We found 375892 price guide item(s) matching your search
There are 375892 lots that match your search criteria. Subscribe now to get instant access to the full price guide service.
Click here to subscribe- List
- Grid
-
375892 item(s)/page
Brothers Grimm. Snowdrop & Other Tales. London. Constable & Co. Ltd. 1920. 20 tipped in plates by Arthur Rackham, 1 detached. Spine dulled; with Kingsley, Charles. The Water Babies. Oxford University Press. C. 1929. 16 plates by A.E. Jackson, most selotaped in; with Caroll, Lewis. Alice’s Adventures in Wonderland. London. Hodder and Stoughton. c. 1920s. 12 tipped in plates by Gwynedd M. Hudson. Some pencil scribbling in the text. Shabby; with J.M. Barries. Peter Pan and Wendy. London. Hodder & Stoughton. c. 1920s. 12 tipped in plates by Mabel Lucie Attwell. Foxing, shaken; with a further 11 illustrated titles; 6 works by A.A. Milne and 2 other books. WAF. (c. 20).
WWI framed Death plaque, together with a pair of the War and Victory medals, presented to M. B. 623. Archibald Allan. C.M.M. R.N.V.R, together his original paperwork and photographs. Archibald Allan, Chief Motor Mechanic of the H.M.S Satellite during the 3rd December-31st December 1916 who was based in the London division and lost his life in Runswick Bay, Whitby.
Masudaya, Japan (TM), battery operated Space Tank, M-18, finished in metallic blue with litho printed detailing, dome cockpit with seated spaceman driver, antena with rear lights surrounded by spring style attachments, opening rear hatch for access to battery compartment, in original card box, operation un-tested. Overall condition is good, showing little wear and tear and no repairs.Slight dent to front left side – see pictureRear red bulb brokenThe box is complete, but does have splits to sides. Please see additional pictures added to the listing.
Children’s Books. Brent-Dyer, Elinor M. Eustacia Goes to the Chalet School. London. W & R Chambers Ltd. 1st edition 1930. 4 plates by Nina K. Brisley. Torn dust wrapper; with Sewell, Anna. Black Beauty. London. Ward, Lock & Co. Ltd. Reprint 1956. 24 plates by Lionel Edwards. Torn dust wrapper; with 31 further books (33)
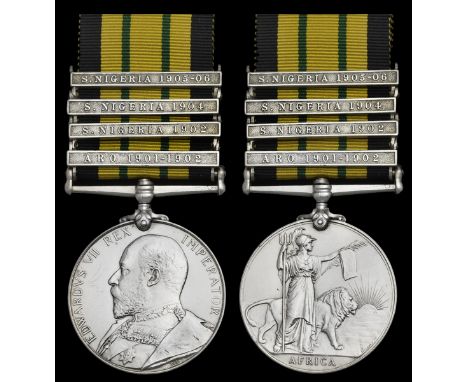
The 24th (2nd Warwickshire) Regiment of FootThe exploits of both Battalions of the 24th Foot during the Zulu War need little introduction. They are perhaps the most storied of all regiments to set foot in South Africa during 1877-79. Scores of worthy titles are recommended, with The Washing of the Spears perhaps a good place to start for one with a new-found enthusiasm.The Zulu War Medal awarded to Private J. M. Meredith, 1st Battalion, 24th (2nd Warwickshire) Regiment of Foot, who was killed in action at the disastrous Battle of Isandlwana on 22 January 1879South Africa 1877-79, 1 clasp, 1879 (293. Pte. J. Meredith. 1-24th. Foot.), rod perhaps tightened at some point, very fineJohn Henry Meredith was born at Rhosyoside, Ruabon, Denbighshire on 27 December 1854, son of Henry and Ann, his father being the local tailor. Young Meredith enlisted at Manchester, Lancashire on 17 June 1874, aged 19 years. He served with 'H' Company and was killed in action at Isandhlwana on 22 January 1879, with his effects, to include the Medal & clasp '1879' were claimed by his father.Both Battalions of the 24th participated in the campaign (each fielding six companies) with the 1st Battalion forming the principal element of Number Three Column, which was under the overall command of Colonel Richard Glyn of the 1st/24th: therefore Brevet Lieutenant-Colonel Henry Pulleine was appointed to command in his stead.Upon crossing the Buffalo River on 11 January, the column (accompanied by the Commander-in-Chief, General the Lord Chelmsford) found itself pitching camp nine days' later at the base of a prominent feature - the hill at Isandlwana. Chelmsford, eager to bring the campaign to a swift conclusion, departed at dawn on 22 January with half the column's strength (some 2,800 men) leaving behind Pulleine with approximately 1,300 men - five companies of the 1st/24th, one company of the 2nd/24th, 700 men of the Natal Native Contingent, two 7-pdr artillery pieces and a rocket battery.Failing to take any defensive measures to secure the camp, Pulleine's force was subsequently surprised by a vast Zulu army totalling some 20,000 warriors which, by additionally using the terrain to their advantage, swept forward to the attack using their traditional 'Horns of the Buffalo' strategy - a central advance supported by encircling forces on both flanks. Pulleine deployed the 24th Foot some way in advance of the camp in an extended firing line, aiming to subdue the Zulus with superior firepower - the young Meredith must have been one of those men in the line; what he likely thought and felt at that moment defies description.For at least an hour, the British held the Zulu warriors at bay, inflicting significant casualties with their powerful Martini-Henry rifles and aided by support from the two 7-pdr guns from N/5 Battery Royal Artillery. However, as the mounted force (commanded by Colonel Anthony Durnford) began to withdraw in the face of mounting numbers of Zulus, this exposed the right flank of the British infantry firing-line; G Company (2nd/24th) was swiftly overrun and the remainder also began a withdrawal, loading and firing as they went, back towards the camp. However, by this point the Zulu encirclement of the position had almost been completed and the remains of the British force were left with no option but to either try to fight their way out or fight to the death - the result has subsequently been recorded as one of the most famous 'Last Stands' in British military history, immortalised in paintings, books, and the 1979 major motion picture 'Zulu Dawn' starring Peter O'Toole and Denholm Elliot amongst many other household names.Of the 1,800 men at Isandlwana over 1,300 of them were killed; the bodies of the slain were afterward buried in mass graves on the battlefield, their last resting places still marked to this day by white-painted stone cairns; Private Meredith is amongst them.In July 2001, DNW sold another Medal (bearing both initials but the incorrect '1878-8-9' clasp) to this man. This Medal was inspected by John Hayward in April 2006 and the assumption that a duplicate must have been made at some time. This Medal was considered entirely as issued.…
