rodgers’ shares had more than doubled and, in 1889, a silver and electro-plate showroom was opened in London. At this time, Rodgers acquired the scissors business of Joseph Hobson & Son. Rodgers’ produced catalogues that were packed with every type of knife imaginable. Pocket knives were made in scores of different styles. Ornate daggers and Bowie knives and complicated horseman’s knives were made routinely. Some patterns, such as the Congress knife and Wharncliffe knife, were Rodgers’ own design. The Wharncliffe – with its serpentine handle and beaked master blade – was apparently designed after a dinner attended by Rodgers’ patron Lord Wharncliffe. The firm’s workmanship was usually backed by the best materials. Rodgers’ ivory cellar in Norfolk Street was crammed with giant tusks and was regarded as one of the hidden sights of the town. Four or five men were constantly employed in sawing the tusks, and around twenty four tons of ivory were used a year around 1882. Rodgers’ appetite for stag was no less insatiable: deer horns and antlers filled another cellar and pearl from the Philippines and was also cut there. Around 1890, Rodgers’ began forging its own shear steel and in 1894 they began melting crucible steel. Newbold retired in 1890 and the grandsons of Maurice Rodgers, Maurice George Rodgers (1855-1898) and John Rodgers (1856-1919), became joint-managing directors. The McKinley Tariff Act of 1890 halved their American business and consequently they toured South Africa. Despite increasing foreign competition and the decline of the American market, Rodgers’ prospered before the First World War. However, workers’ wages were cut while the partners continued to take significant dividend which culminated in a prolonged and bitter strike. The First World War saw a decline in the business which continued steadily until the 1975 when it was absorbed by Richards and ceased trading in 1983. Joseph Rodgers & Sons left an enduring legacy in its knives. Its dazzling exhibition pieces and other fine cutlery show that the company’s reputation as Sheffield’s foremost knife maker was well founded. Abbreviated from Geoffrey Tweedale 2019. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A RARE SILVER-MOUNTED JAMBIYA STYLE DAGGER FOR THE ARAB MARKET, JOSEPH RODGERS AND SONS, CUTLERS TO HER MAJESTY, SHEFFIELD, WILLIAM NEEDHAM, SHEFFIELD, 1897 with curved double-edged blade formed with two long fullers on each face and stamped with the maker’s details and the Royal letters ‘VR’ divided by a crown, silver ferrule, natural staghorn grip of characteristic form, in its leather-covered wooden scabbard with silver locket and leather belt loop, 19.5 cm blade LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 262. In the nineteenth century, Rodgers had an unsurpassed reputation and history that was synonymous with the cutlery trade. The family's first cutler, John Rodgers (1701-85), is recorded around 1724, with a workshop near the present cathedral. In the same year the Company of Cutlers 'let' him a mark, a Star and Maltese Cross, which became world famous in later years. John Rodgers had three sons, John (1731-1811), Joseph (1743-1821), and Maurice (c.1747-1824) who joined the business and succeeded him. They are recorded with more workshops by 1780 and the business soon extended to occupy a nearby block of buildings at 6 Norfolk Street, an address that became as famous as Rodgers’ trade mark. By the early 19th century their trade had expanded from pen and pocket knives to include table cutlery and scissors. By 1817 the General Sheffield Directory lists the firm as ‘merchants, factors, table and pocket knife, and razor manufacturers’. In 1821 John’s son Joseph died and his sons continued the business under the leadership of the younger John (grandson of the founder). John was described as ‘unobtrusive in his manner’ but was ambitious and one of the founding partners of the Sheffield Banking Co. He had a flair for marketing and travelled the country taking orders. Not only was his firm’s output and range greater than any other Sheffield firm, but its quality was superior. The company’s manifesto states: ‘The principle on which the manufacture of cutlery is carried on by this firm is – quality first … [and] … price comes second’. He began making exhibitions knives and presented George IV with a minute specimen of cutlery with 57 blades, which occupied only an inch [25mm] when closed. In 1822, Rodgers’ was awarded its first Royal Warrant. Another fourteen royal appointments, from British and overseas royal dignitaries, followed over the next eighty years, and its company history was duly titled: Under Five Sovereigns. John Rodgers next commissioned the Year Knife, with a blade for every year (1821) and opened his sensational cutlery showroom in Norfolk Street where visitors came to marvel at Rodgers’ creations. Perhaps the greatest highlight shown there was the Norfolk Knife, an over 30 inch long sportsman’s knife with 75 blades and tools, that Rodgers’ produced for the Great Exhibition in 1851. The showroom proved particularly popular with Americans whose trade played a significant role in the firm’s expansion. Additionally, they looked East, with agents in Calcutta, Bombay, and Hong Kong by the mid-19th century. These markets enabled Rodgers to become the largest cutlery factory in Sheffield. The number of workmen appears to have grown from about 300 in the late 1820s, to over 500 in the 1840s. In 1871 the business became a limited company with Joseph Rodgers (1828-1883), grandson of the Joseph Rodgers who had died in 1821 and Robert Newbold as managing directors. Joseph died on 12 May 1883 and Newbold became the chairman and managing director. The firm continued to expand with offices in London, New York, New Orleans, Montreal, Toronto, Calcutta, Bombay and Havana. Their work force in 1871 was around 1,200 and accounted for one-seventh of all Sheffield’s American cutlery trade. In 1876 the American market was stagnating and Rodgers’ began looking elsewhere with a focus on trade in the Middle East, India and Australia. Notably the name ‘Rujjus’ or ‘Rojers’ was said to have entered the language as an adjective expressing superb quality in Persia, India and Ceylon. By 1888, the value of Rodgers’ shares had more than doubled and, in 1889, a silver and electro-plate showroom was opened in London. At this time, Rodgers acquired the scissors business of Joseph Hobson & Son. Rodgers’ produced catalogues that were packed with every type of knife imaginable. Pocket knives were made in scores of different styles. Ornate daggers and Bowie knives and complicated horseman’s knives were made routinely. Some patterns, such as the Congress knife and Wharncliffe knife, were Rodgers’ own design. The Wharncliffe – with its serpentine handle and beaked master blade – was apparently designed after a dinner attended by Rodgers’ patron Lord Wharncliffe. The firm’s workmanship was usually backed by the best materials. Rodgers’ ivory cellar in Norfolk Street was crammed with giant tusks and was regarded as one of the hidden sights of the town. Four or five men were constantly employed in sawing the tusks, and around twenty four tons of ivory were used a year around 1882. Rodgers’ appetite for stag was no less insatiable: deer horns and antlers filled another cellar and pearl from the Philippines and was also cut there. Around 1890, Rodgers’ began forging its own shear steel and in 1894 they began melting crucible steel. Newbold retired in 1890 and the grandsons of Maurice Rodgers, Maurice George Rodgers (1855-1898) and John Rodgers (1856-1919), became joint-managing directors. The McKinley Tariff Act of 1890 halved their American business and consequently they toured South Africa. Despite increasing foreign competition and the decline of the American market, Rodgers’ prospered before the First World War. However, workers’ wages were cut while the partners continued to take significant dividend which culminated in a prolonged and bitter strike. The First World War saw a decline in the business which continued steadily until the 1975 when it was absorbed by Richards and ceased trading in 1983. Joseph Rodgers & Sons left an enduring legacy in its knives. Its dazzling exhibition pieces and other fine cutlery show that the company’s reputation as Sheffield’s foremost knife maker was well founded. Abbreviated from Geoffrey Tweedale 2019. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A CASED SET OF TWENTY-ONE CLEAVERS, PERHAPS FOR PLANTATION USE, JOSEPH RODGERS & SONS, CUTLERS TO HIS MAJESTY, 6 NORFOLK STREET, SHEFFIELD, 20TH CENTURY each with hooked cleaver blade, stamped with the maker’s details, star and cross mark and the royal initials ‘GR’ divided by a crown, and shaped wooden grip, in a wooden case with embossed and gilt trade label, the case: 65.0 cm x 43.0 cm LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 203. In the nineteenth century, Rodgers had an unsurpassed reputation and history that was synonymous with the cutlery trade. The family's first cutler, John Rodgers (1701-85), is recorded around 1724, with a workshop near the present cathedral. In the same year the Company of Cutlers 'let' him a mark, a Star and Maltese Cross, which became world famous in later years. John Rodgers had three sons, John (1731-1811), Joseph (1743-1821), and Maurice (c.1747-1824) who joined the business and succeeded him. They are recorded with more workshops by 1780 and the business soon extended to occupy a nearby block of buildings at 6 Norfolk Street, an address that became as famous as Rodgers’ trade mark. By the early 19th century their trade had expanded from pen and pocket knives to include table cutlery and scissors. By 1817 the General Sheffield Directory lists the firm as ‘merchants, factors, table and pocket knife, and razor manufacturers’. In 1821 John’s son Joseph died and his sons continued the business under the leadership of the younger John (grandson of the founder). John was described as ‘unobtrusive in his manner’ but was ambitious and one of the founding partners of the Sheffield Banking Co. He had a flair for marketing and travelled the country taking orders. Not only was his firm’s output and range greater than any other Sheffield firm, but its quality was superior. The company’s manifesto states: ‘The principle on which the manufacture of cutlery is carried on by this firm is – quality first … [and] … price comes second’. He began making exhibitions knives and presented George IV with a minute specimen of cutlery with 57 blades, which occupied only an inch [25mm] when closed. In 1822, Rodgers’ was awarded its first Royal Warrant. Another fourteen royal appointments, from British and overseas royal dignitaries, followed over the next eighty years, and its company history was duly titled: Under Five Sovereigns. John Rodgers next commissioned the Year Knife, with a blade for every year (1821) and opened his sensational cutlery showroom in Norfolk Street where visitors came to marvel at Rodgers’ creations. Perhaps the greatest highlight shown there was the Norfolk Knife, an over 30 inch long sportsman’s knife with 75 blades and tools, that Rodgers’ produced for the Great Exhibition in 1851. The showroom proved particularly popular with Americans whose trade played a significant role in the firm’s expansion. Additionally, they looked East, with agents in Calcutta, Bombay, and Hong Kong by the mid-19th century. These markets enabled Rodgers to become the largest cutlery factory in Sheffield. The number of workmen appears to have grown from about 300 in the late 1820s, to over 500 in the 1840s. In 1871 the business became a limited company with Joseph Rodgers (1828-1883), grandson of the Joseph Rodgers who had died in 1821 and Robert Newbold as managing directors. Joseph died on 12 May 1883 and Newbold became the chairman and managing director. The firm continued to expand with offices in London, New York, New Orleans, Montreal, Toronto, Calcutta, Bombay and Havana. Their work force in 1871 was around 1,200 and accounted for one-seventh of all Sheffield’s American cutlery trade. In 1876 the American market was stagnating and Rodgers’ began looking elsewhere with a focus on trade in the Middle East, India and Australia. Notably the name ‘Rujjus’ or ‘Rojers’ was said to have entered the language as an adjective expressing superb quality in Persia, India and Ceylon. By 1888, the value of Rodgers’ shares had more than doubled and, in 1889, a silver and electro-plate showroom was opened in London. At this time, Rodgers acquired the scissors business of Joseph Hobson & Son. Rodgers’ produced catalogues that were packed with every type of knife imaginable. Pocket knives were made in scores of different styles. Ornate daggers and Bowie knives and complicated horseman’s knives were made routinely. Some patterns, such as the Congress knife and Wharncliffe knife, were Rodgers’ own design. The Wharncliffe – with its serpentine handle and beaked master blade – was apparently designed after a dinner attended by Rodgers’ patron Lord Wharncliffe. The firm’s workmanship was usually backed by the best materials. Rodgers’ ivory cellar in Norfolk Street was crammed with giant tusks and was regarded as one of the hidden sights of the town. Four or five men were constantly employed in sawing the tusks, and around twenty four tons of ivory were used a year around 1882. Rodgers’ appetite for stag was no less insatiable: deer horns and antlers filled another cellar and pearl from the Philippines and was also cut there. Around 1890, Rodgers’ began forging its own shear steel and in 1894 they began melting crucible steel. Newbold retired in 1890 and the grandsons of Maurice Rodgers, Maurice George Rodgers (1855-1898) and John Rodgers (1856-1919), became joint-managing directors. The McKinley Tariff Act of 1890 halved their American business and consequently they toured South Africa. Despite increasing foreign competition and the decline of the American market, Rodgers’ prospered before the First World War. However, workers’ wages were cut while the partners continued to take significant dividend which culminated in a prolonged and bitter strike. The First World War saw a decline in the business which continued steadily until the 1975 when it was absorbed by Richards and ceased trading in 1983. Joseph Rodgers & Sons left an enduring legacy in its knives. Its dazzling exhibition pieces and other fine cutlery show that the company’s reputation as Sheffield’s foremost knife maker was well founded. Abbreviated from Geoffrey Tweedale 2019. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
