We found 98580 price guide item(s) matching your search
There are 98580 lots that match your search criteria. Subscribe now to get instant access to the full price guide service.
Click here to subscribe- List
- Grid
-
98580 item(s)/page
dating: Early 19th Century provenance: Austria, Smoothbore, round, 17 mm cal. barrel, with base slightly squared off at the sides, with imperial mark, foresight on the barrel bracket. Flintlock, restored cock and pan. Wooden, full stock with iron mounts and ramrod. Socket bayonet with cruciform blade (length 56 cm), with leather-covered wooden scabbard and metal mounts. length 150 cm.
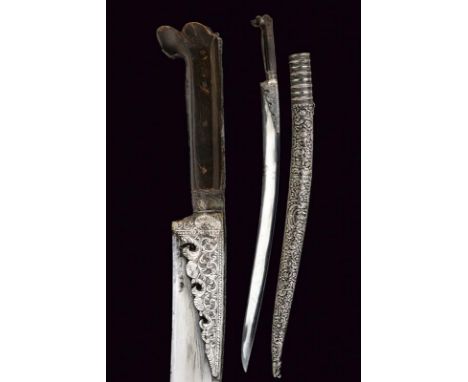
dating: Late 19th Century provenance: Caucasia, Straight, double-edged blade with triple groove and remains of engraving, the base signed 'BUTAEV'. Beautiful handle completely covered in finely engraved, nieloed and gilded silver foil depicting floral and geometric motifs. Marked '84' and 'KI' '8' in Cyrillic. Engraved and nieloed silver scabbard with remains of gilding, marked en suite and with Arabic inscription. Rare. length 49.5 cm.
dating: First half of the 19th Century provenance: Southern Italy, One with a straight, double-edged blade with central fuller, the tang engraved with floral motifs. The other with a double-edged blade ribbed in the middle. Both with horn grip with discs (missing parts) and leather scabbard. The shorter one with white metal mounts, the other without. length 23.1 - 32 cm.
dating: First half of the 19th Century provenance: Southern Italy, Solid, steel, double-edged blade, with fuller at the center and engraved with floral motifs; tang engraved and carved with curls. Horn handle (missing parts) with engraved, white metal cap and ring nut. Leather scabbard with mounts decorated en suite. length 28 cm.
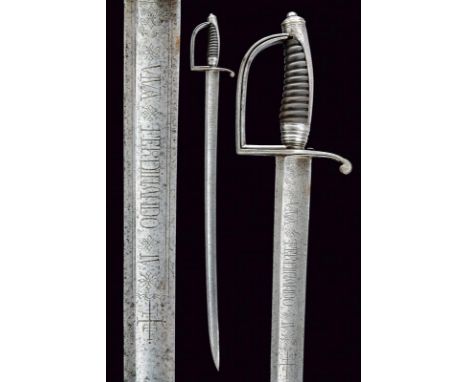
dating: first quarter of the 19th Century provenance: Kingdom of the Two Sicilies, Wide, slightly-curved blade with fuller, strong pitting especially at the tip,with the motto 'VIVA FERDINANDO IV' / 'RE DELLE DUE SICILIE' at the forte. Iron hilt with palmed stirrup guard near the pommel. Featuring a loop-guard under the guard that can be turned outwards and is provided with a stop. Long smooth cap. Ebony or horn handle decorated with strong grooves. Pitting. Missing scabbard. length 96,5 cm.
dating: Early 19th Century provenance: Kingdom fo Italy (Napoleonic), Straight, single-and third- edged blade, with fuller up to the beginning of the false edge, with remains of light-blue finishing at the forte, featuring small engraving depicting racemes with remains of gilding. Brass, Empire-style hilt with remains if silver-plating. A flaming grenade on the shell-guard. The guard decorated with architectural motifs (probably a small reparation in the curved part). The pommel featuring a five-pointed crown on one side in relied, and another star on the opposite side. Knurled ebony handle. Without scabbard. length 94,3 cm.
dating: Early 19th Century provenance: Turkey, Slightly curved, single-edged blade with thin back groove, with brass mark and decoration on the right side. Handle covered in embossed silver foil depicting floral motifs in bas-relief. Wooden scabbard, small opening covered in brown velvet (completely worn), long silver mounts decorated en suite with the handle. length 52.5 cm.