Seven: Warrant Officer Class 2 M. McDonald, 3rd (The King's Own) Hussars, late 'B' Company, Kildare Battalion, Irish Republican ArmyIreland, Free State, General Service Medal 1917-21, with top riband bar and in box of issue, this inscribed in ink 'Presented to Michael McDonald, Golden Falls for War of Independence, with forwarding slip; United Kingdom, 1939-45 Star; Africa Star, clasp, 8th Army; Italy Star; Defence and War Medals 1939-45; Army L.S. & G.C., G.VI.R., Regular Army (7882816 W.O.Cl.2 M. McDonald. 3H.), good very fine (7)Michael McDonald was born on 24 February 1903 and was living at Golden Falls, Ballymore Eustace, Kildare. During the War of Independence he served in 'B' Company, Kildare Battalion, Irish Republican Army under Thomas Lawlor, Arthur Doran, Martin O'Neill and James McGrath. McDonald was duly issued with his Medal in August 1952.He has the highly unusual record of having served with distinction in the British Army from April 1939-November 1949. During that time the 3rd Hussars fought in North Africa from 1940-41. Having then split into two Squadrons, one was captured in its entirety on Java by the Japanese in 1942, but the other - with McDonald no doubt present - shared in the breakthrough at El Alamein in 1942. These events left it so short of men that it was transferred to Syria and Lebanon until April 1944, when it joined the Italian campaign.Sold together with a German Fuhrer Kompass 38 (Fk. 38), numbered P21113, by Ludolph Bremerhaven, captured by McDonald from a downed Luftwaffe from the Western Desert.…
A rare campaign group of four awarded to Engine Room Artificer Class I H. T. Johnson, Royal Navy, who was taken prisoner of war with H.M.S. Seal, the only British submarine surrendered to the enemy during the Second World WarInterned at Marlag Camp he joined several others - including 'Tubby' Lister of Colditz fame - in digging an escape tunnel: Johnson actually made it out of the camp but was re-captured soon after1939-45 Star; Atlantic Star; War Medal 1939-45; Royal Navy L.S. & G.C., G.V.R. (M.36487 H.T. Johnson. E.A.1. H.M.S. Pembroke.), some polishing and contact marks, overall very fine (4)Henry Thomas Johnson was born at Sheerness on 4 May 1900, the son of Thomas and Florence Johnson of 67 Richmond Street, Marine Town, Sheerness. Joining the Royal Air Force as a Flying Cadet on 15 July 1918 he received no medal entitlement with them. Instead he enlisted with the Royal Navy on 4 May 1923 as Engine Room Artificer Class IV with his R.A.F. service of 176 days being carried towards his pension.Joining at Vernon on 4 May 1922 his first service afloat was with the light cruiser H.M.S. Dunedin on 19 May 1922. Appointed Engine Room Artificer Class II with Cumberland on 4 May 1928 and further advanced Engine Room Artificer Class I whilst ashore on 4 May 1933. Johnson transferred to submarine service with Dolphine on 9 June and served with a number of vessels throughout the late 30s.He was posted to the crew of Seal on 1 January 1939 not long after she was launched. This Grampus-class mine-laying submarine carried a compliment of 60 men and 50 mines as well as torpedoes and a 4-inch deck gun. When the Second World War broke out Seal was enroute to China however she was detained at Aden and launched several patrols in the area.Returning to Britain they were patrolling Norwegian waters when Germany invaded and infiltrated Stavangerfjord entering the port of Stavanger. Despite the boldness of the operation it produced few results as the harbour contained no German craft with a deep enough draft to attack with torpedoes. She returned to Britain for a brief refit before setting off back to Norway to undertake Operation DF 7.They set out of for the Kattegat Sea between Norway, Denmark and Sweden, on 29 April 1940. She had a narrow escape from a Heinkel seaplane but reached the area of operations in good time and completed her mission. As they turned for home they discovered a flotilla of anti-submarine patrol ships ahead of them, with armed trawlers behind them as well. Diving to avoid the enemy the submarine was unable to run deep owning to the shallow depth of the Kattegat Sea, instead they undertook a zig-zag pattern before settling at the bottom of the sea.Tragically they had entered a minefield and the cable from one of the mines had become caught on one of Seal's hydroplanes. The mine was pulled into the ship and detonated against the hull, causing serious damage. When the dust had settled the situation was grim, the boat had shifted ten degrees upwards due to the amount of water they had taken on, however the enemy warships had failed to notice the explosion and they left the area.Repeated attempts were made to surface as soon as it was safe however all failed, eventually they dropped their 'drop keel', making it impossible for them to dive again if they made the surface. The pressure of the situation, combined with the worsening quality of the air caused a great deal of pressure all around, Johnson however was not one to be put out by stress, as is made clear in Will Not We Fear which states:'Throughout the boat men were apathetically accepting the inevitability of death. There really seemed to be nothing left, no other possibility to be worth while trying. And in these circumstances there could be recourse only to humour and to idiosyncrasy and to routine.The petty officers' mess was the scene of a surprising amount of activity. Electrical Artificer Johnstone [SIC] began removing first the sleeves and then the trousers of his overall suit. "What the hell are you doing, Johnno?" he was asked. "Changing into my Number Ones," he replied. And as soon as he had laboriously dressed himself in his best suit he hoisted himself into his bunk and relaxed… and wait'Eventually after over a day beneath the waves they managed to refloat Seal, the crew were exhausted and light headed after the stress and oxygen depravation of the day. Making for Swedish waters the submarine came under attack by German aircraft, at this moment one of their engines failed, leaving them becalmed. The two Lewis guns they brought to the deck for protection both jammed and- under increasingly accurate fire- they were forced to surrender.Seal was the only British Submarine to strike her colours during the war, her crew were taken initially to Stalag XXA, Thorn. Soon afterwards a new camp was completed for Naval personnel called Marlag XB, attached to Stalag 10B. From there they were transferred again to Marlag und Milag Nord, here Johnson was involved in an escape attempt, as outlined in Fatal Ascent:'Lister and Johnson, Seal ratings, with Hammond of the submarine Shark and eleven others, including Lt. Trevor Beet, participated in a tunnel escape from Marlag at Sandbostel. Once they were on the outside, everybody split up, but they did not get very far before they were nabbed by guards.'His two companions, Lister and Hammond, were taken to Colditz as a result of their attempt however Johnson seems to have remained at Marlag und Milag Nord.'"After Tubby Lister and his pal Johnson got caught," commented Mickey Reynolds, "there was hell to pay, but we didn't mind, as we knew we were doing our little bit to keep Jerry occupied." Usually, the escapers and helpers were put in solitary confinement with bread and water for a few days following the Geneva Convention.'(IBID)Johnson was repatriated on 19 May 1945 and discharged to the reserve that same year. He served in the Sheerness Dockyard Smithy and lived at "Dunedin", 9 Century Road, Rainham. Johnson died at Kent County Hospital, Chatham in 1976; sold together with a copy of Fatal Ascent and Will Not We Fear along with copied service papers.…