˜ FOUR JOSEPH RODGERS PATENT QUILL MACHINES AND SEVEN POCKET MANICURE SETS, LATE 19TH/EARLY 20TH CENTURY the first with steel blades, hardwood bodies, brass clips with the maker’s details and cross marks, and each in its case (one blade missing); the second all of folding scissor type, three with mother-of-pearl scales, three with tortoiseshell scales, and one with brass scales, the first: 13.5 cm (11) LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 122, 125. In the nineteenth century, Rodgers had an unsurpassed reputation and history that was synonymous with the cutlery trade. The family's first cutler, John Rodgers (1701-85), is recorded around 1724, with a workshop near the present cathedral. In the same year the Company of Cutlers 'let' him a mark, a Star and Maltese Cross, which became world famous in later years. John Rodgers had three sons, John (1731-1811), Joseph (1743-1821), and Maurice (c.1747-1824) who joined the business and succeeded him. They are recorded with more workshops by 1780 and the business soon extended to occupy a nearby block of buildings at 6 Norfolk Street, an address that became as famous as Rodgers’ trade mark. By the early 19th century their trade had expanded from pen and pocket knives to include table cutlery and scissors. By 1817 the General Sheffield Directory lists the firm as ‘merchants, factors, table and pocket knife, and razor manufacturers’. In 1821 John’s son Joseph died and his sons continued the business under the leadership of the younger John (grandson of the founder). John was described as ‘unobtrusive in his manner’ but was ambitious and one of the founding partners of the Sheffield Banking Co. He had a flair for marketing and travelled the country taking orders. Not only was his firm’s output and range greater than any other Sheffield firm, but its quality was superior. The company’s manifesto states: ‘The principle on which the manufacture of cutlery is carried on by this firm is – quality first … [and] … price comes second’. He began making exhibitions knives and presented George IV with a minute specimen of cutlery with 57 blades, which occupied only an inch [25mm] when closed. In 1822, Rodgers’ was awarded its first Royal Warrant. Another fourteen royal appointments, from British and overseas royal dignitaries, followed over the next eighty years, and its company history was duly titled: Under Five Sovereigns. John Rodgers next commissioned the Year Knife, with a blade for every year (1821) and opened his sensational cutlery showroom in Norfolk Street where visitors came to marvel at Rodgers’ creations. Perhaps the greatest highlight shown there was the Norfolk Knife, an over 30 inch long sportsman’s knife with 75 blades and tools, that Rodgers’ produced for the Great Exhibition in 1851. The showroom proved particularly popular with Americans whose trade played a significant role in the firm’s expansion. Additionally, they looked East, with agents in Calcutta, Bombay, and Hong Kong by the mid-19th century. These markets enabled Rodgers to become the largest cutlery factory in Sheffield. The number of workmen appears to have grown from about 300 in the late 1820s, to over 500 in the 1840s. In 1871 the business became a limited company with Joseph Rodgers (1828-1883), grandson of the Joseph Rodgers who had died in 1821 and Robert Newbold as managing directors. Joseph died on 12 May 1883 and Newbold became the chairman and managing director. The firm continued to expand with offices in London, New York, New Orleans, Montreal, Toronto, Calcutta, Bombay and Havana. Their work force in 1871 was around 1,200 and accounted for one-seventh of all Sheffield’s American cutlery trade. In 1876 the American market was stagnating and Rodgers’ began looking elsewhere with a focus on trade in the Middle East, India and Australia. Notably the name ‘Rujjus’ or ‘Rojers’ was said to have entered the language as an adjective expressing superb quality in Persia, India and Ceylon. By 1888, the value of Rodgers’ shares had more than doubled and, in 1889, a silver and electro-plate showroom was opened in London. At this time, Rodgers acquired the scissors business of Joseph Hobson & Son. Rodgers’ produced catalogues that were packed with every type of knife imaginable. Pocket knives were made in scores of different styles. Ornate daggers and Bowie knives and complicated horseman’s knives were made routinely. Some patterns, such as the Congress knife and Wharncliffe knife, were Rodgers’ own design. The Wharncliffe – with its serpentine handle and beaked master blade – was apparently designed after a dinner attended by Rodgers’ patron Lord Wharncliffe. The firm’s workmanship was usually backed by the best materials. Rodgers’ ivory cellar in Norfolk Street was crammed with giant tusks and was regarded as one of the hidden sights of the town. Four or five men were constantly employed in sawing the tusks, and around twenty four tons of ivory were used a year around 1882. Rodgers’ appetite for stag was no less insatiable: deer horns and antlers filled another cellar and pearl from the Philippines and was also cut there. Around 1890, Rodgers’ began forging its own shear steel and in 1894 they began melting crucible steel. Newbold retired in 1890 and the grandsons of Maurice Rodgers, Maurice George Rodgers (1855-1898) and John Rodgers (1856-1919), became joint-managing directors. The McKinley Tariff Act of 1890 halved their American business and consequently they toured South Africa. Despite increasing foreign competition and the decline of the American market, Rodgers’ prospered before the First World War. However, workers’ wages were cut while the partners continued to take significant dividend which culminated in a prolonged and bitter strike. The First World War saw a decline in the business which continued steadily until the 1975 when it was absorbed by Richards and ceased trading in 1983. Joseph Rodgers & Sons left an enduring legacy in its knives. Its dazzling exhibition pieces and other fine cutlery show that the company’s reputation as Sheffield’s foremost knife maker was well founded. Abbreviated from Geoffrey Tweedale 2019. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
TEN JOSEPH RODGERS PATENT QUILL MACHINES, LATE 19TH/EARLY 20TH CENTURY each with steel blade, hardwood body, brass clip with the maker’s details and star and cross marks, in its case, the first: 13.5 cm (10) LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 125. In the nineteenth century, Rodgers had an unsurpassed reputation and history that was synonymous with the cutlery trade. The family's first cutler, John Rodgers (1701-85), is recorded around 1724, with a workshop near the present cathedral. In the same year the Company of Cutlers 'let' him a mark, a Star and Maltese Cross, which became world famous in later years. John Rodgers had three sons, John (1731-1811), Joseph (1743-1821), and Maurice (c.1747-1824) who joined the business and succeeded him. They are recorded with more workshops by 1780 and the business soon extended to occupy a nearby block of buildings at 6 Norfolk Street, an address that became as famous as Rodgers’ trade mark. By the early 19th century their trade had expanded from pen and pocket knives to include table cutlery and scissors. By 1817 the General Sheffield Directory lists the firm as ‘merchants, factors, table and pocket knife, and razor manufacturers’. In 1821 John’s son Joseph died and his sons continued the business under the leadership of the younger John (grandson of the founder). John was described as ‘unobtrusive in his manner’ but was ambitious and one of the founding partners of the Sheffield Banking Co. He had a flair for marketing and travelled the country taking orders. Not only was his firm’s output and range greater than any other Sheffield firm, but its quality was superior. The company’s manifesto states: ‘The principle on which the manufacture of cutlery is carried on by this firm is – quality first … [and] … price comes second’. He began making exhibitions knives and presented George IV with a minute specimen of cutlery with 57 blades, which occupied only an inch [25mm] when closed. In 1822, Rodgers’ was awarded its first Royal Warrant. Another fourteen royal appointments, from British and overseas royal dignitaries, followed over the next eighty years, and its company history was duly titled: Under Five Sovereigns. John Rodgers next commissioned the Year Knife, with a blade for every year (1821) and opened his sensational cutlery showroom in Norfolk Street where visitors came to marvel at Rodgers’ creations. Perhaps the greatest highlight shown there was the Norfolk Knife, an over 30 inch long sportsman’s knife with 75 blades and tools, that Rodgers’ produced for the Great Exhibition in 1851. The showroom proved particularly popular with Americans whose trade played a significant role in the firm’s expansion. Additionally, they looked East, with agents in Calcutta, Bombay, and Hong Kong by the mid-19th century. These markets enabled Rodgers to become the largest cutlery factory in Sheffield. The number of workmen appears to have grown from about 300 in the late 1820s, to over 500 in the 1840s. In 1871 the business became a limited company with Joseph Rodgers (1828-1883), grandson of the Joseph Rodgers who had died in 1821 and Robert Newbold as managing directors. Joseph died on 12 May 1883 and Newbold became the chairman and managing director. The firm continued to expand with offices in London, New York, New Orleans, Montreal, Toronto, Calcutta, Bombay and Havana. Their work force in 1871 was around 1,200 and accounted for one-seventh of all Sheffield’s American cutlery trade. In 1876 the American market was stagnating and Rodgers’ began looking elsewhere with a focus on trade in the Middle East, India and Australia. Notably the name ‘Rujjus’ or ‘Rojers’ was said to have entered the language as an adjective expressing superb quality in Persia, India and Ceylon. By 1888, the value of Rodgers’ shares had more than doubled and, in 1889, a silver and electro-plate showroom was opened in London. At this time, Rodgers acquired the scissors business of Joseph Hobson & Son. Rodgers’ produced catalogues that were packed with every type of knife imaginable. Pocket knives were made in scores of different styles. Ornate daggers and Bowie knives and complicated horseman’s knives were made routinely. Some patterns, such as the Congress knife and Wharncliffe knife, were Rodgers’ own design. The Wharncliffe – with its serpentine handle and beaked master blade – was apparently designed after a dinner attended by Rodgers’ patron Lord Wharncliffe. The firm’s workmanship was usually backed by the best materials. Rodgers’ ivory cellar in Norfolk Street was crammed with giant tusks and was regarded as one of the hidden sights of the town. Four or five men were constantly employed in sawing the tusks, and around twenty four tons of ivory were used a year around 1882. Rodgers’ appetite for stag was no less insatiable: deer horns and antlers filled another cellar and pearl from the Philippines and was also cut there. Around 1890, Rodgers’ began forging its own shear steel and in 1894 they began melting crucible steel. Newbold retired in 1890 and the grandsons of Maurice Rodgers, Maurice George Rodgers (1855-1898) and John Rodgers (1856-1919), became joint-managing directors. The McKinley Tariff Act of 1890 halved their American business and consequently they toured South Africa. Despite increasing foreign competition and the decline of the American market, Rodgers’ prospered before the First World War. However, workers’ wages were cut while the partners continued to take significant dividend which culminated in a prolonged and bitter strike. The First World War saw a decline in the business which continued steadily until the 1975 when it was absorbed by Richards and ceased trading in 1983. Joseph Rodgers & Sons left an enduring legacy in its knives. Its dazzling exhibition pieces and other fine cutlery show that the company’s reputation as Sheffield’s foremost knife maker was well founded. Abbreviated from Geoffrey Tweedale 2019. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A SALESMAN’S KNIFE DISPLAY AND A TOOL SET CASE, JOSEPH RODGERS, SHEFFIELD, LATE 19TH/EARLY 20TH CENTURY the first of stiffened leather, lined in blue baize, with provision for eighteen knives, with embossed gilt label ‘Joseph Rodgers & Sons Ltd', with star and cross trademark and ‘grant date 1682'; the second with provision for fourteen tools, embossed in gilt letters ‘Rodgers Tool Set’ and with star and cross mark on the inside (2) In the nineteenth century, Rodgers had an unsurpassed reputation and history that was synonymous with the cutlery trade. The family's first cutler, John Rodgers (1701-85), is recorded around 1724, with a workshop near the present cathedral. In the same year the Company of Cutlers 'let' him a mark, a Star and Maltese Cross, which became world famous in later years. John Rodgers had three sons, John (1731-1811), Joseph (1743-1821), and Maurice (c.1747-1824) who joined the business and succeeded him. They are recorded with more workshops by 1780 and the business soon extended to occupy a nearby block of buildings at 6 Norfolk Street, an address that became as famous as Rodgers’ trade mark. By the early 19th century their trade had expanded from pen and pocket knives to include table cutlery and scissors. By 1817 the General Sheffield Directory lists the firm as ‘merchants, factors, table and pocket knife, and razor manufacturers’. In 1821 John’s son Joseph died and his sons continued the business under the leadership of the younger John (grandson of the founder). John was described as ‘unobtrusive in his manner’ but was ambitious and one of the founding partners of the Sheffield Banking Co. He had a flair for marketing and travelled the country taking orders. Not only was his firm’s output and range greater than any other Sheffield firm, but its quality was superior. The company’s manifesto states: ‘The principle on which the manufacture of cutlery is carried on by this firm is – quality first … [and] … price comes second’. He began making exhibitions knives and presented George IV with a minute specimen of cutlery with 57 blades, which occupied only an inch [25mm] when closed. In 1822, Rodgers’ was awarded its first Royal Warrant. Another fourteen royal appointments, from British and overseas royal dignitaries, followed over the next eighty years, and its company history was duly titled: Under Five Sovereigns. John Rodgers next commissioned the Year Knife, with a blade for every year (1821) and opened his sensational cutlery showroom in Norfolk Street where visitors came to marvel at Rodgers’ creations. Perhaps the greatest highlight shown there was the Norfolk Knife, an over 30 inch long sportsman’s knife with 75 blades and tools, that Rodgers’ produced for the Great Exhibition in 1851. The showroom proved particularly popular with Americans whose trade played a significant role in the firm’s expansion. Additionally, they looked East, with agents in Calcutta, Bombay, and Hong Kong by the mid-19th century. These markets enabled Rodgers to become the largest cutlery factory in Sheffield. The number of workmen appears to have grown from about 300 in the late 1820s, to over 500 in the 1840s. In 1871 the business became a limited company with Joseph Rodgers (1828-1883), grandson of the Joseph Rodgers who had died in 1821 and Robert Newbold as managing directors. Joseph died on 12 May 1883 and Newbold became the chairman and managing director. The firm continued to expand with offices in London, New York, New Orleans, Montreal, Toronto, Calcutta, Bombay and Havana. Their work force in 1871 was around 1,200 and accounted for one-seventh of all Sheffield’s American cutlery trade. In 1876 the American market was stagnating and Rodgers’ began looking elsewhere with a focus on trade in the Middle East, India and Australia. Notably the name ‘Rujjus’ or ‘Rojers’ was said to have entered the language as an adjective expressing superb quality in Persia, India and Ceylon. By 1888, the value of Rodgers’ shares had more than doubled and, in 1889, a silver and electro-plate showroom was opened in London. At this time, Rodgers acquired the scissors business of Joseph Hobson & Son. Rodgers’ produced catalogues that were packed with every type of knife imaginable. Pocket knives were made in scores of different styles. Ornate daggers and Bowie knives and complicated horseman’s knives were made routinely. Some patterns, such as the Congress knife and Wharncliffe knife, were Rodgers’ own design. The Wharncliffe – with its serpentine handle and beaked master blade – was apparently designed after a dinner attended by Rodgers’ patron Lord Wharncliffe. The firm’s workmanship was usually backed by the best materials. Rodgers’ ivory cellar in Norfolk Street was crammed with giant tusks and was regarded as one of the hidden sights of the town. Four or five men were constantly employed in sawing the tusks, and around twenty four tons of ivory were used a year around 1882. Rodgers’ appetite for stag was no less insatiable: deer horns and antlers filled another cellar and pearl from the Philippines and was also cut there. Around 1890, Rodgers’ began forging its own shear steel and in 1894 they began melting crucible steel. Newbold retired in 1890 and the grandsons of Maurice Rodgers, Maurice George Rodgers (1855-1898) and John Rodgers (1856-1919), became joint-managing directors. The McKinley Tariff Act of 1890 halved their American business and consequently they toured South Africa. Despite increasing foreign competition and the decline of the American market, Rodgers’ prospered before the First World War. However, workers’ wages were cut while the partners continued to take significant dividend which culminated in a prolonged and bitter strike. The First World War saw a decline in the business which continued steadily until the 1975 when it was absorbed by Richards and ceased trading in 1983. Joseph Rodgers & Sons left an enduring legacy in its knives. Its dazzling exhibition pieces and other fine cutlery show that the company’s reputation as Sheffield’s foremost knife maker was well founded. Abbreviated from Geoffrey Tweedale 2019. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