dating: circa 1900 provenance: Caucasia, Long, straight double-edged blade with deep asymmetrical groove and remains of an inscription. Handle with walrus tusk grips and mounts made of engraved and nieloed silver depicting floral and geometric motifs. Marked '84' and with another barely-legible mark. Leather-covered wooden scabbard with silver mounts and Russian marks. length 55.5 cm.
dating: 19th Century provenance: Turkey, Curved, flat, single-edged blade with Arabic inscriptions and silver-inlaid floral motifs, areas with rust damage. Silver hilt decorated with small rosettes (a small missing part). Walrus tooth grips (a small restoration). Wooden scabbard covered with brown velvet, smooth, silver-foil cap with suspension ring, silver chape decorated with floral motifs in bas-relief and with ends shaped as monster's heads. length 68.5 cm.
dating: Third quarter of the 19th Century provenance: Papal States, Straight, double-edged blade of hexagonal section, engraved halfway along its length with the mottoes 'VIVA PIO IX' and 'VIVA L'ITALIA', between raceme decorations. At the base the mark 'LOLLINI IN BOLOGNA' only partially legible. Well-preserved, brass hilt of typical shape, with double-valve guard and holding ring. German silver grip (very slight defect in the centre). Leaf-carved and gilded ring nuts. Iron scabbard with brass bands and brass mouthpiece. length 103.5 cm.
dating: 19th Century provenance: Turkey, Flat, curved, single-edged blade made of damask, on the right side a short, silver-inlaid inscription in Arabic on a dark background. Brass hilt with remains of silver plating decorated with floral motifs in low-relief. Horn grip scales with angled pommel decorated with two threads tassels and sequins. Leather-covered wooden scabbard with mounts worked en suite. Three suspension rings. length 91 cm.
dating: First half of the 19th Century provenance: Europe, Triangular blade from an English small sword marked 'Honi Soit qui Mal y Pense' under a sun and between floral motifs on both sides. Brass hilt, S-shaped shell-guard and quillon engraved with floral motifs. Typical horn grip (missing parts) with brass cap. Wooden scabbard with remains of covering, the cap is missing. length 32.5 cm.
dating: Late 19th Century provenance: China, Blades of triangular section with flat, slightly ribbed base; solid brass mounts, quillon block with dragon's head in relief, pommel engraved with floral motifs and brown horn handle decorated with ribs. Fine wooden scabbard covered with green ray skin and featuring partially pierced and engraved brass mounts. Two suspension rings. length 55.5 cm.
dating: Third quarter of the 19th Century provenance: Papal States, Round, rifled, 12 mm cal. barrel (slightly dusty bore, with visible rifling), octagonal base marked with pontifical mark, mark of the Liège test bench, serial number '45xx' and with other marks, a little further the mark 'E. M. & L. NAGANT A LIEGE'; with foresight, clutch for the bayonet, foldaway and adjustable rear sight. Iron frame marked 'BREVET REMINGTON', various marks including 'X' and 'S' under crown, serial number matching the barrel. Rolling block bolt with marks and serial number also matching the barrel. Working mechanism. Wooden butt and fore-end (a couple of woodworm holes on the butt), still visible on the right side of the butt stock, the stamp 'CATHOLIQUES BELGES' with date '1868'. Iron mounts and ramrod. Together with a yatagan bayonet (length 69.5 cm) with matching serial number, iron scabbard. length 130.5 cm.
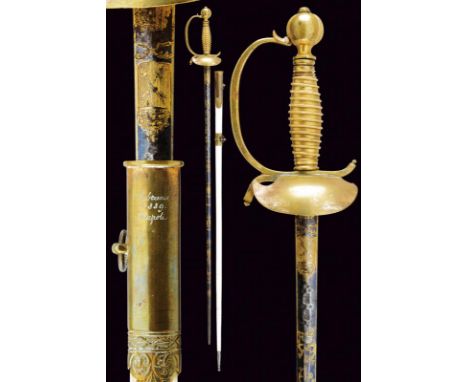
dating: Mid 19th Century provenance: Papal States, Beautiful, straight blade (18th century?) of hexagonal section, blued for almost its entire length and richly decorated with engravings featuring remains of gilding. On the right side, starting from the tang: heraldic badge in the shape of a starred shield, Papal shield with decussate keys and triregnum, the motto 'Viva Lo Stato della Chiesa' (Long Live the Church State) among scrolls, followed by floral friezes, a trophy, a depiction of a person holding a palm and a sword, and finally a cartouche with the inscription 'ALA / VORTONE' (?). The left side decorated en suite up to the motto, then featuring floral friezes and trophies, different from the ones on the other side, and with a depiction of an angel armed with a sword. The engravings and the bluing at the tip have partially faded. Brass hilt with remains of gilding. Simple smooth shell-guard. Handle in one piece, worked like the wire binding. White lacquered wooden scabbard (later lacquer?) with brass mounts, silver-coloured metal chape and cap marked 'Labruna 1859 Napoli'. length 96 cm.