South Africa 1877-79, 1 clasp, 1879 (14135, Sapper M. A. Ardron, R.E.), good very fineServed in 5th Company, who had in its number a Lieutenant by the name John Rouse Merriott Chard. That Lieutenant rather distinguished himself - and the Corps - at Rorke's Drift in winning his Victoria Cross.…
Chinese Imperial Maritime Customs Service cap Badge, 32mm x 65mm, two lugs to reverse, depicting two dragons either side of a shield with characters, flaming sun above, with 'I. M. Customs' below, very fineThe Imperial Maritime Customs Service was founded in 1854, their badges were produced by J. R. Gaunt, London.…
South Africa 1877-79, 1 clasp, 1879 (Pte. S. Barnett. C. M. Rifles.), very fineSamuel Barnett was born in 1853 and served in the Cape Mounted Rifles from June 1878-July 1881. During this period he served on campaign and was put into the Defaulters' Book on several occasions. The unit shared in the attacks on Moirosi's Mountain, when Sergeant Scott & Trooper Brown each won the Victoria Cross on 8 April 1879 and Surgeon Major Hartley on 5 June 1879. Barnett was probably present on these days.His Medal was issued to him when living at 10 West 20th Street, New York in December 1882.…
An excellent 'Burma 1944' M.M. awarded to Sapper J. Ghag, Bombay Sappers and Miners Group, Indian Engineer Corps, who was extremely unlucky to have his award downgraded from the I.D.S.M.Military Medal, G.VI.R. (53241 Spr. Jaising Ghag Bombay S & M G R I E), heavy contact marks, very fineM.M. London Gazette 16 November 1944, the original recommendation states:'At Phalbung near Palel on the 25th of April 1944 No. 53241 Sapper Jaising Ghag was a member of a Patrol- Part of the patrol- was surrounded in open ground by the enemy- Jemadar Bajrang Kale with four men, including Sapper Jaising Ghag, were detailed to give covering fire to the remainder whilst they escaped. The Jemadar and his party then found themselves cut off so they had to withdraw by another route which was blocked by a party of Japanese. Without hesitation they charged again but being outnumbered were all overpowered and left for dead- Jemadar Bajrang Kale was killed by the sword of a Japanese officer. Sapper Jaising Ghag received a blow from a sword which cut the back of his neck from ear to ear severing the muscle and bone from the back of his skull and leaving it hanging loose down his back. After about two days Sapper Jaising Ghag, recovering consciousness found himself lying amongst a number of dead Japanese, without his boots and part of his clothing. He took some boots off a dead Japanese and searching the bodies obtained a valuable identification. After five days, during which time he was without food, he met a Gurkha Patrol which brought him in.By his gallant action and devotion to duty Sapper Jaising Ghag not only helped to kill several Japanese but also brought in a valuable identification which was the object of the Patrol.'Jaising Ghag was serving with No. 402 (R.B.) Indian Field Company, Indian Engineers when he won his award, attached to 80 Brigade, 20th Division. He was recommended for the I.D.S.M. but was downgraded to the M.M.; sold together with copied research.…
Sold by Order of a Direct DescendantThe unique and superbly well-documented 'Far East Communication Squadron 1950' A.F.M. group of seven awarded to Master Signaller J. B. C. Browne, Royal Air Force, who was awarded his Nuclear Test Medal for the 'Christmas Airways' flights to Christmas Island during Operation GrappleBrowne's remarkable career saw him flying during the Second World War, earning his A.F.M. in the east for flights which included missions to China redacted from his service papers and flying the Royal Couple during their 1961 Royal Tour of NepalAir Force Medal, G.VI.R. (571907 Sig. I. J. B. C. Browne. R.A.F.); 1939-45 Star; Defence and War Medals 1939-45; General Service 1918-62, 2 clasps, Malaya, Arabian Peninsula (571907 Sig. I.A. J. B. C. Browne. R.A.F.), the second detached in its named box of issue; Royal Air Force L.S. & G.C., E.II.R. (M. Sig. J. B.C. Browne. (571907) R.A.F.); Nuclear Test Medal, unnamed as issued, the first six mounted as worn, the last in its named box of issue, sold together with a large archive including the recipient's flying log books, minor contact wear to sixth, overall good very fine (7)A.F.M. London Gazette 8 June 1950, the original recommendation states:'Signaller I Browne joined the Squadron in October, 1948, having been in Japan from October, 1947, and has been employed as a V.I.P. Signaller. He is a first class non-commissioned officer with exceptional technical ability, having consistently held an 'A' category since August, 1946. During the last six months he has completed 300 flying hours on some of the most important flights assigned to this Squadron, and he has also extended his 'A' category to cover York aircraft as well as the Dakota, the type in which he is primarily signaller and, on numerous long distance flights during his tour of duty in the Far East Communication Squadron, he has carried out his duties in an exemplary manner. He has shown ability, coolness and enthusiasm and is an outstanding non-commissioned officer.'Note the Recipient's Flying Log Book for the period of 1947-1952 is missing, it is believed to have been recalled owning to a redacted mission in China rather than misplaced or lost.John Blake Cameron Browne (who later changed his surname to Howard) was born in Kensington, London on 19 February 1922, the son of Andrew and Wilhelmina 'Billy' Browne. His father was a former professional soldier who served as a Sergeant-Major with the Essex Regiment and was seriously wounded in the leg at Gallipoli. He appears to have suffered from post-traumatic stress disorder and left the family in 1929 leaving his wife to raise the children herself. The young Browne received only a basic education however this was enough for him to pass the entrance tests for an apprenticeship at R.A.F. Halton on 24 August 1937.He