JOSEPH RODGERS & SONS LTD, 6 NORFOLK STREET, SHEFFIELD: THREE CATALOGUES, AND SIXTEEN EARLY PRINTS, 20TH CENTURY the first 124 pp., extensively illustrated, original printed board covers; the second 194 pp. extensively illustrated, paper covers (worn, losses); the third 26 pp. paper covered and bound with a plastic spine bar, the fourth comprising sixteen photographs of penknives and cutlery, probably proof pieces for a catalogue (4) In the nineteenth century, Rodgers had an unsurpassed reputation and history that was synonymous with the cutlery trade. The family's first cutler, John Rodgers (1701-85), is recorded around 1724, with a workshop near the present cathedral. In the same year the Company of Cutlers 'let' him a mark, a Star and Maltese Cross, which became world famous in later years. John Rodgers had three sons, John (1731-1811), Joseph (1743-1821), and Maurice (c.1747-1824) who joined the business and succeeded him. They are recorded with more workshops by 1780 and the business soon extended to occupy a nearby block of buildings at 6 Norfolk Street, an address that became as famous as Rodgers’ trade mark. By the early 19th century their trade had expanded from pen and pocket knives to include table cutlery and scissors. By 1817 the General Sheffield Directory lists the firm as ‘merchants, factors, table and pocket knife, and razor manufacturers’. In 1821 John’s son Joseph died and his sons continued the business under the leadership of the younger John (grandson of the founder). John was described as ‘unobtrusive in his manner’ but was ambitious and one of the founding partners of the Sheffield Banking Co. He had a flair for marketing and travelled the country taking orders. Not only was his firm’s output and range greater than any other Sheffield firm, but its quality was superior. The company’s manifesto states: ‘The principle on which the manufacture of cutlery is carried on by this firm is – quality first … [and] … price comes second’. He began making exhibitions knives and presented George IV with a minute specimen of cutlery with 57 blades, which occupied only an inch [25mm] when closed. In 1822, Rodgers’ was awarded its first Royal Warrant. Another fourteen royal appointments, from British and overseas royal dignitaries, followed over the next eighty years, and its company history was duly titled: Under Five Sovereigns. John Rodgers next commissioned the Year Knife, with a blade for every year (1821) and opened his sensational cutlery showroom in Norfolk Street where visitors came to marvel at Rodgers’ creations. Perhaps the greatest highlight shown there was the Norfolk Knife, an over 30 inch long sportsman’s knife with 75 blades and tools, that Rodgers’ produced for the Great Exhibition in 1851. The showroom proved particularly popular with Americans whose trade played a significant role in the firm’s expansion. Additionally, they looked East, with agents in Calcutta, Bombay, and Hong Kong by the mid-19th century. These markets enabled Rodgers to become the largest cutlery factory in Sheffield. The number of workmen appears to have grown from about 300 in the late 1820s, to over 500 in the 1840s. In 1871 the business became a limited company with Joseph Rodgers (1828-1883), grandson of the Joseph Rodgers who had died in 1821 and Robert Newbold as managing directors. Joseph died on 12 May 1883 and Newbold became the chairman and managing director. The firm continued to expand with offices in London, New York, New Orleans, Montreal, Toronto, Calcutta, Bombay and Havana. Their work force in 1871 was around 1,200 and accounted for one-seventh of all Sheffield’s American cutlery trade. In 1876 the American market was stagnating and Rodgers’ began looking elsewhere with a focus on trade in the Middle East, India and Australia. Notably the name ‘Rujjus’ or ‘Rojers’ was said to have entered the language as an adjective expressing superb quality in Persia, India and Ceylon. By 1888, the value of Rodgers’ shares had more than doubled and, in 1889, a silver and electro-plate showroom was opened in London. At this time, Rodgers acquired the scissors business of Joseph Hobson & Son. Rodgers’ produced catalogues that were packed with every type of knife imaginable. Pocket knives were made in scores of different styles. Ornate daggers and Bowie knives and complicated horseman’s knives were made routinely. Some patterns, such as the Congress knife and Wharncliffe knife, were Rodgers’ own design. The Wharncliffe – with its serpentine handle and beaked master blade – was apparently designed after a dinner attended by Rodgers’ patron Lord Wharncliffe. The firm’s workmanship was usually backed by the best materials. Rodgers’ ivory cellar in Norfolk Street was crammed with giant tusks and was regarded as one of the hidden sights of the town. Four or five men were constantly employed in sawing the tusks, and around twenty four tons of ivory were used a year around 1882. Rodgers’ appetite for stag was no less insatiable: deer horns and antlers filled another cellar and pearl from the Philippines and was also cut there. Around 1890, Rodgers’ began forging its own shear steel and in 1894 they began melting crucible steel. Newbold retired in 1890 and the grandsons of Maurice Rodgers, Maurice George Rodgers (1855-1898) and John Rodgers (1856-1919), became joint-managing directors. The McKinley Tariff Act of 1890 halved their American business and consequently they toured South Africa. Despite increasing foreign competition and the decline of the American market, Rodgers’ prospered before the First World War. However, workers’ wages were cut while the partners continued to take significant dividend which culminated in a prolonged and bitter strike. The First World War saw a decline in the business which continued steadily until the 1975 when it was absorbed by Richards and ceased trading in 1983. Joseph Rodgers & Sons left an enduring legacy in its knives. Its dazzling exhibition pieces and other fine cutlery show that the company’s reputation as Sheffield’s foremost knife maker was well founded. Abbreviated from Geoffrey Tweedale 2019. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A RARE KNIFE PATTERN BOOK, SHEFFIELD, CIRCA 1833-1910, INCLUDING DESIGNS FOR RODGERS the front section including over sixty five illustrated pages of penknife elements comprising blades, scales, fillets, designs for etching and finished knives, including Knights Dagger, Sportsman’s Wharncliffe Knife, Civil Service Patterns, a War department design dated 1889, numbered consecutively from 1-918, the back section titled ‘Robert Sorby Patterns May 1833’, with summary descriptions and prices, numbered from 1-263, three pages of designs for folders, and a series of turned handle designs, marbled end-papers and original boards (worn, small losses) LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, pp. 12-13. In the nineteenth century, Rodgers had an unsurpassed reputation and history that was synonymous with the cutlery trade. The family's first cutler, John Rodgers (1701-85), is recorded around 1724, with a workshop near the present cathedral. In the same year the Company of Cutlers 'let' him a mark, a Star and Maltese Cross, which became world famous in later years. John Rodgers had three sons, John (1731-1811), Joseph (1743-1821), and Maurice (c.1747-1824) who joined the business and succeeded him. They are recorded with more workshops by 1780 and the business soon extended to occupy a nearby block of buildings at 6 Norfolk Street, an address that became as famous as Rodgers’ trade mark. By the early 19th century their trade had expanded from pen and pocket knives to include table cutlery and scissors. By 1817 the General Sheffield Directory lists the firm as ‘merchants, factors, table and pocket knife, and razor manufacturers’. In 1821 John’s son Joseph died and his sons continued the business under the leadership of the younger John (grandson of the founder). John was described as ‘unobtrusive in his manner’ but was ambitious and one of the founding partners of the Sheffield Banking Co. He had a flair for marketing and travelled the country taking orders. Not only was his firm’s output and range greater than any other Sheffield firm, but its quality was superior. The company’s manifesto states: ‘The principle on which the manufacture of cutlery is carried on by this firm is – quality first … [and] … price comes second’. He began making exhibitions knives and presented George IV with a minute specimen of cutlery with 57 blades, which occupied only an inch [25mm] when closed. In 1822, Rodgers’ was awarded its first Royal Warrant. Another fourteen royal appointments, from British and overseas royal dignitaries, followed over the next eighty years, and its company history was duly titled: Under Five Sovereigns. John Rodgers next commissioned the Year Knife, with a blade for every year (1821) and opened his sensational cutlery showroom in Norfolk Street where visitors came to marvel at Rodgers’ creations. Perhaps the greatest highlight shown there was the Norfolk Knife, an over 30 inch long sportsman’s knife with 75 blades and tools, that Rodgers’ produced for the Great Exhibition in 1851. The showroom proved particularly popular with Americans whose trade played a significant role in the firm’s expansion. Additionally, they looked East, with agents in Calcutta, Bombay, and Hong Kong by the mid-19th century. These markets enabled Rodgers to become the largest cutlery factory in Sheffield. The number of workmen appears to have grown from about 300 in the late 1820s, to over 500 in the 1840s. In 1871 the business became a limited company with Joseph Rodgers (1828-1883), grandson of the Joseph Rodgers who had died in 1821 and Robert Newbold as managing directors. Joseph died on 12 May 1883 and Newbold became the chairman and managing director. The firm continued to expand with offices in London, New York, New Orleans, Montreal, Toronto, Calcutta, Bombay and Havana. Their work force in 1871 was around 1,200 and accounted for one-seventh of all Sheffield’s American cutlery trade. In 1876 the American market was stagnating and Rodgers’ began looking elsewhere with a focus on trade in the Middle East, India and Australia. Notably the name ‘Rujjus’ or ‘Rojers’ was said to have entered the language as an adjective expressing superb quality in Persia, India and Ceylon. By 1888, the value of Rodgers’ shares had more than doubled and, in 1889, a silver and electro-plate showroom was opened in London. At this time, Rodgers acquired the scissors business of Joseph Hobson & Son. Rodgers’ produced catalogues that were packed with every type of knife imaginable. Pocket knives were made in scores of different styles. Ornate daggers and Bowie knives and complicated horseman’s knives were made routinely. Some patterns, such as the Congress knife and Wharncliffe knife, were Rodgers’ own design. The Wharncliffe – with its serpentine handle and beaked master blade – was apparently designed after a dinner attended by Rodgers’ patron Lord Wharncliffe. The firm’s workmanship was usually backed by the best materials. Rodgers’ ivory cellar in Norfolk Street was crammed with giant tusks and was regarded as one of the hidden sights of the town. Four or five men were constantly employed in sawing the tusks, and around twenty four tons of ivory were used a year around 1882. Rodgers’ appetite for stag was no less insatiable: deer horns and antlers filled another cellar and pearl from the Philippines and was also cut there. Around 1890, Rodgers’ began forging its own shear steel and in 1894 they began melting crucible steel. Newbold retired in 1890 and the grandsons of Maurice Rodgers, Maurice George Rodgers (1855-1898) and John Rodgers (1856-1919), became joint-managing directors. The McKinley Tariff Act of 1890 halved their American business and consequently they toured South Africa. Despite increasing foreign competition and the decline of the American market, Rodgers’ prospered before the First World War. However, workers’ wages were cut while the partners continued to take significant dividend which culminated in a prolonged and bitter strike. The First World War saw a decline in the business which continued steadily until the 1975 when it was absorbed by Richards and ceased trading in 1983. Joseph Rodgers & Sons left an enduring legacy in its knives. Its dazzling exhibition pieces and other fine cutlery show that the company’s reputation as Sheffield’s foremost knife maker was well founded. Abbreviated from Geoffrey Tweedale 2019. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A FINE LARGE MULTI-BLADE PENKNIFE FOR EXHIBITION, GEORGE WOSTENHOLM I.XL, SHEFFIELD, 20TH CENTURY with over one hundred folding blades and accessories, including saws, picks, scissors and corkscrew, some stamped ‘George Wostenholm I.XL.’, fitted at each side with highly figured select quality mother-of-pearl scales each retained by four minute screws, with sliding tweezers and picks top and bottom, and in fine condition throughout, 12.0 cm (closed) LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 73. It is likely that the founder of George Wostenholm & Son Ltd was George Wolstenholme (1775-1833), a fork maker at Thomas Lane. Apprenticed to John Micklethwaite, a cutler, in 1790 and granted his Freedom in 1799, George later moved to Broad Lane where he made spring knives. He was first listed in a Sheffield directory in 1816 as a pen and pocket knife manufacturer at Rockingham Street, where he had registered a silver mark in 1809. His workshops expanded to become Rockingham Works and he apparently shortened his name to ‘Wostenholm’ to facilitate its stamping on blades. His son, George Wostenholm (1802-1876) was apprenticed to his father and they are described in 1825 as ‘George Wolstenholme & Son, manufacturers of table knives, and forks, pen, pocket, and sportsman’s knives, and general dealers in cutlery, 78 Rockingham Street’. George Wostenholm became a Freeman in 1826, a practical cutler and a dynamic salesman he found scope for his prodigious energy in America where, in 1830, the father and son launched a partnership with William Stenton, an experienced cutlery merchant. However, this did not last and the partnership was dissolved the following year when they were also granted their trademark ‘I*XL. ‘, bought by George Senior in 1826 and originally granted to William Aldam Smith in 1787. In 1833 George Senior died and the business continued under his son who opened a New York office in 1844, and by the middle of the century had agents in Philadelphia and Boston. America was the ideal market with its expanding frontier and enormous demand for folding knives, razors, and weapons. The firm’s trade became almost exclusively American and Wostenholm made little attempt to nurture other markets. In 1848 the Washington Works was acquired and American orders continued to roll in. The workforce increased significantly to 850 in 1861, having been around a hundred or so in the 1830s. The high quality of the firm’s Bowie and spring knives was achieved by ‘drilling’, in which every knife was critically examined. It had the desired effect and soon ‘I*XL’ vied with Rodgers’ star and Maltese cross as a badge of quality. Like Rodgers, Wostenholm made its share of exhibition pieces. At the Great Exhibition in 1851 Wostenholm displayed a set of ornate sheath knives, including one commissioned from the well-known artist Alfred Stevens. The company also displayed a collection of exhibition multi-blades. The display won a Prize Medal for Wostenholm. The firm also carried off prize medals at exhibitions in Paris (1855) and London (1862). George Wostenholm had remarkable stamina. In early 1869, in his late sixties, he set off for a tour of Europe and in October the same year he made another trip to New York. In 1872, he again visited New York. He was active until the end, though he sold out to his business associates in 1875, when Wostenholm’s became a limited liability company. George Wostenholm died in 1876, aged 74 and left a remarkable fortune of nearly £250,000. The new company chairman and directors had little or no experience of the cutlery trade. Initially, Wostenholm’s continued to make good profit but the McKinley Tariff of 1890 raised the duties on their American exports to unprecedented heights and caused a crisis. Wostenholm’s refused to abandon the American trade and maintained an unprofitable New York office open until the early 1930s while they had little success breaking into the Australian and other markets. In the early 20th century they opposed machine technology and consequently were in decline a decade before the First World War. Not long after, Washington Works was becoming a relic. In 1971, Wostenholm was bought by Joseph Rodgers & Sons and the new company (Rodgers-Wostenholm) moved into premises at Guernsey Road, Heeley. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A FINE MULTI-BLADE PENKNIFE FOR EXHIBITION, GEORGE WOSTENHOLM I.XL, SHEFFIELD, EARLY 20TH CENTURY with over forty-eight folding blades and accessories, including saws, picks, scissors and corkscrew, some stamped ‘George Wostenholm I.XL.’, fitted at each side with highly figured composition scales each retained by four minute screws, with sliding tweezers and picks top and bottom, and in fine condition throughout, 12.0 cm (closed) LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 73. It is likely that the founder of George Wostenholm & Son Ltd was George Wolstenholme (1775-1833), a fork maker at Thomas Lane. Apprenticed to John Micklethwaite, a cutler, in 1790 and granted his Freedom in 1799, George later moved to Broad Lane where he made spring knives. He was first listed in a Sheffield directory in 1816 as a pen and pocket knife manufacturer at Rockingham Street, where he had registered a silver mark in 1809. His workshops expanded to become Rockingham Works and he apparently shortened his name to ‘Wostenholm’ to facilitate its stamping on blades. His son, George Wostenholm (1802-1876) was apprenticed to his father and they are described in 1825 as ‘George Wolstenholme & Son, manufacturers of table knives, and forks, pen, pocket, and sportsman’s knives, and general dealers in cutlery, 78 Rockingham Street’. George Wostenholm became a Freeman in 1826, a practical cutler and a dynamic salesman he found scope for his prodigious energy in America where, in 1830, the father and son launched a partnership with William Stenton, an experienced cutlery merchant. However, this did not last and the partnership was dissolved the following year when they were also granted their trademark ‘I*XL. ‘, bought by George Senior in 1826 and originally granted to William Aldam Smith in 1787. In 1833 George Senior died and the business continued under his son who opened a New York office in 1844, and by the middle of the century had agents in Philadelphia and Boston. America was the ideal market with its expanding frontier and enormous demand for folding knives, razors, and weapons. The firm’s trade became almost exclusively American and Wostenholm made little attempt to nurture other markets. In 1848 the Washington Works was acquired and American orders continued to roll in. The workforce increased significantly to 850 in 1861, having been around a hundred or so in the 1830s. The high quality of the firm’s Bowie and spring knives was achieved by ‘drilling’, in which every knife was critically examined. It had the desired effect and soon ‘I*XL’ vied with Rodgers’ star and Maltese cross as a badge of quality. Like Rodgers, Wostenholm made its share of exhibition pieces. At the Great Exhibition in 1851 Wostenholm displayed a set of ornate sheath knives, including one commissioned from the well-known artist Alfred Stevens. The company also displayed a collection of exhibition multi-blades. The display won a Prize Medal for Wostenholm. The firm also carried off prize medals at exhibitions in Paris (1855) and London (1862). George Wostenholm had remarkable stamina. In early 1869, in his late sixties, he set off for a tour of Europe and in October the same year he made another trip to New York. In 1872, he again visited New York. He was active until the end, though he sold out to his business associates in 1875, when Wostenholm’s became a limited liability company. George Wostenholm died in 1876, aged 74 and left a remarkable fortune of nearly £250,000. The new company chairman and directors had little or no experience of the cutlery trade. Initially, Wostenholm’s continued to make good profit but the McKinley Tariff of 1890 raised the duties on their American exports to unprecedented heights and caused a crisis. Wostenholm’s refused to abandon the American trade and maintained an unprofitable New York office open until the early 1930s while they had little success breaking into the Australian and other markets. In the early 20th century they opposed machine technology and consequently were in decline a decade before the First World War. Not long after, Washington Works was becoming a relic. In 1971, Wostenholm was bought by Joseph Rodgers & Sons and the new company (Rodgers-Wostenholm) moved into premises at Guernsey Road, Heeley. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A SMALL MULTI-BLADE PENKNIFE FOR EXHIBITION, GEORGE WOSTENHOLM I.XL, SHEFFIELD, EARLY 20TH CENTURY with over twenty folding blades and accessories, including saw, picks, scissors and corkscrew, the main blade stamped ‘George Wostenholm I.XL.’, fitted at each side with highly figured select quality mother-of-pearl scales each retained by three minute screws, with sliding tweezers and picks, and in fine condition throughout, 8.1 cm (closed) LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 73. It is likely that the founder of George Wostenholm & Son Ltd was George Wolstenholme (1775-1833), a fork maker at Thomas Lane. Apprenticed to John Micklethwaite, a cutler, in 1790 and granted his Freedom in 1799, George later moved to Broad Lane where he made spring knives. He was first listed in a Sheffield directory in 1816 as a pen and pocket knife manufacturer at Rockingham Street, where he had registered a silver mark in 1809. His workshops expanded to become Rockingham Works and he apparently shortened his name to ‘Wostenholm’ to facilitate its stamping on blades. His son, George Wostenholm (1802-1876) was apprenticed to his father and they are described in 1825 as ‘George Wolstenholme & Son, manufacturers of table knives, and forks, pen, pocket, and sportsman’s knives, and general dealers in cutlery, 78 Rockingham Street’. George Wostenholm became a Freeman in 1826, a practical cutler and a dynamic salesman he found scope for his prodigious energy in America where, in 1830, the father and son launched a partnership with William Stenton, an experienced cutlery merchant. However, this did not last and the partnership was dissolved the following year when they were also granted their trademark ‘I*XL. ‘, bought by George Senior in 1826 and originally granted to William Aldam Smith in 1787. In 1833 George Senior died and the business continued under his son who opened a New York office in 1844, and by the middle of the century had agents in Philadelphia and Boston. America was the ideal market with its expanding frontier and enormous demand for folding knives, razors, and weapons. The firm’s trade became almost exclusively American and Wostenholm made little attempt to nurture other markets. In 1848 the Washington Works was acquired and American orders continued to roll in. The workforce increased significantly to 850 in 1861, having been around a hundred or so in the 1830s. The high quality of the firm’s Bowie and spring knives was achieved by ‘drilling’, in which every knife was critically examined. It had the desired effect and soon ‘I*XL’ vied with Rodgers’ star and Maltese cross as a badge of quality. Like Rodgers, Wostenholm made its share of exhibition pieces. At the Great Exhibition in 1851 Wostenholm displayed a set of ornate sheath knives, including one commissioned from the well-known artist Alfred Stevens. The company also displayed a collection of exhibition multi-blades. The display won a Prize Medal for Wostenholm. The firm also carried off prize medals at exhibitions in Paris (1855) and London (1862). George Wostenholm had remarkable stamina. In early 1869, in his late sixties, he set off for a tour of Europe and in October the same year he made another trip to New York. In 1872, he again visited New York. He was active until the end, though he sold out to his business associates in 1875, when Wostenholm’s became a limited liability company. George Wostenholm died in 1876, aged 74 and left a remarkable fortune of nearly £250,000. The new company chairman and directors had little or no experience of the cutlery trade. Initially, Wostenholm’s continued to make good profit but the McKinley Tariff of 1890 raised the duties on their American exports to unprecedented heights and caused a crisis. Wostenholm’s refused to abandon the American trade and maintained an unprofitable New York office open until the early 1930s while they had little success breaking into the Australian and other markets. In the early 20th century they opposed machine technology and consequently were in decline a decade before the First World War. Not long after, Washington Works was becoming a relic. In 1971, Wostenholm was bought by Joseph Rodgers & Sons and the new company (Rodgers-Wostenholm) moved into premises at Guernsey Road, Heeley. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
SIX POCKET KNIVES, GEORGE WOSTENHOLM, SHEFFIELD, 20TH CENTURY the first with two folding blades, each stamped by the maker at the ricasso, the larger blade marked ‘I.XL’, brass fillets, chased German silver terminals and a small ivory central scales, one with a vacant German silver escutcheon; the second with two folding blades and cast body including the initials ‘I.XL’; the third and fourth with a single blade, the ferrules marked ‘I.XL; and two further knives, each in their original box, the first: 11.3 cm (closed) (6) LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 143. It is likely that the founder of George Wostenholm & Son Ltd was George Wolstenholme (1775-1833), a fork maker at Thomas Lane. Apprenticed to John Micklethwaite, a cutler, in 1790 and granted his Freedom in 1799, George later moved to Broad Lane where he made spring knives. He was first listed in a Sheffield directory in 1816 as a pen and pocket knife manufacturer at Rockingham Street, where he had registered a silver mark in 1809. His workshops expanded to become Rockingham Works and he apparently shortened his name to ‘Wostenholm’ to facilitate its stamping on blades. His son, George Wostenholm (1802-1876) was apprenticed to his father and they are described in 1825 as ‘George Wolstenholme & Son, manufacturers of table knives, and forks, pen, pocket, and sportsman’s knives, and general dealers in cutlery, 78 Rockingham Street’. George Wostenholm became a Freeman in 1826, a practical cutler and a dynamic salesman he found scope for his prodigious energy in America where, in 1830, the father and son launched a partnership with William Stenton, an experienced cutlery merchant. However, this did not last and the partnership was dissolved the following year when they were also granted their trademark ‘I*XL. ‘, bought by George Senior in 1826 and originally granted to William Aldam Smith in 1787. In 1833 George Senior died and the business continued under his son who opened a New York office in 1844, and by the middle of the century had agents in Philadelphia and Boston. America was the ideal market with its expanding frontier and enormous demand for folding knives, razors, and weapons. The firm’s trade became almost exclusively American and Wostenholm made little attempt to nurture other markets. In 1848 the Washington Works was acquired and American orders continued to roll in. The workforce increased significantly to 850 in 1861, having been around a hundred or so in the 1830s. The high quality of the firm’s Bowie and spring knives was achieved by ‘drilling’, in which every knife was critically examined. It had the desired effect and soon ‘I*XL’ vied with Rodgers’ star and Maltese cross as a badge of quality. Like Rodgers, Wostenholm made its share of exhibition pieces. At the Great Exhibition in 1851 Wostenholm displayed a set of ornate sheath knives, including one commissioned from the well-known artist Alfred Stevens. The company also displayed a collection of exhibition multi-blades. The display won a Prize Medal for Wostenholm. The firm also carried off prize medals at exhibitions in Paris (1855) and London (1862). George Wostenholm had remarkable stamina. In early 1869, in his late sixties, he set off for a tour of Europe and in October the same year he made another trip to New York. In 1872, he again visited New York. He was active until the end, though he sold out to his business associates in 1875, when Wostenholm’s became a limited liability company. George Wostenholm died in 1876, aged 74 and left a remarkable fortune of nearly £250,000. The new company chairman and directors had little or no experience of the cutlery trade. Initially, Wostenholm’s continued to make good profit but the McKinley Tariff of 1890 raised the duties on their American exports to unprecedented heights and caused a crisis. Wostenholm’s refused to abandon the American trade and maintained an unprofitable New York office open until the early 1930s while they had little success breaking into the Australian and other markets. In the early 20th century they opposed machine technology and consequently were in decline a decade before the First World War. Not long after, Washington Works was becoming a relic. In 1971, Wostenholm was bought by Joseph Rodgers & Sons and the new company (Rodgers-Wostenholm) moved into premises at Guernsey Road, Heeley. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
TWO ‘NON XLL’ POCKET KNIVES, SHEFFIELD, EARLY 20TH CENTURY AND SIX FURTHER POCKET KNIVES the first two probably Wostenholm, each with two folding blades, iron ferrule stamped ‘Non XLL’, and natural staghorn scales (one restored), the third Joseph Eliott, with two folding blades and natural staghorn scales; the fourth and fifth with cast bodies; and three further similar knives, the first: 8.5 cm (closed) (8) LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 139. It is likely that the founder of George Wostenholm & Son Ltd was George Wolstenholme (1775-1833), a fork maker at Thomas Lane. Apprenticed to John Micklethwaite, a cutler, in 1790 and granted his Freedom in 1799, George later moved to Broad Lane where he made spring knives. He was first listed in a Sheffield directory in 1816 as a pen and pocket knife manufacturer at Rockingham Street, where he had registered a silver mark in 1809. His workshops expanded to become Rockingham Works and he apparently shortened his name to ‘Wostenholm’ to facilitate its stamping on blades. His son, George Wostenholm (1802-1876) was apprenticed to his father and they are described in 1825 as ‘George Wolstenholme & Son, manufacturers of table knives, and forks, pen, pocket, and sportsman’s knives, and general dealers in cutlery, 78 Rockingham Street’. George Wostenholm became a Freeman in 1826, a practical cutler and a dynamic salesman he found scope for his prodigious energy in America where, in 1830, the father and son launched a partnership with William Stenton, an experienced cutlery merchant. However, this did not last and the partnership was dissolved the following year when they were also granted their trademark ‘I*XL. ‘, bought by George Senior in 1826 and originally granted to William Aldam Smith in 1787. In 1833 George Senior died and the business continued under his son who opened a New York office in 1844, and by the middle of the century had agents in Philadelphia and Boston. America was the ideal market with its expanding frontier and enormous demand for folding knives, razors, and weapons. The firm’s trade became almost exclusively American and Wostenholm made little attempt to nurture other markets. In 1848 the Washington Works was acquired and American orders continued to roll in. The workforce increased significantly to 850 in 1861, having been around a hundred or so in the 1830s. The high quality of the firm’s Bowie and spring knives was achieved by ‘drilling’, in which every knife was critically examined. It had the desired effect and soon ‘I*XL’ vied with Rodgers’ star and Maltese cross as a badge of quality. Like Rodgers, Wostenholm made its share of exhibition pieces. At the Great Exhibition in 1851 Wostenholm displayed a set of ornate sheath knives, including one commissioned from the well-known artist Alfred Stevens. The company also displayed a collection of exhibition multi-blades. The display won a Prize Medal for Wostenholm. The firm also carried off prize medals at exhibitions in Paris (1855) and London (1862). George Wostenholm had remarkable stamina. In early 1869, in his late sixties, he set off for a tour of Europe and in October the same year he made another trip to New York. In 1872, he again visited New York. He was active until the end, though he sold out to his business associates in 1875, when Wostenholm’s became a limited liability company. George Wostenholm died in 1876, aged 74 and left a remarkable fortune of nearly £250,000. The new company chairman and directors had little or no experience of the cutlery trade. Initially, Wostenholm’s continued to make good profit but the McKinley Tariff of 1890 raised the duties on their American exports to unprecedented heights and caused a crisis. Wostenholm’s refused to abandon the American trade and maintained an unprofitable New York office open until the early 1930s while they had little success breaking into the Australian and other markets. In the early 20th century they opposed machine technology and consequently were in decline a decade before the First World War. Not long after, Washington Works was becoming a relic. In 1971, Wostenholm was bought by Joseph Rodgers & Sons and the new company (Rodgers-Wostenholm) moved into premises at Guernsey Road, Heeley. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A MASSIVE EXHIBITION HUNTING KNIFE, GEORGE WOSTENHOLM & SON, WASHINGTON WORKS, I.XL, LATE 19TH CENTURY with long blade formed with a spear point and with three panels of deeply filed grooves on the back-edge (small areas of light wear and staining), stamped with the maker’s details including ‘None are genuine but those marked I. XL.’, and eagle, ‘Geo. Wostenholm & Sons Celebrated’ in a linear panel, and in large elaborate letters ‘For Stags and Buffalos’ on one face, rectangular ricasso, elliptical German silver cross-piece, and natural staghorn grips retained by five rivets, 35.2 cm blade It is likely that the founder of George Wostenholm & Son Ltd was George Wolstenholme (1775-1833), a fork maker at Thomas Lane. Apprenticed to John Micklethwaite, a cutler, in 1790 and granted his Freedom in 1799, George later moved to Broad Lane where he made spring knives. He was first listed in a Sheffield directory in 1816 as a pen and pocket knife manufacturer at Rockingham Street, where he had registered a silver mark in 1809. His workshops expanded to become Rockingham Works and he apparently shortened his name to ‘Wostenholm’ to facilitate its stamping on blades. His son, George Wostenholm (1802-1876) was apprenticed to his father and they are described in 1825 as ‘George Wolstenholme & Son, manufacturers of table knives, and forks, pen, pocket, and sportsman’s knives, and general dealers in cutlery, 78 Rockingham Street’. George Wostenholm became a Freeman in 1826, a practical cutler and a dynamic salesman he found scope for his prodigious energy in America where, in 1830, the father and son launched a partnership with William Stenton, an experienced cutlery merchant. However, this did not last and the partnership was dissolved the following year when they were also granted their trademark ‘I*XL. ‘, bought by George Senior in 1826 and originally granted to William Aldam Smith in 1787. In 1833 George Senior died and the business continued under his son who opened a New York office in 1844, and by the middle of the century had agents in Philadelphia and Boston. America was the ideal market with its expanding frontier and enormous demand for folding knives, razors, and weapons. The firm’s trade became almost exclusively American and Wostenholm made little attempt to nurture other markets. In 1848 the Washington Works was acquired and American orders continued to roll in. The workforce increased significantly to 850 in 1861, having been around a hundred or so in the 1830s. The high quality of the firm’s Bowie and spring knives was achieved by ‘drilling’, in which every knife was critically examined. It had the desired effect and soon ‘I*XL’ vied with Rodgers’ star and Maltese cross as a badge of quality. Like Rodgers, Wostenholm made its share of exhibition pieces. At the Great Exhibition in 1851 Wostenholm displayed a set of ornate sheath knives, including one commissioned from the well-known artist Alfred Stevens. The company also displayed a collection of exhibition multi-blades. The display won a Prize Medal for Wostenholm. The firm also carried off prize medals at exhibitions in Paris (1855) and London (1862). George Wostenholm had remarkable stamina. In early 1869, in his late sixties, he set off for a tour of Europe and in October the same year he made another trip to New York. In 1872, he again visited New York. He was active until the end, though he sold out to his business associates in 1875, when Wostenholm’s became a limited liability company. George Wostenholm died in 1876, aged 74 and left a remarkable fortune of nearly £250,000. The new company chairman and directors had little or no experience of the cutlery trade. Initially, Wostenholm’s continued to make good profit but the McKinley Tariff of 1890 raised the duties on their American exports to unprecedented heights and caused a crisis. Wostenholm’s refused to abandon the American trade and maintained an unprofitable New York office open until the early 1930s while they had little success breaking into the Australian and other markets. In the early 20th century they opposed machine technology and consequently were in decline a decade before the First World War. Not long after, Washington Works was becoming a relic. In 1971, Wostenholm was bought by Joseph Rodgers & Sons and the new company (Rodgers-Wostenholm) moved into premises at Guernsey Road, Heeley. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A RARE BOWIE KNIFE PRESENTED TO JOHN CAMPBELL, SURGEON, JALAPA 1847, GEORGE WOSTENHOLM & SON, I.XL, WASHINGTON WORKS, SHEFFIELD with curved blade formed with a clipped point, engraved with an eagle displayed, ‘None are genuine but those marked I.XL.’, the maker’s details and presentation inscription, iron cross-guard with scrolling terminals, Indian style carved brown hardstone grip, in its leather-covered wooden scabbard (light wear, chape missing), 30.2 cm blade LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 234. The presentation inscription reads: John Campbell Surgeon Jalapa 1847 in Highest Esteem. On 18th April 1847 a force of thirteen thousand Mexican troops met nine thousand Americans at a mountain pass near Jalapa. Bitter hand-to-hand fighting ensued and the Mexicans were forced to flee. The American army continued, under General Winfield Scott, towards Mexico city, storming a Mexican fortress at Contreras and then routing a large Mexican force at Churubusco. It is likely that the founder of George Wostenholm & Son Ltd was George Wolstenholme (1775-1833), a fork maker at Thomas Lane. Apprenticed to John Micklethwaite, a cutler, in 1790 and granted his Freedom in 1799, George later moved to Broad Lane where he made spring knives. He was first listed in a Sheffield directory in 1816 as a pen and pocket knife manufacturer at Rockingham Street, where he had registered a silver mark in 1809. His workshops expanded to become Rockingham Works and he apparently shortened his name to ‘Wostenholm’ to facilitate its stamping on blades. His son, George Wostenholm (1802-1876) was apprenticed to his father and they are described in 1825 as ‘George Wolstenholme & Son, manufacturers of table knives, and forks, pen, pocket, and sportsman’s knives, and general dealers in cutlery, 78 Rockingham Street’. George Wostenholm became a Freeman in 1826, a practical cutler and a dynamic salesman he found scope for his prodigious energy in America where, in 1830, the father and son launched a partnership with William Stenton, an experienced cutlery merchant. However, this did not last and the partnership was dissolved the following year when they were also granted their trademark ‘I*XL. ‘, bought by George Senior in 1826 and originally granted to William Aldam Smith in 1787. In 1833 George Senior died and the business continued under his son who opened a New York office in 1844, and by the middle of the century had agents in Philadelphia and Boston. America was the ideal market with its expanding frontier and enormous demand for folding knives, razors, and weapons. The firm’s trade became almost exclusively American and Wostenholm made little attempt to nurture other markets. In 1848 the Washington Works was acquired and American orders continued to roll in. The workforce increased significantly to 850 in 1861, having been around a hundred or so in the 1830s. The high quality of the firm’s Bowie and spring knives was achieved by ‘drilling’, in which every knife was critically examined. It had the desired effect and soon ‘I*XL’ vied with Rodgers’ star and Maltese cross as a badge of quality. Like Rodgers, Wostenholm made its share of exhibition pieces. At the Great Exhibition in 1851 Wostenholm displayed a set of ornate sheath knives, including one commissioned from the well-known artist Alfred Stevens. The company also displayed a collection of exhibition multi-blades. The display won a Prize Medal for Wostenholm. The firm also carried off prize medals at exhibitions in Paris (1855) and London (1862). George Wostenholm had remarkable stamina. In early 1869, in his late sixties, he set off for a tour of Europe and in October the same year he made another trip to New York. In 1872, he again visited New York. He was active until the end, though he sold out to his business associates in 1875, when Wostenholm’s became a limited liability company. George Wostenholm died in 1876, aged 74 and left a remarkable fortune of nearly £250,000. The new company chairman and directors had little or no experience of the cutlery trade. Initially, Wostenholm’s continued to make good profit but the McKinley Tariff of 1890 raised the duties on their American exports to unprecedented heights and caused a crisis. Wostenholm’s refused to abandon the American trade and maintained an unprofitable New York office open until the early 1930s while they had little success breaking into the Australian and other markets. In the early 20th century they opposed machine technology and consequently were in decline a decade before the First World War. Not long after, Washington Works was becoming a relic. In 1971, Wostenholm was bought by Joseph Rodgers & Sons and the new company (Rodgers-Wostenholm) moved into premises at Guernsey Road, Heeley. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A BOWIE KNIFE, GEORGE WOSTENHOLM & SON, WASHINGTON WORKS, SHEFFIELD, CIRCA 1960 with broad blade formed with a clipped-back point, stamped with the maker’s details, ‘I.XL’, ‘The Hunter’s Companion’, and ‘The real I.XL knife’, engraved with an eagle and with the makers name and ‘California Knife’ in gilt letters, recessed rectangular ricasso stamped with the maker’s details in full, German silver guard, milled copper alloy fillets, natural staghorn scales and vacant German silver escutcheon, in its wooden scabbard with tooled leather covering stamped ‘I.XL’ in gilt letters and with German silver mounts, 24.0 cm blade LiteratureRichard Washer, The Sheffield Bowie & Pocket-Knife makers 1825-1925, Nottingham 1974, cover and frontispiece illustration.David Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 280. It is likely that the founder of George Wostenholm & Son Ltd was George Wolstenholme (1775-1833), a fork maker at Thomas Lane. Apprenticed to John Micklethwaite, a cutler, in 1790 and granted his Freedom in 1799, George later moved to Broad Lane where he made spring knives. He was first listed in a Sheffield directory in 1816 as a pen and pocket knife manufacturer at Rockingham Street, where he had registered a silver mark in 1809. His workshops expanded to become Rockingham Works and he apparently shortened his name to ‘Wostenholm’ to facilitate its stamping on blades. His son, George Wostenholm (1802-1876) was apprenticed to his father and they are described in 1825 as ‘George Wolstenholme & Son, manufacturers of table knives, and forks, pen, pocket, and sportsman’s knives, and general dealers in cutlery, 78 Rockingham Street’. George Wostenholm became a Freeman in 1826, a practical cutler and a dynamic salesman he found scope for his prodigious energy in America where, in 1830, the father and son launched a partnership with William Stenton, an experienced cutlery merchant. However, this did not last and the partnership was dissolved the following year when they were also granted their trademark ‘I*XL. ‘, bought by George Senior in 1826 and originally granted to William Aldam Smith in 1787. In 1833 George Senior died and the business continued under his son who opened a New York office in 1844, and by the middle of the century had agents in Philadelphia and Boston. America was the ideal market with its expanding frontier and enormous demand for folding knives, razors, and weapons. The firm’s trade became almost exclusively American and Wostenholm made little attempt to nurture other markets. In 1848 the Washington Works was acquired and American orders continued to roll in. The workforce increased significantly to 850 in 1861, having been around a hundred or so in the 1830s. The high quality of the firm’s Bowie and spring knives was achieved by ‘drilling’, in which every knife was critically examined. It had the desired effect and soon ‘I*XL’ vied with Rodgers’ star and Maltese cross as a badge of quality. Like Rodgers, Wostenholm made its share of exhibition pieces. At the Great Exhibition in 1851 Wostenholm displayed a set of ornate sheath knives, including one commissioned from the well-known artist Alfred Stevens. The company also displayed a collection of exhibition multi-blades. The display won a Prize Medal for Wostenholm. The firm also carried off prize medals at exhibitions in Paris (1855) and London (1862). George Wostenholm had remarkable stamina. In early 1869, in his late sixties, he set off for a tour of Europe and in October the same year he made another trip to New York. In 1872, he again visited New York. He was active until the end, though he sold out to his business associates in 1875, when Wostenholm’s became a limited liability company. George Wostenholm died in 1876, aged 74 and left a remarkable fortune of nearly £250,000. The new company chairman and directors had little or no experience of the cutlery trade. Initially, Wostenholm’s continued to make good profit but the McKinley Tariff of 1890 raised the duties on their American exports to unprecedented heights and caused a crisis. Wostenholm’s refused to abandon the American trade and maintained an unprofitable New York office open until the early 1930s while they had little success breaking into the Australian and other markets. In the early 20th century they opposed machine technology and consequently were in decline a decade before the First World War. Not long after, Washington Works was becoming a relic. In 1971, Wostenholm was bought by Joseph Rodgers & Sons and the new company (Rodgers-Wostenholm) moved into premises at Guernsey Road, Heeley. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A BOWIE KNIFE, GEORGE WOSTENHOLM & SON, WASHINGTON WORKS, SHEFFIELD, 20TH CENTURY with broad blade formed with a clipped-back point, stamped with the maker’s details, ‘I.XL’, and ‘The real I.XL knife’, engraved with an eagle and etched and gilt with two captioned portraits of General Garibaldi and Vittore Emanuel (worn), recessed rectangular ricasso stamped with the maker’s details in full, German silver guard, milled copper alloy fillets, natural staghorn scales and vacant German silver escutcheon, in its wooden scabbard with tooled leather covering stamped ‘I.XL’ in gilt letters and with German silver mounts, 24.3 cm blade LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 280. It is likely that the founder of George Wostenholm & Son Ltd was George Wolstenholme (1775-1833), a fork maker at Thomas Lane. Apprenticed to John Micklethwaite, a cutler, in 1790 and granted his Freedom in 1799, George later moved to Broad Lane where he made spring knives. He was first listed in a Sheffield directory in 1816 as a pen and pocket knife manufacturer at Rockingham Street, where he had registered a silver mark in 1809. His workshops expanded to become Rockingham Works and he apparently shortened his name to ‘Wostenholm’ to facilitate its stamping on blades. His son, George Wostenholm (1802-1876) was apprenticed to his father and they are described in 1825 as ‘George Wolstenholme & Son, manufacturers of table knives, and forks, pen, pocket, and sportsman’s knives, and general dealers in cutlery, 78 Rockingham Street’. George Wostenholm became a Freeman in 1826, a practical cutler and a dynamic salesman he found scope for his prodigious energy in America where, in 1830, the father and son launched a partnership with William Stenton, an experienced cutlery merchant. However, this did not last and the partnership was dissolved the following year when they were also granted their trademark ‘I*XL. ‘, bought by George Senior in 1826 and originally granted to William Aldam Smith in 1787. In 1833 George Senior died and the business continued under his son who opened a New York office in 1844, and by the middle of the century had agents in Philadelphia and Boston. America was the ideal market with its expanding frontier and enormous demand for folding knives, razors, and weapons. The firm’s trade became almost exclusively American and Wostenholm made little attempt to nurture other markets. In 1848 the Washington Works was acquired and American orders continued to roll in. The workforce increased significantly to 850 in 1861, having been around a hundred or so in the 1830s. The high quality of the firm’s Bowie and spring knives was achieved by ‘drilling’, in which every knife was critically examined. It had the desired effect and soon ‘I*XL’ vied with Rodgers’ star and Maltese cross as a badge of quality. Like Rodgers, Wostenholm made its share of exhibition pieces. At the Great Exhibition in 1851 Wostenholm displayed a set of ornate sheath knives, including one commissioned from the well-known artist Alfred Stevens. The company also displayed a collection of exhibition multi-blades. The display won a Prize Medal for Wostenholm. The firm also carried off prize medals at exhibitions in Paris (1855) and London (1862). George Wostenholm had remarkable stamina. In early 1869, in his late sixties, he set off for a tour of Europe and in October the same year he made another trip to New York. In 1872, he again visited New York. He was active until the end, though he sold out to his business associates in 1875, when Wostenholm’s became a limited liability company. George Wostenholm died in 1876, aged 74 and left a remarkable fortune of nearly £250,000. The new company chairman and directors had little or no experience of the cutlery trade. Initially, Wostenholm’s continued to make good profit but the McKinley Tariff of 1890 raised the duties on their American exports to unprecedented heights and caused a crisis. Wostenholm’s refused to abandon the American trade and maintained an unprofitable New York office open until the early 1930s while they had little success breaking into the Australian and other markets. In the early 20th century they opposed machine technology and consequently were in decline a decade before the First World War. Not long after, Washington Works was becoming a relic. In 1971, Wostenholm was bought by Joseph Rodgers & Sons and the new company (Rodgers-Wostenholm) moved into premises at Guernsey Road, Heeley. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A BOWIE KNIFE, GEORGE WOSTENHOLM & SON, WASHINGTON WORKS, SHEFFIELD, 20TH CENTURY with broad blade formed with a clipped-back point, stamped with the maker’s details, ‘I.XL’, and ‘The real I.XL knife’, engraved with an eagle and etched with two captioned portraits (worn), recessed rectangular ricasso stamped ‘I.XL’, German silver guard, milled copper alloy fillets, polished horn scales and vacant German silver escutcheon, 24.3 cm blade LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 281. It is likely that the founder of George Wostenholm & Son Ltd was George Wolstenholme (1775-1833), a fork maker at Thomas Lane. Apprenticed to John Micklethwaite, a cutler, in 1790 and granted his Freedom in 1799, George later moved to Broad Lane where he made spring knives. He was first listed in a Sheffield directory in 1816 as a pen and pocket knife manufacturer at Rockingham Street, where he had registered a silver mark in 1809. His workshops expanded to become Rockingham Works and he apparently shortened his name to ‘Wostenholm’ to facilitate its stamping on blades. His son, George Wostenholm (1802-1876) was apprenticed to his father and they are described in 1825 as ‘George Wolstenholme & Son, manufacturers of table knives, and forks, pen, pocket, and sportsman’s knives, and general dealers in cutlery, 78 Rockingham Street’. George Wostenholm became a Freeman in 1826, a practical cutler and a dynamic salesman he found scope for his prodigious energy in America where, in 1830, the father and son launched a partnership with William Stenton, an experienced cutlery merchant. However, this did not last and the partnership was dissolved the following year when they were also granted their trademark ‘I*XL. ‘, bought by George Senior in 1826 and originally granted to William Aldam Smith in 1787. In 1833 George Senior died and the business continued under his son who opened a New York office in 1844, and by the middle of the century had agents in Philadelphia and Boston. America was the ideal market with its expanding frontier and enormous demand for folding knives, razors, and weapons. The firm’s trade became almost exclusively American and Wostenholm made little attempt to nurture other markets. In 1848 the Washington Works was acquired and American orders continued to roll in. The workforce increased significantly to 850 in 1861, having been around a hundred or so in the 1830s. The high quality of the firm’s Bowie and spring knives was achieved by ‘drilling’, in which every knife was critically examined. It had the desired effect and soon ‘I*XL’ vied with Rodgers’ star and Maltese cross as a badge of quality. Like Rodgers, Wostenholm made its share of exhibition pieces. At the Great Exhibition in 1851 Wostenholm displayed a set of ornate sheath knives, including one commissioned from the well-known artist Alfred Stevens. The company also displayed a collection of exhibition multi-blades. The display won a Prize Medal for Wostenholm. The firm also carried off prize medals at exhibitions in Paris (1855) and London (1862). George Wostenholm had remarkable stamina. In early 1869, in his late sixties, he set off for a tour of Europe and in October the same year he made another trip to New York. In 1872, he again visited New York. He was active until the end, though he sold out to his business associates in 1875, when Wostenholm’s became a limited liability company. George Wostenholm died in 1876, aged 74 and left a remarkable fortune of nearly £250,000. The new company chairman and directors had little or no experience of the cutlery trade. Initially, Wostenholm’s continued to make good profit but the McKinley Tariff of 1890 raised the duties on their American exports to unprecedented heights and caused a crisis. Wostenholm’s refused to abandon the American trade and maintained an unprofitable New York office open until the early 1930s while they had little success breaking into the Australian and other markets. In the early 20th century they opposed machine technology and consequently were in decline a decade before the First World War. Not long after, Washington Works was becoming a relic. In 1971, Wostenholm was bought by Joseph Rodgers & Sons and the new company (Rodgers-Wostenholm) moved into premises at Guernsey Road, Heeley. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A BOWIE KNIFE, G. WOSTENHOLM & SON, WASHINGTON WORKS, SHEFFIELD, EARLY 20TH CENTURY AND A DAGGER FOR THE AMERICAN MARKET, LATE 19TH CENTURY the first with broad blade formed with a long clipped point, signed on the back-edge, recessed rectangular ricasso marked ‘I.XL’, German silver guard, natural staghorn scales and vacant German silver escutcheon, in its tooled leather scabbard marked ‘I.XL’ in gilt letters; the second with tapering blade of flattened-diamond section, rectangular ricasso, German silver cross-piece with moulded terminals and natural staghorn scales, the first: 21.0 cm (2) LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 287. It is likely that the founder of George Wostenholm & Son Ltd was George Wolstenholme (1775-1833), a fork maker at Thomas Lane. Apprenticed to John Micklethwaite, a cutler, in 1790 and granted his Freedom in 1799, George later moved to Broad Lane where he made spring knives. He was first listed in a Sheffield directory in 1816 as a pen and pocket knife manufacturer at Rockingham Street, where he had registered a silver mark in 1809. His workshops expanded to become Rockingham Works and he apparently shortened his name to ‘Wostenholm’ to facilitate its stamping on blades. His son, George Wostenholm (1802-1876) was apprenticed to his father and they are described in 1825 as ‘George Wolstenholme & Son, manufacturers of table knives, and forks, pen, pocket, and sportsman’s knives, and general dealers in cutlery, 78 Rockingham Street’. George Wostenholm became a Freeman in 1826, a practical cutler and a dynamic salesman he found scope for his prodigious energy in America where, in 1830, the father and son launched a partnership with William Stenton, an experienced cutlery merchant. However, this did not last and the partnership was dissolved the following year when they were also granted their trademark ‘I*XL. ‘, bought by George Senior in 1826 and originally granted to William Aldam Smith in 1787. In 1833 George Senior died and the business continued under his son who opened a New York office in 1844, and by the middle of the century had agents in Philadelphia and Boston. America was the ideal market with its expanding frontier and enormous demand for folding knives, razors, and weapons. The firm’s trade became almost exclusively American and Wostenholm made little attempt to nurture other markets. In 1848 the Washington Works was acquired and American orders continued to roll in. The workforce increased significantly to 850 in 1861, having been around a hundred or so in the 1830s. The high quality of the firm’s Bowie and spring knives was achieved by ‘drilling’, in which every knife was critically examined. It had the desired effect and soon ‘I*XL’ vied with Rodgers’ star and Maltese cross as a badge of quality. Like Rodgers, Wostenholm made its share of exhibition pieces. At the Great Exhibition in 1851 Wostenholm displayed a set of ornate sheath knives, including one commissioned from the well-known artist Alfred Stevens. The company also displayed a collection of exhibition multi-blades. The display won a Prize Medal for Wostenholm. The firm also carried off prize medals at exhibitions in Paris (1855) and London (1862). George Wostenholm had remarkable stamina. In early 1869, in his late sixties, he set off for a tour of Europe and in October the same year he made another trip to New York. In 1872, he again visited New York. He was active until the end, though he sold out to his business associates in 1875, when Wostenholm’s became a limited liability company. George Wostenholm died in 1876, aged 74 and left a remarkable fortune of nearly £250,000. The new company chairman and directors had little or no experience of the cutlery trade. Initially, Wostenholm’s continued to make good profit but the McKinley Tariff of 1890 raised the duties on their American exports to unprecedented heights and caused a crisis. Wostenholm’s refused to abandon the American trade and maintained an unprofitable New York office open until the early 1930s while they had little success breaking into the Australian and other markets. In the early 20th century they opposed machine technology and consequently were in decline a decade before the First World War. Not long after, Washington Works was becoming a relic. In 1971, Wostenholm was bought by Joseph Rodgers & Sons and the new company (Rodgers-Wostenholm) moved into premises at Guernsey Road, Heeley. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A DAGGER, GEORGE WOSTENHOLM, SHEFFIELD, THIRD QUARTER OF THE 19TH CENTURY with doubled-edged broad blade, signed rectangular ricasso marked ‘I.XL’, German silver guard, and a pair of mother-of-pearl scales retained by four rivets, the outer with vacant German silver escutcheon, in its leather scabbard, 15.2 cm blade LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 295. It is likely that the founder of George Wostenholm & Son Ltd was George Wolstenholme (1775-1833), a fork maker at Thomas Lane. Apprenticed to John Micklethwaite, a cutler, in 1790 and granted his Freedom in 1799, George later moved to Broad Lane where he made spring knives. He was first listed in a Sheffield directory in 1816 as a pen and pocket knife manufacturer at Rockingham Street, where he had registered a silver mark in 1809. His workshops expanded to become Rockingham Works and he apparently shortened his name to ‘Wostenholm’ to facilitate its stamping on blades. His son, George Wostenholm (1802-1876) was apprenticed to his father and they are described in 1825 as ‘George Wolstenholme & Son, manufacturers of table knives, and forks, pen, pocket, and sportsman’s knives, and general dealers in cutlery, 78 Rockingham Street’. George Wostenholm became a Freeman in 1826, a practical cutler and a dynamic salesman he found scope for his prodigious energy in America where, in 1830, the father and son launched a partnership with William Stenton, an experienced cutlery merchant. However, this did not last and the partnership was dissolved the following year when they were also granted their trademark ‘I*XL. ‘, bought by George Senior in 1826 and originally granted to William Aldam Smith in 1787. In 1833 George Senior died and the business continued under his son who opened a New York office in 1844, and by the middle of the century had agents in Philadelphia and Boston. America was the ideal market with its expanding frontier and enormous demand for folding knives, razors, and weapons. The firm’s trade became almost exclusively American and Wostenholm made little attempt to nurture other markets. In 1848 the Washington Works was acquired and American orders continued to roll in. The workforce increased significantly to 850 in 1861, having been around a hundred or so in the 1830s. The high quality of the firm’s Bowie and spring knives was achieved by ‘drilling’, in which every knife was critically examined. It had the desired effect and soon ‘I*XL’ vied with Rodgers’ star and Maltese cross as a badge of quality. Like Rodgers, Wostenholm made its share of exhibition pieces. At the Great Exhibition in 1851 Wostenholm displayed a set of ornate sheath knives, including one commissioned from the well-known artist Alfred Stevens. The company also displayed a collection of exhibition multi-blades. The display won a Prize Medal for Wostenholm. The firm also carried off prize medals at exhibitions in Paris (1855) and London (1862). George Wostenholm had remarkable stamina. In early 1869, in his late sixties, he set off for a tour of Europe and in October the same year he made another trip to New York. In 1872, he again visited New York. He was active until the end, though he sold out to his business associates in 1875, when Wostenholm’s became a limited liability company. George Wostenholm died in 1876, aged 74 and left a remarkable fortune of nearly £250,000. The new company chairman and directors had little or no experience of the cutlery trade. Initially, Wostenholm’s continued to make good profit but the McKinley Tariff of 1890 raised the duties on their American exports to unprecedented heights and caused a crisis. Wostenholm’s refused to abandon the American trade and maintained an unprofitable New York office open until the early 1930s while they had little success breaking into the Australian and other markets. In the early 20th century they opposed machine technology and consequently were in decline a decade before the First World War. Not long after, Washington Works was becoming a relic. In 1971, Wostenholm was bought by Joseph Rodgers & Sons and the new company (Rodgers-Wostenholm) moved into premises at Guernsey Road, Heeley. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A BOWIE KNIFE, GEORGE WOSTENHOLM & SON, WASHINGTON WORKS, SHEFFIELD, NUMBER 4 OF 1,000 TO CELEBRATE THE 150TH ANNIVERSARY OF THE BATTLE OF THE ALAMO, 1986 with broad blade formed with a clipped-back point, stamped with the maker’s details, ‘I.XL’, ‘The Hunter’s Companion’, and ‘The real I.XL knife’, engraved with an eagle and with the makers name and ‘California Knife’ in part gilt letters, recessed rectangular ricasso stamped with the maker’s details in full, German silver guard, milled copper alloy fillets, natural staghorn scales and German silver escutcheon engraved ‘4/1,000’, in its fitted presentation case with certificate, the lid embossed ‘I. XL. In gilt letters on the outside, 24.0 cm blade It is likely that the founder of George Wostenholm & Son Ltd was George Wolstenholme (1775-1833), a fork maker at Thomas Lane. Apprenticed to John Micklethwaite, a cutler, in 1790 and granted his Freedom in 1799, George later moved to Broad Lane where he made spring knives. He was first listed in a Sheffield directory in 1816 as a pen and pocket knife manufacturer at Rockingham Street, where he had registered a silver mark in 1809. His workshops expanded to become Rockingham Works and he apparently shortened his name to ‘Wostenholm’ to facilitate its stamping on blades. His son, George Wostenholm (1802-1876) was apprenticed to his father and they are described in 1825 as ‘George Wolstenholme & Son, manufacturers of table knives, and forks, pen, pocket, and sportsman’s knives, and general dealers in cutlery, 78 Rockingham Street’. George Wostenholm became a Freeman in 1826, a practical cutler and a dynamic salesman he found scope for his prodigious energy in America where, in 1830, the father and son launched a partnership with William Stenton, an experienced cutlery merchant. However, this did not last and the partnership was dissolved the following year when they were also granted their trademark ‘I*XL. ‘, bought by George Senior in 1826 and originally granted to William Aldam Smith in 1787. In 1833 George Senior died and the business continued under his son who opened a New York office in 1844, and by the middle of the century had agents in Philadelphia and Boston. America was the ideal market with its expanding frontier and enormous demand for folding knives, razors, and weapons. The firm’s trade became almost exclusively American and Wostenholm made little attempt to nurture other markets. In 1848 the Washington Works was acquired and American orders continued to roll in. The workforce increased significantly to 850 in 1861, having been around a hundred or so in the 1830s. The high quality of the firm’s Bowie and spring knives was achieved by ‘drilling’, in which every knife was critically examined. It had the desired effect and soon ‘I*XL’ vied with Rodgers’ star and Maltese cross as a badge of quality. Like Rodgers, Wostenholm made its share of exhibition pieces. At the Great Exhibition in 1851 Wostenholm displayed a set of ornate sheath knives, including one commissioned from the well-known artist Alfred Stevens. The company also displayed a collection of exhibition multi-blades. The display won a Prize Medal for Wostenholm. The firm also carried off prize medals at exhibitions in Paris (1855) and London (1862). George Wostenholm had remarkable stamina. In early 1869, in his late sixties, he set off for a tour of Europe and in October the same year he made another trip to New York. In 1872, he again visited New York. He was active until the end, though he sold out to his business associates in 1875, when Wostenholm’s became a limited liability company. George Wostenholm died in 1876, aged 74 and left a remarkable fortune of nearly £250,000. The new company chairman and directors had little or no experience of the cutlery trade. Initially, Wostenholm’s continued to make good profit but the McKinley Tariff of 1890 raised the duties on their American exports to unprecedented heights and caused a crisis. Wostenholm’s refused to abandon the American trade and maintained an unprofitable New York office open until the early 1930s while they had little success breaking into the Australian and other markets. In the early 20th century they opposed machine technology and consequently were in decline a decade before the First World War. Not long after, Washington Works was becoming a relic. In 1971, Wostenholm was bought by Joseph Rodgers & Sons and the new company (Rodgers-Wostenholm) moved into premises at Guernsey Road, Heeley. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A FINE AND RARE LARGE FOLDING KNIFE FOR EXHIBITION, LOCKWOOD BROTHERS, SHEFFIELD, MID-19TH CENTURY with two burnished broad folding blades, each double-edged over the upper portion, formed with a scalloped back-edge, stamped ‘Lockwood Brothers’ divided by an engraved running rhea above ‘Pampa’ on one face, stamped ‘Lockwood Brothers Sheffield’ at the base and with the letters ‘CX’ divided by a pair of vertically arranged crosses (small areas of staining), finely milled gilt liners and spring backs, highly figured exotic hardwood chamfered scales retained by seven rivets with German silver caps, one inlaid with the maker’s name ‘Lockwood Brothers’ divided by a running rhea above the letters ‘Pampa’ , with finely milled and engraved German silver terminals decorated with scrolls and foliage, those at the pivot end with a vacant panel, perhaps for the date, on each face, and remaining in fine condition throughout, 40.5 cm (closed) LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 77. Stated to have been made for the 1851 Great Exhibition and shown at thirty one subsequent cutlery exhibitions until 1905. The apparent founder of Lockwood Brother Ltd was John Lockwood of Ecclesfield, who was apprenticed to file maker John Burgin and became a Freeman in 1767, when he was assigned the mark ‘CX’. His two sons were John Lockwood Jun. (1769-1856) and William Lockwood (1775-1829). The latter moved to Sheffield in the 1790s and, in 1803, married Ann Sorby, linking his family to the local tool making dynasty. They had four sons, William (1806-1873), John (1813-1876), Joseph (1815-1902), and Charles (1822-1872). In 1817, Lockwood & Sorby are recorded as factors in Arundel Street and merchants and file manufacturers in 1822. William died in 1829 and his four sons who became the ‘Lockwood brothers’ ultimately continued the business, first recorded 1837. In 1861 Lockwoods employed 500 staff and in 1865 they expanded their premises at Arundel Street. The enterprise became more closely involved in cutlery and trade catalogues show a wide range of knives and pocket cutlery with an emphasis on complicated sportsman’s patterns, hunting and skinning knives. By 1862 German counterfeiting had forced the company to adopt another mark: a Pampas rhea with the words ‘REAL KNIFE’ and ‘PAMPA’. The firm’s main trade mark was ‘C:X’. Lockwood’s also acquired a Maltese cross ‘L’ mark. Three of the Lockwood brothers died in the early 1870s: Charles (1872), William (1873), and John (1876). Joseph continued the business and around 1891 they became a limited company. By the First World War, Lockwood’s was in decline and losing money, in 1919 it became part of Sheffield Cutlery Manufacturers Ltd and were acquired by Elliott in 1927. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A MULTI-BLADE PENKNIFE FOR EXHIBITION with over one hundred folding blades and accessories including awls, borers, saws, corkscrews, tweezers, scissors, pincers, scribes, bodkins, needles, nail files, bradawls, and spanners, fitted at each side with mother-of-pearl scales (small cracks) retained by five minute screws and with elaborately writhen German silver borders at the top and bottom, 12.0 cm (closed) ProvenanceThe directors of Lockwoods, Sheffield. LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 73. The apparent founder of Lockwood Brother Ltd was John Lockwood of Ecclesfield, who was apprenticed to file maker John Burgin and became a Freeman in 1767, when he was assigned the mark ‘CX’. His two sons were John Lockwood Jun. (1769-1856) and William Lockwood (1775-1829). The latter moved to Sheffield in the 1790s and, in 1803, married Ann Sorby, linking his family to the local tool making dynasty. They had four sons, William (1806-1873), John (1813-1876), Joseph (1815-1902), and Charles (1822-1872). In 1817, Lockwood & Sorby are recorded as factors in Arundel Street and merchants and file manufacturers in 1822. William died in 1829 and his four sons who became the ‘Lockwood brothers’ ultimately continued the business, first recorded 1837. In 1861 Lockwoods employed 500 staff and in 1865 they expanded their premises at Arundel Street. The enterprise became more closely involved in cutlery and trade catalogues show a wide range of knives and pocket cutlery with an emphasis on complicated sportsman’s patterns, hunting and skinning knives. By 1862 German counterfeiting had forced the company to adopt another mark: a Pampas rhea with the words ‘REAL KNIFE’ and ‘PAMPA’. The firm’s main trade mark was ‘C:X’. Lockwood’s also acquired a Maltese cross ‘L’ mark. Three of the Lockwood brothers died in the early 1870s: Charles (1872), William (1873), and John (1876). Joseph continued the business and around 1891 they became a limited company. By the First World War, Lockwood’s was in decline and losing money, in 1919 it became part of Sheffield Cutlery Manufacturers Ltd and were acquired by Elliott in 1927. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
˜ A SALESMAN’S DISPLAY OF TWENTY-FIVE POCKET KNIVES, LOCKWOOD BROTHERS, SHEFFIELD, LATE 19TH/EARLY 20TH CENTURY each struck with the maker’s details at the ricasso, comprising twenty-one with ‘Real Pampa’ blades; four with natural staghorn scales, eleven with polished horn scales, one with ivory scales, one with brass scales stamped ‘Goldfinger knife’ and the remainder with hardwood scales, mounted on board with stock numbers in ink and makers details in gilt letters, with cover, 43.0 x 35.0 cm LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 196. The apparent founder of Lockwood Brother Ltd was John Lockwood of Ecclesfield, who was apprenticed to file maker John Burgin and became a Freeman in 1767, when he was assigned the mark ‘CX’. His two sons were John Lockwood Jun. (1769-1856) and William Lockwood (1775-1829). The latter moved to Sheffield in the 1790s and, in 1803, married Ann Sorby, linking his family to the local tool making dynasty. They had four sons, William (1806-1873), John (1813-1876), Joseph (1815-1902), and Charles (1822-1872). In 1817, Lockwood & Sorby are recorded as factors in Arundel Street and merchants and file manufacturers in 1822. William died in 1829 and his four sons who became the ‘Lockwood brothers’ ultimately continued the business, first recorded 1837. In 1861 Lockwoods employed 500 staff and in 1865 they expanded their premises at Arundel Street. The enterprise became more closely involved in cutlery and trade catalogues show a wide range of knives and pocket cutlery with an emphasis on complicated sportsman’s patterns, hunting and skinning knives. By 1862 German counterfeiting had forced the company to adopt another mark: a Pampas rhea with the words ‘REAL KNIFE’ and ‘PAMPA’. The firm’s main trade mark was ‘C:X’. Lockwood’s also acquired a Maltese cross ‘L’ mark. Three of the Lockwood brothers died in the early 1870s: Charles (1872), William (1873), and John (1876). Joseph continued the business and around 1891 they became a limited company. By the First World War, Lockwood’s was in decline and losing money, in 1919 it became part of Sheffield Cutlery Manufacturers Ltd and were acquired by Elliott in 1927. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
˜ A SALESMAN’S DISPLAY OF TWENTY-FOUR POCKET KNIVES, LOCKWOOD BROTHERS, SHEFFIELD, LATE 19TH/EARLY 20TH CENTURY each struck with the maker’s details at the ricasso, comprising thirteen with ‘Real Pampa’ blades; twelve with natural staghorn scales, seven with polished horn scales, three with ivory scales, one two with hardwood scales, mounted on board with stock reference numbers in ink and makers details in gilt letters, with cover, 43.0 x 35.0 cm LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 199. The apparent founder of Lockwood Brother Ltd was John Lockwood of Ecclesfield, who was apprenticed to file maker John Burgin and became a Freeman in 1767, when he was assigned the mark ‘CX’. His two sons were John Lockwood Jun. (1769-1856) and William Lockwood (1775-1829). The latter moved to Sheffield in the 1790s and, in 1803, married Ann Sorby, linking his family to the local tool making dynasty. They had four sons, William (1806-1873), John (1813-1876), Joseph (1815-1902), and Charles (1822-1872). In 1817, Lockwood & Sorby are recorded as factors in Arundel Street and merchants and file manufacturers in 1822. William died in 1829 and his four sons who became the ‘Lockwood brothers’ ultimately continued the business, first recorded 1837. In 1861 Lockwoods employed 500 staff and in 1865 they expanded their premises at Arundel Street. The enterprise became more closely involved in cutlery and trade catalogues show a wide range of knives and pocket cutlery with an emphasis on complicated sportsman’s patterns, hunting and skinning knives. By 1862 German counterfeiting had forced the company to adopt another mark: a Pampas rhea with the words ‘REAL KNIFE’ and ‘PAMPA’. The firm’s main trade mark was ‘C:X’. Lockwood’s also acquired a Maltese cross ‘L’ mark. Three of the Lockwood brothers died in the early 1870s: Charles (1872), William (1873), and John (1876). Joseph continued the business and around 1891 they became a limited company. By the First World War, Lockwood’s was in decline and losing money, in 1919 it became part of Sheffield Cutlery Manufacturers Ltd and were acquired by Elliott in 1927. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A DISPLAY BOARD FOR THE MANUFACTURE OF A TWO-BLADE POCKET KNIFE ‘PAMPA’, LOCKWOOD BROTHERS, LAST QUARTER OF THE 19TH CENTURY, formed of a paper-covered board inscribed in gilt letters with the manufacturer’s details, displaying the thirty-seven stages of manufacture, comprising the two spring bars each in five stages, spear and pen blades each in seven stages, bolsters, brass fillets and final assembly in five stages, consecutively numbered in ink, 30.5 cm x 25.5 cm LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 69. The apparent founder of Lockwood Brother Ltd was John Lockwood of Ecclesfield, who was apprenticed to file maker John Burgin and became a Freeman in 1767, when he was assigned the mark ‘CX’. His two sons were John Lockwood Jun. (1769-1856) and William Lockwood (1775-1829). The latter moved to Sheffield in the 1790s and, in 1803, married Ann Sorby, linking his family to the local tool making dynasty. They had four sons, William (1806-1873), John (1813-1876), Joseph (1815-1902), and Charles (1822-1872). In 1817, Lockwood & Sorby are recorded as factors in Arundel Street and merchants and file manufacturers in 1822. William died in 1829 and his four sons who became the ‘Lockwood brothers’ ultimately continued the business, first recorded 1837. In 1861 Lockwoods employed 500 staff and in 1865 they expanded their premises at Arundel Street. The enterprise became more closely involved in cutlery and trade catalogues show a wide range of knives and pocket cutlery with an emphasis on complicated sportsman’s patterns, hunting and skinning knives. By 1862 German counterfeiting had forced the company to adopt another mark: a Pampas rhea with the words ‘REAL KNIFE’ and ‘PAMPA’. The firm’s main trade mark was ‘C:X’. Lockwood’s also acquired a Maltese cross ‘L’ mark. Three of the Lockwood brothers died in the early 1870s: Charles (1872), William (1873), and John (1876). Joseph continued the business and around 1891 they became a limited company. By the First World War, Lockwood’s was in decline and losing money, in 1919 it became part of Sheffield Cutlery Manufacturers Ltd and were acquired by Elliott in 1927. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
FIVE LOCK KNIVES BY LOCKWOOD BROTHERS, SHEFFIELD, LATE 19TH CENTURY, A FIGHTING KNIFE AND THREE FURTHER POCKET KNIVES the first five with ‘Real Pampa’ blades, three with natural staghorn scales, one with polished horn scales and one with hardwood scales; the sixth with folding locking blade signed ‘Taylor’ and ‘Real Knife Witness’, German silver double quillons and natural staghorn scales, and three further pocket knives with natural staghorn scales, the first: 12.8 cm (closed) (10) LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 243. The apparent founder of Lockwood Brother Ltd was John Lockwood of Ecclesfield, who was apprenticed to file maker John Burgin and became a Freeman in 1767, when he was assigned the mark ‘CX’. His two sons were John Lockwood Jun. (1769-1856) and William Lockwood (1775-1829). The latter moved to Sheffield in the 1790s and, in 1803, married Ann Sorby, linking his family to the local tool making dynasty. They had four sons, William (1806-1873), John (1813-1876), Joseph (1815-1902), and Charles (1822-1872). In 1817, Lockwood & Sorby are recorded as factors in Arundel Street and merchants and file manufacturers in 1822. William died in 1829 and his four sons who became the ‘Lockwood brothers’ ultimately continued the business, first recorded 1837. In 1861 Lockwoods employed 500 staff and in 1865 they expanded their premises at Arundel Street. The enterprise became more closely involved in cutlery and trade catalogues show a wide range of knives and pocket cutlery with an emphasis on complicated sportsman’s patterns, hunting and skinning knives. By 1862 German counterfeiting had forced the company to adopt another mark: a Pampas rhea with the words ‘REAL KNIFE’ and ‘PAMPA’. The firm’s main trade mark was ‘C:X’. Lockwood’s also acquired a Maltese cross ‘L’ mark. Three of the Lockwood brothers died in the early 1870s: Charles (1872), William (1873), and John (1876). Joseph continued the business and around 1891 they became a limited company. By the First World War, Lockwood’s was in decline and losing money, in 1919 it became part of Sheffield Cutlery Manufacturers Ltd and were acquired by Elliott in 1927. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