dating: First half of the 19th Century provenance: Persia, Curved, double-edged blade with dark damask rib at the center (small areas with pitting), the base with gold decoration (or mark?). Walrus tusk handle (a restored break and small missing parts) deeply sculpted on one side with an important character holding a shield and a mace and sitting on a chair, and another character sitting under a palm tree on the other side; the ends with geometric decoration. Leather-covered wooden scabbard. length 38 cm.
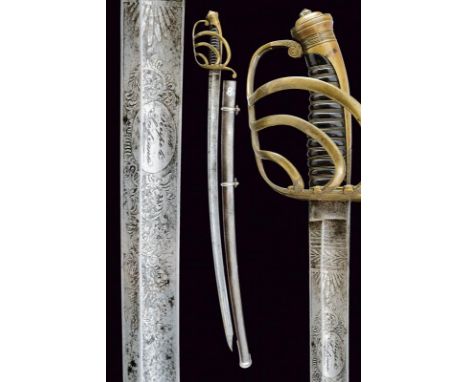
dating: Second quarter of the 19th Century provenance: Europe, Straight, single-and-false-edged blade, first with fuller and then of lenticular section, the first part finely engraved and gilded with trophies and floral motifs on a blue background. Gilt brass, one-quillon hilt, with small shell-guard, the center of crossguard with anchor without crown. Plumed helmet pommel, solid grip. Leather scabbard with gilt and engraved brass mounts. Austria? length 99 cm.
dating: 19th Century provenance: Turkey, Slightly curved, single-edged blade, with Arabic mark and date '1216' in Arabic on the third side. Beautiful hilt entirely made of silver and richly decorated in filigree featuring red cabochon stones. Leather-covered wooden scabbard (missing parts) and sewn in metal wire, simple metal cap, yellow metal chape with tip shaped as a monster's head. length 57.7 cm.
dating: Second quarter of the 19th Century provenance: Kingdom of the Two Sicilies, Straight, double-edged blade of lenticular section, with fuller at the forte. In the first part three engraved and gilded trophies and floral elements on a blue background, alternating with two unburnished segments, the first of these also featuring the inscription 'FABRICA DE TOLEDO' on both sides. Pierced brass hilt with remains of gilding, featuring a fine Bourbon shield in relief and pierced, surmounted by the royal crown, set in an oak wreath. Fish-skin covered grip with wire binding and copper wire. Long cap decorated with palmette. Metal scabbard with two lugs and gilded bronze bands. length 99.5 cm.
dating: late 18th Century provenance: Pressburg, Slightly curved, single-and false-edged blade, the base engraved with a figure under the inscription 'PANDUR', the back featuring the mark of a manufacturer from Presburg (partly legible). Brass mounts, the shell-guard shaped as a grouse, wooden grips (missing) parts with brass ring nut and rivets. Remains of the leather scabbard with brass cap, missing chape. length 51.2 cm.
dating: Mid 19th Century provenance: Belgium, Straight blade of lozenge section, engraved with floral bands on half of its length; smooth tang. Bronze-coloured, metal hilt with remains of gilding. The rear valve with the Belgian Lion in relief on a banner featuring laurel and oak fronds below, and set between two five-pointed stars. The guard with oak fronds in relief. The pommel with the rods of Jupiter and floral decorations. Dark horn handle with copper wire binding. The rear valve is turned and with and embossed trophy of arms. Leather scabbard with metal mounts featuring remains of gilding. Together with a sword knot in worse condition. length 99,5 cm.
dating: early 20th Century provenance: India, Slightly curved, double-undulated-edged blade with reinforced tip, the base engraved with floral motifs and silver frame. Iron handle shaped as a double 'T' and with remains of silver decoration depicting geometric motifs. Wooden scabbard completely covered with iron and decorated en suite. length 42 cm.