was initially posted to the Electrical and Wireless School before transferring to No. 2 Wireless School on 26 March 1938. He must have proven himself a quick learner as he was soon selected to leave Halton for Cranwell, where he specialised as a Signaller. He was still there on the outbreak of the Second World War on 3 September 1940, they spent the day dispersing the aircraft around the perimeter of the airfield in case of air raids.The Second World WarQualifying as Wireless Electrical Mechanic on 29 January 1940, Browne reached his majority the next month on 19 February and was appointed Aircraftman Class I the same day. Posted first to No. 29 Squadron and advanced Leading Aircraftman on 1 April 1940 he served with them at R.A.F. Digby. Here he was on the receiving end of several bombing raids, being promoted Corporal on 31 December 1940. The Squadron re-equipped with Bristol Beaufighters to replace their old Blenheims not long later.Transferring to R.A.F. Pembury he undertook an air gunner's course, becoming qualified on 6 January 1943 and advanced Sergeant on 7 January. Joining No. 10 Radio School Carew Cheriton, he served there until 17 February 1943 when he was posted to Coastal Command's 131 Operational Training Unit which was located on Loch Erne in Northern Ireland. There he had his first flight on a Catalina flying boat on 18 February.Having qualified, Browne was posted to the newly formed 265 Squadron based in Northern Madagascar. After a gruelling journey across Africa, he finally reached the posting in early June and began to undertake fleet escort and search and rescue missions as Wireless Operator/Air Gunner. Racking up increasing Operational flying time in December he had 250 hours and was advanced Flight Sergeant on 6 January 1944.Over the next year he was to continue in this role, adding Meteorological Flights to his duties. The last of Browne's wartime flying was with 265 Squadron having undertaken 562 hours of Operational flight with them and an impressive 1076 hours in total. Posted to R.A.F. Wymeswold on 5 May 1945, he arrived on 8 May - V.E. Day - to discover the station all but deserted, the guard on the front gate informed him that everyone was celebrating in the pub.V.I.P. Flying, a Redacted Mission and a Crash LandingBrowne retrained with Douglas Dakotas and was soon posted to 147 Squadron, flying for Transport Command. This Squadron flew from Britain to Europe allowing Browne to assemble a collection of European banknotes which he stuck into his log books.Joining 24 Squadron for V.I.P. transport flights in October 1946 he was posted to the British Commonwealth Air Force in Japan the following year. The next year Browne again moved, this time to the Far East Communications Squadron. Two months after he joined them a period of one week on his service records is redacted, this combined with his missing log book covering this period is suggestive of a clandestine mission. The cataloguer must leave it to the reader to imagine the nature of this work however it occurred at a time that Browne was known to have been flying to China, then embroiled in the Civil War.Returning to Britain in April 1950 he was awarded the Air Force Medal at R.A.F. North Luffenham for his work with the Far East Communication Squadron. His work there had also entitled him to the Malaya bar for his General Service Medal however this would not be issued at the time and Browne was to receive the G.S.M. for a separate campaign. Joining 242 Operational Conversion Unit as a Trainer and he was recommended a Commission at that point however he rejected the offer, feeling that he preferred his role as a Warrant Officer.Returning to No. 24 Squadron on 6 December 1953 he rang in the new year with a promotion to Master Signaller on 31 December. One of his early flights here on 22 May 1954 was transporting Anthony Eden (then Foreign Secretary) and Lord Ismay (then Secretary General of Nato) from Geneva to Paris and thence to Britain. A further flight in July almost led to disaster as the crew lost their way between Suffield, Alberta and Britain. An S.O.S. signal was sent out and after a tense period of waiting were picked up by a passing liner which was able to give them their co-ordinates, with their available fuel they were just able to make an emergency stop at the Azores Islands.That same year he performed trips to Australia which included the transport of material and personnel involved in the developing Nuclear programme. During one routine training mission the next year out of R.A.F. Abingdon the Hastings aircraft Browne was flying in crashed on landing. Fortunately the crew were all unharmed although the aircraft itself lost a wing. The next year he transferred to No. 47 Squadron flying mostly to the Middle East, Cyprus and Malta.Christmas Island Airways and Operation GrappleBrowne had alr…
Maharajpoor Star 1843 (Private George Walker H. M. 16th Lancers), fitted with contemporary ornate suspension featuring dual sabres and crown, riband buckle, very fineGeorge Walker was born in St. James, Dublin in 1810 and attested with the 16th Lancers at London on 10 July 1830 at the age of twenty, after having made his living as a labourer. Walker was to serve abroad in the East Indies for 21 years of what was to become a 23-year career in the service.Walker was promoted Corporal five years after entering the service and then to Sergeant three years later. However, he was not to retain this rank for long as he was reduced to Private in August 1843 following his sentencing by court martial for drunkenness. He was advanced Corporal once again in July 1844 and in this rank transferred to the 3rd Light Dragoons on 1 December 1845. He was made Sergeant in March 1847 before again being court martialled for drunkenness and reduced to Private just four months later in July.Despite these repeated instances of drunken behaviour, Walker again found himself promoted to Corporal in March 1850, and this time managed to hang on to the rank. He volunteered for the 9th Lancers on 1 November 1852 and served with them as Corporal for the remainder of his time with the Colours. Walker was discharged at Umballa on 30 September 1853, being found medically unfit for further service resulting from his length of service and the harsh climate. His discharge papers make note of the impressive breadth and experience of Walker's long service. He served for the whole length of the First Afghan War with the 16th Lancers, including the assault and capture of Ghuznee, and then went on to serve at Maharajpoor in December 1843. Walker was then an active participant in the Second Anglo-Sikh War as part of the 3rd Light Dragoons, and was engaged at the Battle of Ramnagar, the passage of the Chenab River, as well as the actions at Sadoolapore, Chilianwala, and Goojerat in 1848-49.Walker would have likely been further entitled to a Ghuznee Medal 1939 and a Punjab Medal 1848-49 with clasps for Goojerat and Chilianwala; sold together with copied research.…