THREE POCKET KNIVES, LOCKWOOD BROTHERS, SHEFFIELD, LATE 19TH/EARLY 20TH CENTURY AND THIRTEEN FURTHER POCKET KNIVES the first two marked ‘Real Pampa’, signed at the ricasso and with CX’ mark; the third similar, with additional folding blade; five folding knives by Joseph Elliott & Sons, with signed blades and natural staghorn scales; another by the same maker with two folding blade and another smaller knife by the same maker; two by Allen & Son; and four further pocket knives, the first: 10.8 cm (closed) (16) LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 114. The apparent founder of Lockwood Brother Ltd was John Lockwood of Ecclesfield, who was apprenticed to file maker John Burgin and became a Freeman in 1767, when he was assigned the mark ‘CX’. His two sons were John Lockwood Jun. (1769-1856) and William Lockwood (1775-1829). The latter moved to Sheffield in the 1790s and, in 1803, married Ann Sorby, linking his family to the local tool making dynasty. They had four sons, William (1806-1873), John (1813-1876), Joseph (1815-1902), and Charles (1822-1872). In 1817, Lockwood & Sorby are recorded as factors in Arundel Street and merchants and file manufacturers in 1822. William died in 1829 and his four sons who became the ‘Lockwood brothers’ ultimately continued the business, first recorded 1837. In 1861 Lockwoods employed 500 staff and in 1865 they expanded their premises at Arundel Street. The enterprise became more closely involved in cutlery and trade catalogues show a wide range of knives and pocket cutlery with an emphasis on complicated sportsman’s patterns, hunting and skinning knives. By 1862 German counterfeiting had forced the company to adopt another mark: a Pampas rhea with the words ‘REAL KNIFE’ and ‘PAMPA’. The firm’s main trade mark was ‘C:X’. Lockwood’s also acquired a Maltese cross ‘L’ mark. Three of the Lockwood brothers died in the early 1870s: Charles (1872), William (1873), and John (1876). Joseph continued the business and around 1891 they became a limited company. By the First World War, Lockwood’s was in decline and losing money, in 1919 it became part of Sheffield Cutlery Manufacturers Ltd and were acquired by Elliott in 1927. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A PRUNING KNIFE, LOCKWOOD BROTHERS, SHEFFIELD, LATE 19TH EARLY 20TH CENTURY AND SIXTEEN FURTHER PRUNING AND OTHER KNIVES the first with folding ‘Real Pampa’ blade with makers details and stamps at the forte and natural staghorn scales (one flattened, perhaps for display); thirteen further pruning knives, and three pocket knives by various makers; the first: 11.0 cm (closed) (17) The apparent founder of Lockwood Brother Ltd was John Lockwood of Ecclesfield, who was apprenticed to file maker John Burgin and became a Freeman in 1767, when he was assigned the mark ‘CX’. His two sons were John Lockwood Jun. (1769-1856) and William Lockwood (1775-1829). The latter moved to Sheffield in the 1790s and, in 1803, married Ann Sorby, linking his family to the local tool making dynasty. They had four sons, William (1806-1873), John (1813-1876), Joseph (1815-1902), and Charles (1822-1872). In 1817, Lockwood & Sorby are recorded as factors in Arundel Street and merchants and file manufacturers in 1822. William died in 1829 and his four sons who became the ‘Lockwood brothers’ ultimately continued the business, first recorded 1837. In 1861 Lockwoods employed 500 staff and in 1865 they expanded their premises at Arundel Street. The enterprise became more closely involved in cutlery and trade catalogues show a wide range of knives and pocket cutlery with an emphasis on complicated sportsman’s patterns, hunting and skinning knives. By 1862 German counterfeiting had forced the company to adopt another mark: a Pampas rhea with the words ‘REAL KNIFE’ and ‘PAMPA’. The firm’s main trade mark was ‘C:X’. Lockwood’s also acquired a Maltese cross ‘L’ mark. Three of the Lockwood brothers died in the early 1870s: Charles (1872), William (1873), and John (1876). Joseph continued the business and around 1891 they became a limited company. By the First World War, Lockwood’s was in decline and losing money, in 1919 it became part of Sheffield Cutlery Manufacturers Ltd and were acquired by Elliott in 1927. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
FOUR BUTLER’S KNIVES, LOCKWOOD BROTHERS, SHEFFIELD, 19TH CENTURY AND FOUR FURTHER KNIVES the first four with two folding blades of differing size, signed at the ricasso, a further small hooked blade, corkscrew, and nickel bodies engraved with a rhea and ‘Real Pampa’; another, Joseph Elliott; another, John Petty; another, Allen & Son, and a locking knife with nickel body, Joseph Rodgers & Sons, no. 6 Norfolk Street Sheffield, the first: 10.5 cm (closed) (8) LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 139. The apparent founder of Lockwood Brother Ltd was John Lockwood of Ecclesfield, who was apprenticed to file maker John Burgin and became a Freeman in 1767, when he was assigned the mark ‘CX’. His two sons were John Lockwood Jun. (1769-1856) and William Lockwood (1775-1829). The latter moved to Sheffield in the 1790s and, in 1803, married Ann Sorby, linking his family to the local tool making dynasty. They had four sons, William (1806-1873), John (1813-1876), Joseph (1815-1902), and Charles (1822-1872). In 1817, Lockwood & Sorby are recorded as factors in Arundel Street and merchants and file manufacturers in 1822. William died in 1829 and his four sons who became the ‘Lockwood brothers’ ultimately continued the business, first recorded 1837. In 1861 Lockwoods employed 500 staff and in 1865 they expanded their premises at Arundel Street. The enterprise became more closely involved in cutlery and trade catalogues show a wide range of knives and pocket cutlery with an emphasis on complicated sportsman’s patterns, hunting and skinning knives. By 1862 German counterfeiting had forced the company to adopt another mark: a Pampas rhea with the words ‘REAL KNIFE’ and ‘PAMPA’. The firm’s main trade mark was ‘C:X’. Lockwood’s also acquired a Maltese cross ‘L’ mark. Three of the Lockwood brothers died in the early 1870s: Charles (1872), William (1873), and John (1876). Joseph continued the business and around 1891 they became a limited company. By the First World War, Lockwood’s was in decline and losing money, in 1919 it became part of Sheffield Cutlery Manufacturers Ltd and were acquired by Elliott in 1927. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
THREE PENKNIVES, LOCKWOOD BROTHERS, SHEFFIELD, LATE 19TH CENTURY AND FIVE FURTHER KNIVES the first with five folding elements including pick and awl, and natural staghorn scales; the second marked ‘Real Pampa’ and with six folding elements; the third with three folding elements including tuning fork and pincers, the fourth smaller, with four folding elements; the fifth and sixth Allen & Sons, the seventh, Petty, with five folding elements; and the eighth, Joseph Elliott, with two blade and staghorn scales, the first: 8.7 cm (closed) (8) LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 138. The apparent founder of Lockwood Brother Ltd was John Lockwood of Ecclesfield, who was apprenticed to file maker John Burgin and became a Freeman in 1767, when he was assigned the mark ‘CX’. His two sons were John Lockwood Jun. (1769-1856) and William Lockwood (1775-1829). The latter moved to Sheffield in the 1790s and, in 1803, married Ann Sorby, linking his family to the local tool making dynasty. They had four sons, William (1806-1873), John (1813-1876), Joseph (1815-1902), and Charles (1822-1872). In 1817, Lockwood & Sorby are recorded as factors in Arundel Street and merchants and file manufacturers in 1822. William died in 1829 and his four sons who became the ‘Lockwood brothers’ ultimately continued the business, first recorded 1837. In 1861 Lockwoods employed 500 staff and in 1865 they expanded their premises at Arundel Street. The enterprise became more closely involved in cutlery and trade catalogues show a wide range of knives and pocket cutlery with an emphasis on complicated sportsman’s patterns, hunting and skinning knives. By 1862 German counterfeiting had forced the company to adopt another mark: a Pampas rhea with the words ‘REAL KNIFE’ and ‘PAMPA’. The firm’s main trade mark was ‘C:X’. Lockwood’s also acquired a Maltese cross ‘L’ mark. Three of the Lockwood brothers died in the early 1870s: Charles (1872), William (1873), and John (1876). Joseph continued the business and around 1891 they became a limited company. By the First World War, Lockwood’s was in decline and losing money, in 1919 it became part of Sheffield Cutlery Manufacturers Ltd and were acquired by Elliott in 1927. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
SIX POCKET KNIVES, LOCKWOOD BROTHERS, SHEFFIELD, LATE 19TH CENTURY AND TWELVE FURTHER POCKET KNIVES, the first to fourth with three folding blades marked ‘Real Pampa’ and with polished horn scales; the fifth and sixth with a single folding ‘Real Pampa’ blade and natural staghorn bodies; the seventh to tenth, Joseph Elliott, with staghorn bodies; and eight further pocket knives, various makers, the first: 10.5 cm (18) LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 158. The apparent founder of Lockwood Brother Ltd was John Lockwood of Ecclesfield, who was apprenticed to file maker John Burgin and became a Freeman in 1767, when he was assigned the mark ‘CX’. His two sons were John Lockwood Jun. (1769-1856) and William Lockwood (1775-1829). The latter moved to Sheffield in the 1790s and, in 1803, married Ann Sorby, linking his family to the local tool making dynasty. They had four sons, William (1806-1873), John (1813-1876), Joseph (1815-1902), and Charles (1822-1872). In 1817, Lockwood & Sorby are recorded as factors in Arundel Street and merchants and file manufacturers in 1822. William died in 1829 and his four sons who became the ‘Lockwood brothers’ ultimately continued the business, first recorded 1837. In 1861 Lockwoods employed 500 staff and in 1865 they expanded their premises at Arundel Street. The enterprise became more closely involved in cutlery and trade catalogues show a wide range of knives and pocket cutlery with an emphasis on complicated sportsman’s patterns, hunting and skinning knives. By 1862 German counterfeiting had forced the company to adopt another mark: a Pampas rhea with the words ‘REAL KNIFE’ and ‘PAMPA’. The firm’s main trade mark was ‘C:X’. Lockwood’s also acquired a Maltese cross ‘L’ mark. Three of the Lockwood brothers died in the early 1870s: Charles (1872), William (1873), and John (1876). Joseph continued the business and around 1891 they became a limited company. By the First World War, Lockwood’s was in decline and losing money, in 1919 it became part of Sheffield Cutlery Manufacturers Ltd and were acquired by Elliott in 1927. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
˜ A SMALL PENKNIFE, LOCKWOOD BROTHERS, SHEFFIELD, LATE 19TH CENTURY, AND TWENTY-ONE FURTHER SMALL PENKNIVES the first with signed folding ‘Real Pampa’ main blade, two further folding accessories, and German silver-mounted staghorn scales; the second by the same, with four folding blades and tortoiseshell scales; a premium stock knife, George Wostenholm, Sheffield, with three folding elements, in associated box; two fruit knives, Brookes & Crookes, Sheffield, with folding blades and mother-of-pearl scales, and seventeen further small penknives, the first: 9.0 cm (closed) (22) The apparent founder of Lockwood Brother Ltd was John Lockwood of Ecclesfield, who was apprenticed to file maker John Burgin and became a Freeman in 1767, when he was assigned the mark ‘CX’. His two sons were John Lockwood Jun. (1769-1856) and William Lockwood (1775-1829). The latter moved to Sheffield in the 1790s and, in 1803, married Ann Sorby, linking his family to the local tool making dynasty. They had four sons, William (1806-1873), John (1813-1876), Joseph (1815-1902), and Charles (1822-1872). In 1817, Lockwood & Sorby are recorded as factors in Arundel Street and merchants and file manufacturers in 1822. William died in 1829 and his four sons who became the ‘Lockwood brothers’ ultimately continued the business, first recorded 1837. In 1861 Lockwoods employed 500 staff and in 1865 they expanded their premises at Arundel Street. The enterprise became more closely involved in cutlery and trade catalogues show a wide range of knives and pocket cutlery with an emphasis on complicated sportsman’s patterns, hunting and skinning knives. By 1862 German counterfeiting had forced the company to adopt another mark: a Pampas rhea with the words ‘REAL KNIFE’ and ‘PAMPA’. The firm’s main trade mark was ‘C:X’. Lockwood’s also acquired a Maltese cross ‘L’ mark. Three of the Lockwood brothers died in the early 1870s: Charles (1872), William (1873), and John (1876). Joseph continued the business and around 1891 they became a limited company. By the First World War, Lockwood’s was in decline and losing money, in 1919 it became part of Sheffield Cutlery Manufacturers Ltd and were acquired by Elliott in 1927. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
FIVE PRUNING KNIVES, LOCKWOOD BROTHERS, SHEFFIELD, AND NINETEEN FURTHER PRUNING KNIVES, LATE 19TH/EARLY 20TH CENTURY with natural staghorn scales, the first and second with two folding blades, the larger marked ‘Real Pampa’; the third, fourth and fifth with single folding ‘Real Pampa’ blade; the sixth, Lockwood Sons, with single folding blade; five large pruning knives, Allen & Son, Sheffield; six smaller pruning knives, Allen & Son, Sheffield; another by the same, with two blades; and six further pruning knives, the first: 9.8 cm (closed) (24) LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 160. The apparent founder of Lockwood Brother Ltd was John Lockwood of Ecclesfield, who was apprenticed to file maker John Burgin and became a Freeman in 1767, when he was assigned the mark ‘CX’. His two sons were John Lockwood Jun. (1769-1856) and William Lockwood (1775-1829). The latter moved to Sheffield in the 1790s and, in 1803, married Ann Sorby, linking his family to the local tool making dynasty. They had four sons, William (1806-1873), John (1813-1876), Joseph (1815-1902), and Charles (1822-1872). In 1817, Lockwood & Sorby are recorded as factors in Arundel Street and merchants and file manufacturers in 1822. William died in 1829 and his four sons who became the ‘Lockwood brothers’ ultimately continued the business, first recorded 1837. In 1861 Lockwoods employed 500 staff and in 1865 they expanded their premises at Arundel Street. The enterprise became more closely involved in cutlery and trade catalogues show a wide range of knives and pocket cutlery with an emphasis on complicated sportsman’s patterns, hunting and skinning knives. By 1862 German counterfeiting had forced the company to adopt another mark: a Pampas rhea with the words ‘REAL KNIFE’ and ‘PAMPA’. The firm’s main trade mark was ‘C:X’. Lockwood’s also acquired a Maltese cross ‘L’ mark. Three of the Lockwood brothers died in the early 1870s: Charles (1872), William (1873), and John (1876). Joseph continued the business and around 1891 they became a limited company. By the First World War, Lockwood’s was in decline and losing money, in 1919 it became part of Sheffield Cutlery Manufacturers Ltd and were acquired by Elliott in 1927. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
TWO PRUNING KNIVES, LOCKWOOD BROTHERS AND SIX FURTHER PRUNING KNIVES, SHEFFIELD, LATE 19TH/EARLY 20TH CENTURY with folding blades, the first two marked ‘Real Knife Pampa’ and with rhea on one face, struck with the maker’s details, ‘CX’ and cross marks at the ricasso, and with polished and natural staghorn scales respectively; the third to sixth similar, by Joseph Elliott & Sons, with natural staghorn scales; the seventh by W. Saynor Ltd and the eighth by Allen & Scott, the first: 9,.5 cm (closed) (8) LiteratureDavid Hayden-Wright, The Heritage of English Knives, Atglen, Pennsylvania, 2008, p. 112. The apparent founder of Lockwood Brother Ltd was John Lockwood of Ecclesfield, who was apprenticed to file maker John Burgin and became a Freeman in 1767, when he was assigned the mark ‘CX’. His two sons were John Lockwood Jun. (1769-1856) and William Lockwood (1775-1829). The latter moved to Sheffield in the 1790s and, in 1803, married Ann Sorby, linking his family to the local tool making dynasty. They had four sons, William (1806-1873), John (1813-1876), Joseph (1815-1902), and Charles (1822-1872). In 1817, Lockwood & Sorby are recorded as factors in Arundel Street and merchants and file manufacturers in 1822. William died in 1829 and his four sons who became the ‘Lockwood brothers’ ultimately continued the business, first recorded 1837. In 1861 Lockwoods employed 500 staff and in 1865 they expanded their premises at Arundel Street. The enterprise became more closely involved in cutlery and trade catalogues show a wide range of knives and pocket cutlery with an emphasis on complicated sportsman’s patterns, hunting and skinning knives. By 1862 German counterfeiting had forced the company to adopt another mark: a Pampas rhea with the words ‘REAL KNIFE’ and ‘PAMPA’. The firm’s main trade mark was ‘C:X’. Lockwood’s also acquired a Maltese cross ‘L’ mark. Three of the Lockwood brothers died in the early 1870s: Charles (1872), William (1873), and John (1876). Joseph continued the business and around 1891 they became a limited company. By the First World War, Lockwood’s was in decline and losing money, in 1919 it became part of Sheffield Cutlery Manufacturers Ltd and were acquired by Elliott in 1927. Part proceeds to benefit the Acquisition Fund of the Arms and Armor department, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
-
596780 item(s)/page