dating: Mid 19th Century provenance: Liege, Straight, double-edged blade with fuller at the centre, marked 'Doumonthier' and 'Brevete'; on the sides of the blade two round, smoothbore, 9 mm. cal barrels, the two parry quillons form the hammers, the quillon block contains the pistons; the foldaway trigger placed on the side of the grip activates the hammers in sequence. Curved (pistol-shaped) grip featuring horn grips decorated with oblique grooves and containing both the springs and mechanisms. Complete with green-painted wooden scabbard with leather covering and iron-foil cap, the chape with small damage. Rare. length 32 cm.
dating: late 18th Century provenance: France, Long, straight, single-and short false-edged blade, with double fuller along the whole length, short tang. Iron hilt, loop-guard shaped as spirals ('fleurons'), fleur-de-lis welded between the quillon and the loop-guard. Leather-covered grip with metal wire binding, iron cap with hole for the sword knot. Leather band for the thums fixed to the loop-guard. Leather scabbard with iron and brass mounts, two lugs. Rare. This rare sword was produced for only four years. For similar examples refer to 'Armes blanches militaires Francaises' Volume Aries 1968, plate VII and in 'Des sabres et des epee' by M. Petartd, Vol. 1, page 104-105. length 110,4 cm.
dating: First half of the 20th Century provenance: USA, Long, straight, single-and short false-edged blade, deep groove at the back, tang. Crossbar with ring marked 'WINCHESTER REPEATING ARMS CO.'. Grip with wooden grip scales, working spring. Browned iron scabbard with leather belt frog. length 52 cm.
dating: early 20th Century provenance: Europe, Short, straight, single-edged blade (light pitting). Light cow horn grip, provided with release button. Stick-shaped scabbard with black canvas umbrella (well preserved, with small missing parts). Metal shoe. Total length when closed: 90.5 cm. Rare. length 48,3 cm.
dating: late 17th Century provenance: Hungary, Wide, curved, single-and-false-edged blade, with wide fuller, enlarged tip, on one side the inscription 'FRINGIA' between round and toothed segments, the other side engraved with sun, moon and stars; iron, cross-shaped hilt, with long langets, pointed, angled, oval, iron pommel, leather-covered wooden grip with flower carved rosette. Leather-covered wooden scabbard with iron mounts and two suspension rings on wide bands. This beautiful and rare sabre is illustrated and documented in the book 'Vivat Hussar - Le Lame degli Ussari' by Tiziano Tonelli, Ermanno Albertelli Editore, Parma, 2010 on page 37. length 93 cm.
dating: 19th Century provenance: Caucasia, Extremely long, double-edged blade with asymmetrical grooves, with an inscription in Arabic on the right side. Typical hilt with horn grips (small missing parts) with yellow, metal rivets. Complete with leather-covered wooden scabbard (missing parts), the opening lined in burgundy velvet and with threaded bands. Iron loop. Rare considering its size. length 79 cm.
dating: Mid 19th Century provenance: Turkey, Curved, flat, single-edged blade made of damask. Silver hilt with cross-shaped helmet and horn grip scales (defects and small missing parts). Wooden scabbard covered with leather stitched in wire. Silver mounts engraved with floral motifs. Two suspension rings. Mounts in yellow patina, need cleaning. length 90 cm.
dating: 19th Century provenance: Turkey, Long, curved, single-edged blade with back groove and ribbed back, with a gold-inlaid cartouche featuring Arabic inscriptions and geometric decoration at the centre of both sides. Gilded and embossed silver hilt with floral and geometric motifs. Large walrus tusk grips with restorations. Wooden scabbard covered in burgundy velvet (partly worn) with beautiful silver mounts (partly gilded) featuring floral and geometric decorations in bas-relief, the chape with a monster's head, the cap with small missing parts. length 72 cm.
dating: circa 1700 provenance: Persia, Curved, single-and false-edged blade made of very fine dark damask, with rib at the center, reinforced tip, the base with finely engraved cartouches depicting floral motifs on a black background and with a gold frame, T-shaped rear side carved and decorated in gold. Iron handle richly decorated with yellow-gold-inlaid floral motifs (small missing parts). Walrus tusk grips featuring pommel shaped as a bird's beak (small missing parts). Wooden scabbard covered with burgundy velvet (later). length 34.5 cm.