A rare post-war K.P.M. for Gallantry awarded to Constable 1st Class E. B. O'Regan, New South Wales Police Force, who was shot while confronting armed robbersKing's Police and Fire Services Medal, for Gallantry, G.VI.R., 1st issue (Const. 1/Cl. Edward B. O'Regan, N.S.W. Police Force), in its Royal Mint case of issue, official naming on pre-prepared ground, extremely fineK.P.M. London Gazette 29 August 1947.Edward Bernard O'Regan was born on 15 August 1916 and joined the New South Walers Police Force as a Constable in July 1939. A native of Lithgow in N.S.W., he was described on his enlistment papers as standing at 6.1 feet and weighing nearly 12 stone.By the time of his K.P.M.-winning exploits in May 1946, he was still serving as a Constable, but he was about to receive accelerated promotion to Constable 1st Class. And of those gallant deeds, his service record states:'Specially commended for the very fine policeman ship and conspicuous bravery displayed when, in company with Constable A. E. Gilchrist, the arrest was affected of an armed bandit, M. J. Delaney, at Harris Park on 23 May 1946, and also in connection with the attempted apprehension of two offenders who were disturbed when about to break into the Cabramatta Post Office at 2 a.m. on 30 May 1946. Promoted to Constable 1st Class as on, from 23 May 1946, and submission made for the award of the King's Police and Fire Services Medal 'for Gallantry' in accordance with the recommendation of the appraisement committee.'Of the incident at Cabramatta - and under the headline 'Two More Police Shot; Big Manhunt' - a local newspaper takes up the story:'The men shot were detectives Regan and Gilchrist. They disturbed the men at the back of Cabramatta Post Office. The men fired shots and wounded both detectives. The wounds were not serious.The men ran across to a black sedan car, in which they drove off at high speed towards Fairfield. All police cars in the metropolitan area were posted to a search for the sedan. Detectives were called from their beds in all parts of the metropolitan area.Detectives Regan and Gilchrist, though wounded, joined in the hunt. Later, however, both detectives had to abandon the hunt and seek treatment at Parramatta Hospital. Regan was shot in the thigh, but the nature of Gilchrist's injuries were not known at 3 a.m. today.The sedan in which the men made their getaway was stolen in Newtown earlier in the night.One of the men was wearing a blue suit. A pocket was torn from his coat during a struggle with the detectives.Three detectives have been shot in two days. On Tuesday night Detective Sergeant Wilson was shot while in plain clothes room of Darlinghurst Police Station.'O'Regan, who was duly recommended for the K.P.M. for Gallantry, resigned from the N.S.W. Police Force in August 1947. He died at Parramatta in July 1967; sold with copied service record and newspaper reports.…
A scarce Boer War Militia Officer's D.S.O. group of four awarded to Major M. A. Foster, 4th Battalion, Somerset Light Infantry, who was further twice 'mentioned'Distinguished Service Order, V.R., silver-gilt and enamel, with integral top riband bar; Jubilee 1897, silver, unnamed as issued; Queen's South Africa 1899-1902, 1 clasp, Cape Colony (Capt. & Adjt. M. A. Foster, D.S.O., Som. L.I.), unit officially corrected to include post-nominals; King's South Africa 1901-02, 2 clasps, South Africa 1901, South Africa 1902 (Maj. & Adjt. M. A. Foster. D.S.O., Som. L.I.), the last three mounted as worn in this order, minor enamel damage to D.S.O. and contact wear overall, very fine (4)Provenance:Noonans, June 2012.Spink, July 2018; April 2023.D.S.O. London Gazette 27 September 1901.M.I.D. London Gazette 10 September 1901, 29 July 1902.Montagu Amos Foster was born on 19 March 1861, the son of William Foster of Wilbury Road, Brighton, Sussex. Foster was privately educated and became a notable linguist over the course of his life. Commissioned Second Lieutenant in the Second East Norfolk (Militia) on 10 December 1879, he was gazetted to a regular commission with the Somerset Light Infantry on 28 January 1882, with the rank of Lieutenant. Promoted Captain in September 1887, he served as an Adjutant in the Militia from May 1899 until February 1904.Foster also returned to the Militia, serving as Captain and Adjutant with the 4th Battalion, Somerset Light Infantry. It was with this role that he appears upon the roll for the Jubilee Medal. Later entering the Boer War, with the Battalion sailing on the Kildonan Castle in Spring 1900, upon arrival they were split up with the majority of the unit divided along the lines of communication between East London and Queenstown, Cape Colony, while some officers were detached to the Staff. Foster's role would likely have been with one of the mobile columns that operated in the region hunting down the Boer Commandos - a role for which he was further 'mentioned' twice on 10 September 1901 and 29 July 1902.Foster certainly came home to receive his D.S.O. in an investiture on 29 October 1901, however, he returned to South Africa, being promoted Major in April 1902 and is listed as stationed there until 13 May. Seeing further service in the East Indies between 1902 and April 1904, Foster returned to Britain on 16 April and served at home until March 1909 when he was placed upon the retired list. Foster had married Ida Frances, the daughter of Brigadier-General W. G. Thompson, C.M.G., D.S.O. and had two children with her, Mary and Cecil William Foster; sold together with copied research comprising a C.D. containing research and photographs, a copied caricature and career summery as well as a Record of Service, medal rolls and extracts from the London Gazette and West Somerset Free Press.…
The 'Tail End Charlie's' D.F.M. group of six awarded to Sergeant R. A. Norcross, Royal Air Force Volunteer Reserve, who downed a FW.109 over HungaryDistinguished Flying Medal, G.VI.R. (1589610 Sgt. R. A. Norcross. R.A.F.); 1939-45 Star; Africa Star; Italy Star; Defence and War Medals 1939-45, mounted court-style for wear, minor pitting, very fine (6)D.F.M. London Gazette 7 July 1944, the original recommendation states:'Sergeant Norcross was posted to this unit in November 1943, and has completed 20 Operational sorties over Italy, Yugo Slavia, Austria and Bulgaria.2. Sergeant Norcross is the rear gunner in a crew which has already carried out many successful operational sorties, and has achieved a high standard of crew co-operation. He is a keen and efficient Air Gunner, and had the complete confidence of his captain and the other members of the crew.3. On the night of 3rd April 1944, Sergeant Norcross had an opportunity of proving his alertness and efficiency when his aircraft had been ordered to attack the [M]anfred Weiss Works at Budapest. Shortly after leaving the target, two enemy aircraft were encountered. One of these aircraft, identified as a FW.190, fired a short burst of tracer at the Wellington, which turned to starboard. The enemy aircraft then continued its course, and passed approximately 20 feet under the Wellington's port Wing. Sergeant Norcross had been told over the intercom. that the FW.190 was "coming up on port at 300 yards 8 o'clock". He fired a three second burst with the FW.190 dead in his sights, and saw it burst into a blue white flame, descending then in a vertical dive. Several other Wellington crews saw the enemy aircraft crash, and Group have officially admitted the claim of one FW.190 destroyed.4. The above incident well illustrates the alertness and efficiency which Sergeant Norcross has displayed in all his operations. His action was typical of the manner in which he invariably carries out his work, and it is submitted that he well deserves the immediate recognition, which is strongly recommended.'Ronald Albert Norcross was serving with No. 37 Squadron based in Southern Italy when he won his award. They completed a number of missions from that region, notably helping to supply the Yugoslavian Partisans resisting German occupation and disrupting their supply routes to the Eastern Front.He was notably present on a raid on 20 January 1944 over the Cecina Railway Bridge in Tuscany. The raid was largely successful except for Norcross' own aircraft, commanded by Flying Officer Stanton, the Squadron Operations book notes:'F/O Stanton in "V" collided with another aircraft ("A" - F/Sgt. Kelly) over the target area but neither aircraft sustained very serious damage.'Despite this Norcross's Wellington found the bombing mechanism damaged, leaving them unable to complete the attack. During the attack over the Manfried Weiss works several months later fifteen Wellington's targeted Budapest to good effect but encountered heavy resistance as the Operations Book makes clear, stating:'The target was well defended, both from the ground and in the air, and moderate to intense H.A.A., and intense L.A.A., with "flaming onions" and 15-20 searchlights were reported. Several enemy fighters were seen in the target area, and one aircraft, captained by F/O Stanton, shot down a FW.190 over the target.'The official recommendation was seconded by The Officer Commanding No. 231 Wing who added his own opinion, stating:'I consider that the coolness and courage displayed by this N.C.O. was largely responsible not only for the destruction of an enemy aircraft but also for his own crew's and the aircraft's safe return to base.'Sold together with copied research.…
The highly emotive Great War M.C., D.F.C. group of five awarded to Captain L. M. Woodhouse, Royal Flying Corps, late Essex YeomanryHe had been forced to write to his father with the excruciating news that his younger brother 'Mole' had been killed attempting to come to his aid in an aerial combat in August 1917; the elder Woodhouse was then himself shot down and killed in action a year laterMilitary Cross, G.V.R., the reverse engraved ‘Awarded 3rd July 1917 1st Battle of Somme. Lieut. Lionel Mostyn Woodhouse, R.F.C., 52nd Squadron’; Distinguished Flying Cross, G.V.R., the reverse engraved ‘Awarded 17th Sept. 1918. Capt. Lionel Mostyn Woodhouse M.C., R.A.F.’; British War and Victory Medals (Capt. L. M. Woodhouse, R.A.F.); Great War Bronze Memorial Plaque (Lionel Mostyn Woodhouse); Great War Memorial Scroll in the name of ‘Capt. Lionel Mostyne Woodhouse, M.C., D.F.C. [red ink] 59th Sqdn. Royal Air Force [blue ink], good very fine (Lot)Provenance:Glendining's, March 1990.M.C. London Gazette 25 August 1917. The original citation states:'For good work. This Officer has done splendid work whilst observing for Artillery. He Observed for over 2,000 rounds during the month of May 1917, of which 121 were O.K.’s. Thirteen emplacements were destroyed, eighteen explosions and six fires were caused.'D.F.C. London Gazette 2 November 1918. The original citation states:'For skill and gallantry. On the 22nd August 1918, this Officer carried out a Special Contact Patrol from a height of from 200 feet to 400 feet. He was throughout subjected to very heavy fire from the ground and his machine was badly shot about. He showed great daring during a heavy counter attack on Logeast Wood and flying at a height of 100 feet he shot up the advancing troops and rendered great assistance in bringing this attack to a standstill and causing very high casualties. He then continued his patrol along the whole Corps front. Throughout the recent operations he has set a very good example of courage and devotion to duty to the whole Squadron.'Lionel Mostyn Woodhouse - or Lio to his friends and comrades - was born at Brooklands, Broomfield, Essex on 10 December 1896. Educated at St. Peter’s Court, Broadstairs and Eton College from 1909-14, he joined Eton O.T.C. as a Private. Whilst at Eton, Woodhouse was in R. S. de Havilland's House, playing in the Cricket XI in 1914.With the outbreak of the Great War, he was appointed 2nd Lieutenant in the 2/1st Essex Yeomanry 1 July 1915 and was seconded to the Royal Flying Corps in August 1916. He served in No. 52 Squadron from October 1916 with R.E.8’s then B.E.2e’s and then back to R.E.8’s on 15 June 1917, returned to Home Establishment on 15 August soon after his brother’s loss six days earlier.The loss of his brother was a hugely emotional event and one which was a huge blow to the entire family. Christopher Courtney wrote on 14 August 1917:'Dear Arthur,I feel I must write to you and give my most sincere and heartfelt sympathy in the loss of your boy. I was terribly shocked to hear of it, but it was some small consolation to know that he went out gallantly fighting.I wonder if your eldest son has told you that he was killed in an endeavour to protect his brother's machine from attack?He probably did not know it but there was an artillery machine being attacked and so he at once dived in order to chase off the enemy; unfortunately he was caught by several enemy scouts and shot down but he certainly succeeded in drawing them off the artillery machine in which, it afterwards turned out, was his brother.I think it was a most gallant death. I went to his