dating: 1910 - 1940 circa provenance: Korea, Almost straight blade with light signs of use and time. Copper ring nut at the base (open on one side). Four-lobed iron quillon featuring remains of embossed markings in ideograms. Wooden grip with fish skin and leather covering. Wooden scabbard with leather covering and a brass lug. Given the similarities with Japanese military blades, it might be a sword from the period of the Japanese occupation. Like all the Korean swords, it is extremely rare. length 73,5 cm.
dating: Second half of the 19th Century provenance: Persia, Wide, slightly short, single-and-false-edged blade, with triple groove engraved with floral motifs, the base with deep gilt mark. Grip covered in silver foil with sheath-guard wings, one of the two quillons incomplete, the pommel shaped as a stylised bird's head. The surface engraved with birds within floral motifs. Wooden scabbard covered with green painted leather and sewn with wire. The long mounts decorated en suite but in bas-relief. length 54 cm.
dating: Second quarter of the 19th Century provenance: Indopersia, Large and solid, curved, single-and false-edged blade with reinforced and ribbed tip (made of damask?), 'T'-shaped back; iron handle with a fleur-de-lis at the base of the rear part, smooth frame and green stone grips decorated with black and white horn bands and mother-of-pearl stars, with a movable suspension ring on the pommel; leather-covered wooden scabbard (small missing parts) with a pierced band and chape decorated with an iron fleur-de-lis. length 42 cm.
dating: 1864 provenance: USA, Round, rifled, 14 mm cal. barrel, with octagonal breech, marks 'N.J', 'V', 'P' and date not fully legible, foldaway, two-regulation rear sight , foresight. Forward spring lock with flat lock plate marked 'U.S. / TRENTON' in the centre and with eagle, tang with date '1864'. Working mechanism. Wooden full stock (butt with a small restoration) with iron mounts and ramrod. Complete with its bayonet (length: 51.2 [cm]) with a blade of triangular section and with marks at the base provided with leather scabbard and iron, button-shaped chape. Refer to Flayderman's Guide, 9th Edition, pages 570-571, 9A-332. Contract with Trenton by J.T. Hodge and A. M. Burton, total quantity agreed: 11.495. length 141 cm.
dating: 19th Century provenance: Solingen, Curved, single-and short false-edged blade, with fuller for a good part of its length, with remains of trophy and floral engravings at the forte, marked 'P. KNECHT / SOLINGEN' at the tang. Brass hilt with three loop-guards. Grip with long cap. Leather cover with remains of brass wire binding. Without scabbard. length 93,5 cm.
dating: First half of the 19th Century provenance: Southern Italy, Triangular, single-and-false-edged blade with slightly raised tip, central groove, carved and ribbed back, the base engraved with floral motifs. Iron knot. Horn handle with disks (missing parts), engraved brass cap and ring nut. Leather-covered wooden scabbard with smooth brass mounts. length 28 cm.
dating: Early 19th Century provenance: Austria, Round, smoothbore, 17 mm cal barrel, the base slightly squared at the sides, with a mark, front sight on the barrel bracket. Flintlock, restored hammer and pan. Full wooden stock with brass mounts and iron ramrod. With socket bayonet featuring a cruciform blade (55 cm long) and leather-covered iron scabbard. length 150 cm.
dating: late 18th Century provenance: Indopersia, Long, curved, damask (barely visible), single-edged blade with reinforced tip and wide T-shaped rear side featuring gilded carvings. Gold-inlaid base with floral motifs and a cartouche on each side featuring an Arabic inscription. Iron hilt with gold decorated frame, beautiful walrus tusk grips (a small restoration). The pommel with ring featuring a tassel . Wooden scabbard covered with burgundy velvet (completely worn) and featuring metal mounts embossed with floral motifs on a granulated background. Rare. length 47 cm.
dating: First half of the 19th Century provenance: Southern Italy, Solid, straight, double-edged blade with deep central groove and floral engravings. Carved with a hound and a lion in low relief at the base. The knot featuring a beaded ring. Horn handle with disks (missing parts) with engraved silver staves, cap and ring nut. Leather-covered wooden scabbard with brass cap, missing chape. length 31.7 cm.
dating: First half of the 19th Century provenance: France, Wide, curve, single-and false-edged blade with wide central fuller and dorsal groove. Brass one-quillon hilt with langets, grooved and ribbed loop-guard and pommel, long and smooth cap. Wooden handle covered with leather featuring metal wire binding. Leather-covered wooden scabbard (of later restoration) with brass mounts and two suspension rings. length 102 cm.
dating: 19th Century provenance: Sardinian Kingdom, Straight blade of hexagonal section, engraved with racemes and trophies at the forte, with mark of Carl Eickhorn of Solingen at the tang. Gilded brass hilt. Fretwork shell-guard in relief, featuring the Savoy eagle surmounted by a five-pointed star. The guard with fretwork and relieved elements depicting scrolls and leaves. Pommel with floral and fretwork decoration. Grip with mother-of-pearl grips. Leather scabbard with two lugs and gilded metal mounts, engraved with rocaille and floral motifs. length 94,5 cm.
dating: Early 19th Century provenance: Southern Italy, Large, straight, single-and false-edged blade with wide fuller, etched with trophies and floral motifs. Faceted, brown horn handle (small missing parts and a crack). White metal ring nut. Leather scabbard with metal hook, missing chape. length 50 cm.
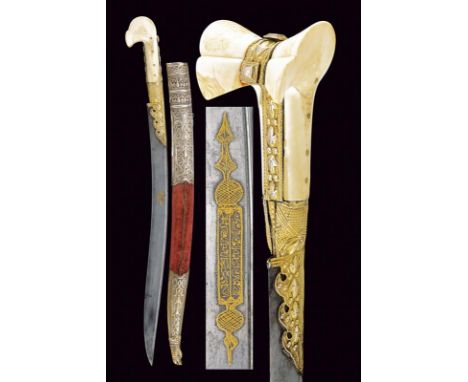
dating: First half of the 19th Century provenance: India Moghul, A beautiful, double-edged blade with four grooves, arrow-shaped fullers, with enlarged tip ribbed at the center, the base carved with an elephant's head at the centre among gold-embossed inscriptions on both sides. Hilt of typical shape; two cross-bars joined by a pierced, floral decoration. The hilt is completely decorated with gold floral and geometric motifs, the base of the handle with other gold inscriptions. The gilding with very small missing parts. Original wooden scabbard covered with burgundy velvet (completely lined and with small missing parts of wood) with remains of a belt frog and another small scabbard for a small knife and tools. Chape made of gilded, engraved and pierced bronze. A very rare weapon, almost certainly manufactured during the Reign of Maharao Raja Ram Singh of Bundi (1811-89) with Sanskrit inscription, in Bundi dialect. An almost identical katar is located at New York Metropolitan Museum (catalogue number 36.25.912).See also 'Arms & Armour of India, Nepal & Sri Lanka: Types, Decoration and Symbolism' by Reddy, Ravinder. London: Hali Publications Limited, 2018. p. 91. length 44.4 cm.
dating: Second half of the 18th Century provenance: Hungary, Curved, single-and short-false-edged blade, with wide fuller, featuring remains of engraving depicting a Turk's head followed by a long inscription (not clearly legible) on the right side; remains of engraving, even less legible, on the left side. Various pitting, especially at the tip. Brass hilt with langets featuring a rayed decoration. Straight parry quillon, stirrup guard. Long cap with rayed decoration. Handle with leather covering. Wooden scabbard with leather covering. Brass mounts decorated with rays. Two lugs. length 92 cm.
dating: Late 19th Century provenance: Burma, Solid, slightly curved, single-edged blade with central fuller and dorsal groove. With silver and copper decorations on a dark background depicting floral motifs on all its length. Typical, cylindrical, metal hilt painted in brown and with handle featuring black dots on a grey background. The cap with a 1835 British coin. Wooden scabbard in two halves held by metal-wire bands. length 79.5 cm.
dating: First half of the 19th Century provenance: Southern Italy, Both with straight, double-edged blades of hexagonal section. One carved with the Savoy coat of arms and floral decorations in bas-relief at the base. The other engraved with floral motifs. Both with horn grip (damaged) and metal mounts. The shorter one complete with leather scabbard with brass mounts. length 25.4 - 35.8 cm.
dating: 1941 provenance: Russia, Curved, single-and-false-edged blade with wide central fuller, tang with date '1941', with mark. Grip with wooden yatagan grip scales and brass ring nut, cap with 'CCCP' monogram and Soviet emblem. Leather-covered wooden scabbard (missing parts and minor defects) with brass mounts and iron bayonet. length 94.5 cm.