funeral, a simple and straightforward one; he is buried under the shadow of the sand-dunes in a quiet and secluded spot.I feel very guilty in not having answered your letter; I am afraid I am a bad correspondent at the best of times; but I had had it in mind for some days to write and tell you that he was in a good squadron and getting on well; his Squadron Commander spoke most highly of him.'Promoted Captain on 16 September 1917, Woodhouse Instructed for a year then on 12 August 1918 he returned to No. 59 Squadron, taking command of ‘B’ Flight on R.E.8’s. On 29 August with his Observer they shot down an enemy Scout. On 1 September they were hit by A.A. but with the Observer, Lieutenant Peel holding his Lewis gun at arms length leaning over the side, managed to help steady the R.E.8 for Woodhouse to get safely back. Peel and Woodhouse’s luck ran out on 27 September 1918 when they were shot down and both lost their lives.Sold together with original letter from his brother 'Jack' on winning the D.F.C., his cloth RFC 'Wings', besides original photographs and a remarkable archive of copied letters, these of a highly emotive and unpublished nature.…
Three: Private M. Wabanoose, 52nd Battalion, Canadian Expeditionary Force, who died of wounds sustained in action on 31 August 1917, shortly after the Battle for Hill 60 - he was a First Nations Canadian from Wiikwemkong on Manitoulin IslandBritish War and Victory Medals (754976 Pte. M. Wabanoose. 52-Can. Inf.); Great War Bronze Memorial Plaque (Michael Wabanoose), good very fine (3)Michael Wabanoose was born on 5 July 1895 at Wikwemikong, Manitoulin Island, Ontaria, son of Antoine Wabanosse. Today, these lands remain a reserve of First Nations Canadians and is occupied by Ojibwa, Odawa, and Potawatomi peoples under the Council of Three Fires. A farmer by trade upon his joining the Canadian Forces in March 1916, his complexion was described as 'swarthy', he served initially with the 119th (Algoma) Battalion, who were based at Sault Ste. Marie, Ontario and took a number of the 'Manitoulin Boys' into their ranks. Sailing from Halifax on 8 August 1916, he joined the 52nd Battalion in the field in France on 4 December 1916. Wabanoose went into action in the Third Battle of Ypres and would have shared in the Battle for Hill 60. He was mortally wounded - with gunshot wounds to his arms and legs - on 26 August 1917, was admitted to 22nd Casualty Clearing Station but died on 31 August 1917. Wabanoose is buried in the Bruay Communal Cemetery Extension.…
A rare Second World War tunneller's 'Gibraltar Key' group of seven awarded to Major D. Taylor, Royal Canadian Engineers, who was subsequently killed in action in Italy in September 19441939-45 Star; Italy Star; Canadian Voluntary Service Medal 1939-45, with overseas clasp; Defence and War Medals 1939-45, silver, in their boxes of issue, together with Canadian Memorial Crosses, G.VI.R. (2), silver, both officially inscribed 'Major D. Taylor' and in their cases of issue, and Royal Canadian Engineers' Gibraltar Key award 1941-42, for use as a watch fob, the reverse officially engraved, 'Major D. Taylor', silver, by B. M. & Co., in its case of issue, extremely fine (8)Around 325 Gibraltar Key awards were issued to Canadian Engineers for their drilling and tunnelling work on the Rock during the last war, few of which appear to have survived. Struck in silver by the Wartime Mining Association in Canada - and based on a design by Sapper R. J. Cunningham, No. 2 Tunnelling Company, R.C.E. - the first awards were presented by General A. G. L. McNaughton, a fellow Canadian, at a special ceremony held on 27 March 1943.David Taylor was born in Surbiton, Surrey on 28 October 1911 but was working as a bank teller in Canada by the outbreak of hostilities. Enlisting in the Royal Canadian Engineers in Toronto in January 1940, direct from an appointment in the Militia, he was commissioned as a 2nd Lieutenant and embarked for the U.K.The RockIn November 1940, at the head of No. 1 Tunnelling Company, R.C.E. - a detachment of four officers and 99 men - Taylor arrived for duties in Gibraltar, the first Canadian troops to ever be stationed on the Rock. His sappers were to use their special skills in diamond drilling and hard-rock mining in close co-operation with the Royal Engineers, to develop and perfect the subterranean works required to bolster the Rock's defences. They arrived with 219 cases of equipment and were soon at work, the arrival of No. 2 Tunnelling Company in March 1941 adding to the valuable work undertaken by the Canadians.That work is described at length in Major George F. G. Stanley's article Canadian Tunnellers at Gibraltar, which was published in the Canadian Geographical Journal in June 1944, and a copy of which is included. But by way of eye-opening statistics, it is said that excavation work in Gibraltar in the last war amounted to shifting 1,087,905 cubic yards of rock and rubble.ItalyTaylor finally departed Gibraltar for the U.K. in early 1942, where he was posted to the Shetlands to carry out work on an old iron mine near Sollum. Having then been advanced to Major at the year's end, and taken command of No. 1 Tunnelling Company, he was embarked for Naples, Italy in January 1944.The unit then moved to Bianchi to help construct an underground Command Centre, where it was re-titled No. 1 Drilling Company, R.C.E., followed by further construction work at Taranto, Cassino and elsewhere. Tragically, however, as related in the pages of The History of the Corps of Royal Canadian Engineers, Taylor met his end in the course of subsequent operations:'On 1 September [1944] Major D. Taylor was killed while making too early a reconnaissance in Pesaro, on the Polish front. Company Sergeant-Major S. Dempster lost his life at the same time. Captain J. M. Thompson was driving their jeep; while he turned it around, Taylor and Dempster went to make a last check of the area before returning to camp and ran into an ambush. Thompson managed to avoid capture and escaped to take over command as Major. It had been understood that the town was clear of enemy and they had passed through the Polish troops on the outskirts without receiving any information to the contrary.'Taylor, who left a widow, was buried in Ancona Military Cemetery; sold with copied research, including a statement of services that credits him with a mention in despatches.…