dating: Late 19th Century provenance: Turkey, Slightly-curved, single-edged blade with slightly enlarged back and beautiful Arabic mark on the right side. The base with silver-foil wings holding the blade finely engraved with floral motifs (small damaged parts). Silver hilt (damaged and missing parts) and brown horn grips. Beautiful, wooden scabbard completely covered in silver foil richly embossed with floral motifs, the chape shaped as a monster's head and cap with bands. Suspension ring. length 74.5 cm.
dating: Late 19th Century provenance: France, Solid, straight, double-edged blade with central rib and two grooves, areas with pitting. Partially gilded, bronze hilt decorated in relief and featuring a heraldic coat of arms at the centre on a trophy of arms. Faceted, horn handle. Bronze scabbard decorated en suite on both sides. length 28.5 cm.
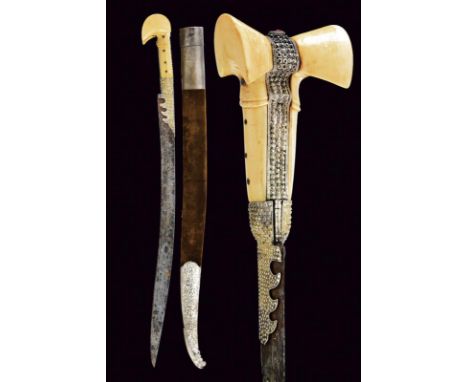
dating: Late 19th Century provenance: Caucasia, Wide and long, double-edged blade with two and four grooves at the centre, damask structure, the first part gold-inlaid with floral motifs and inscriptions, with a long axe featuring a gold point and arrow at the weak. Imposing hilt of typical shape, covered with silver foil finely engraved and nielloed with floral and geometric motifs, octagonal handle covered with silver-thread wire binding. Leather-covered wooden scabbard with silver-foil mounts decorated en suite. A rosette of the handle and a rivet of the scabbard rivet are missing. Extraordinary weapon of astonishing size. length 63.3 cm.
dating: 1864 provenance: Naples, Curved blade with double fuller towards the tip, with clearly visible engravings depicting racemes and trophies on the right side; the left side is is in slightly poorer condition, engraved with racemes and featuring an elliptical cartouche with the date and signature '1864 Napoli Labruna'. Short tang without marks. Brass hilt with wide guard featuring three thin loop-guards on the side, long smooth cap with frame engraved with laurel branches. Brown horn grip with brass wire binding. Iron scabbard with two lugs. length 92 cm.
dating: Late 19th Century provenance: Tibet, Strong, straight, single-edged blade. Hilt covered in silver foil with trefoil-shaped pommel decorated with a red cabochon stone, the grip covered with yellow metal wire binding. Scabbard with iron frame and silver foil mounts finely embossed with dragons, tigers and floral motifs and decorated with four cabochon stones. Loop on the back side. Small damages. length 58 cm.
dating: 1856 provenance: Kingdom of the Two Sicilies, Round, rifled, 17,7 mm cal. barrel, with octagonal base (bore with pitting, no longer visible rifling), with breech marked 'FRANCOTTE LIEGE', 'ED 1856', 'A', mark of the Liège test bench and various other marks, with adjustable and foldaway rear sight up to '1000', provided with clutch for the bayonet (marked '5308'). Backward spring lock signed 'A. FRANCOTTE LIEGE'; wooden, full stock with brass and iron mounts. Butt plate marked '13 C.B.C. 8. C 30' and with mark. The left side marked 'TO 1856'. Iron ramrod. Complete with its bayonet, blade marked 'V.W' and 'C', iron crossbar marked '13. B.C. 1.C. 128', with brass scabbard and mounts. length 125.5 cm.
dating: about 1620 provenance: North Italy, Made of iron, round and convex, with a raised and twisted edge, majestically embossed and engraved with a battle scene depicting horseback warriors at the foot of a hill with a fortress, sun and clouds on the background; a beautiful execution of arms and armor. The lowered edge is fully decorated with garlands and floral motifs. A row of rivets inside, with remains of the leather scabbard; leather handles fixed with brass rosettes at the center. diameter 56 cm.
-
98580 item(s)/page