'My dear dear Dad, I am writing to you not Mum, so that you may break it more gently to her. Poor little Mole is dead. Oh it is too awful just Nick and then my favourite brother. I saw the whole thing at the time & had a terrible feeling that it was one of our machines and not a Hun and that if that was the case it would be him. He died protecting me.They went over to attack these Huns as they came up to the line and fought for about five minutes and then one machine broke away on fire. It was the most glorious fight for life ever put up. All who saw it say the same thing, what a wonderful Pilot he must have been.He was seen to be his by his Flight Commander before the fire started and then with the machine under control brought to down from 7,000ft to 100ft in a series of side slips so keeping the flames off himself, when it then broke up.I can't give you any hope and I think perhaps it was better for him to have been killed at the finish. I have kept nothing from you and I will leave it to you to say what you feel best to Mum.He was wonderful and loved by all. It nearly kills me to write this, but we must all try and bear up.Your broken hearted son, Lio.'Captain Woodhouse writes home to his father on the death of his brother, Lieutenant M. G. 'Mole' WoodhouseThe campaign group of three awarded to Flight Sub-Lieutenant M. G. Woodhouse, Royal Naval Air Service, who was tragically killed in action on 9 August 1917, by 37-kill Ace Leutnant Julius Buckler of Jasta 17; he had gone in to combat in order that he might save his elder brother who was also in the same aerial combatBritish War and Victory Medals (Flt. S. Lt., M. G. Woodhouse, R.N.A.S.); Great War Bronze Memorial Plaque (Mosley Gordon Woodhouse); Great War Memorial Scroll in the name of ‘Flight Sub-Lt. Mosley Gordon Woodhouse, R.N.', the V.M. with officially re-impressed naming, good very fine (3)Provenance:Glendining's, March 1990.Mosley Gordon Woodhouse - or Mole/Moley to his friends and comrades - was born on 26 October 1898. The family at that time lived at ‘Tofts’, Little Baddow, Essex.Having joined the Royal Naval Air Service as a Probationary Flying Officer at Dover 5 November 1916, he was slightly injured on 2 March 1917 when in a forced landing after engine failure on Avro 504 at R.N.A.S. Redcar. Posted to No. 3 (Naval) Squadron flying Sopwith Pups, he was advanced Flight Sub-Lieutenant on 10 June 1917 and crashed on 20 June 1917. Woodhouse joined No. 12 Squadron on 25 June 1917 at Dunkirk and sent to the front with No. 9 Squadron on 30 June 1917, equipped with Sopwith Pups, and Triplanes but by 12 July were exchanged for Sopwith Camels. On 9 August, while out on Patrol with Flight Commander Simpson and Flight Sub-Lieutenant Mellersh, took part in a fight with Albatros Scouts which were attacking an R.E.8., which turned out to be Piloted by his brother. His machine was shot down in flames by Vzfw. J. Buckler of Jasta 17, as his 12 'kill' of an eventual 35.Christopher Courtney wrote to his father on 14 August 1917:'Dear Arthur,I feel I must write to you and give my most sincere and heartfelt sympathy in the loss of your boy. I was terribly shocked to hear of it, but it was some small consolation to know that he went out gallantly fighting.I wonder if your eldest son has told you that he was killed in an endeavour to protect his brother's machine from attack?He probably did not know it but there was an artillery machine being attacked and so he at once dived in order to chase off the enemy; unfortunately he was caught by several enemy scouts and shot down but he certainly succeeded in drawing them off the artillery machine in which, it afterwards turned out, was his brother.I think it was a most gallant death. I went to his funeral, a simple and straightforward one; he is buried under the shadow of the sand-dunes in a quiet and secluded spot.I feel very guilty in not having answered your letter; I am afraid I am a bad correspondent at the best of times; but I had had it in mind for some days to write and tell you that he was in a good squadron and getting on well; his Squadron Commander spoke most highly of him.'Sold together with the original - highly poignant - letter from Lio Woodhouse to his father, on the loss of 'Mole', besides forwarding letter for his campaign Medals, besides photographs and a quantity of copied research, including his Flying Log Book.…
The 'Great War' M.C. group of eight awarded to Honorary Colonel J. G. Chapple, Royal Army Ordnance Corps, later Royal Electrical and Mechanical Engineers, who served on the Western Front inspecting and repairing artillery, later becoming the Officer in Command of all Ordnance Workshops in Mesopotamia during the Iraqi Revolt, later he served in France during the 1940 campaignMilitary Cross, G.V.R.; 1914-15 Star (Lieut. I. O. M. J. G. Chapple. A.O.D.); British War and Victory Medals (Major J. G. Chapple.); General Service 1918-62, 1 clasp, Iraq (Major J. G. Chapple. R.A.O.C.); 1939-45 Star; Defence and War Medals 1939-45, mounted as worn, overall good very fine (8)Provenance:Purchased Spink Numismatic Circular, March 1979.M.C. London Gazette 4 June 1917.John Gardiner Chapple was born in Mauritius on 11 February 1886, the son of James Chapple. He was initially schooled privately before joining the Woolwich Polytechnic in 1902 and remaining there until 1910. Chapple was initially employed as an Inspector of Royal Engineers Stores, Woolwich from 1910-1914 when he undertook a course at the Royal Military Academy Woolwich and was commissioned Lieutenant (Inspector of Ordnance Machinery Class III).Entering the war in France on 30 May 1915 his application for the Institution of Mechanical Engineers lists his duties at the time which included 'Inspection & Repair of Artillery & War Material'. Advanced Captain and Inspector of Ordnance Machinery Class II he was further appointed Works Manager of the Calais Workshops.Transferred to Italy in 1917 Chapple was further advanced Major and Inspector of Ordnance Class I on 7 March 1917. It was not long after this that he was awarded the M.C., likely for his services in France prior to transferring to Italy.Chapple was confirmed in the rank of Major on 5 November 1918 and remained in the Military after the war, being appointed Officer in Command of all Ordnance Workshops in Mesopotamia from 1920. This placed him in the region as both Senior Inspector of Ordnance Machinery and Technical Advisor during the Iraqi Revolt, remaining there until 1922.Returning to Britain he was appointed back to the Royal Engineers Stores at Woolwich as a Chief Draughtsman where he was responsible for designing new stores for the War Office. Joining the Air Ministry in 1926 Chapple was working at R.A.F. Halton as the stationed Electrical and Mechanical Officer in 1926.Still serving as a Major in 1939 whilst living in Nottinghamshire he saw service in France in 1940 however did not return to the continent in 1944. Chapple was discharged having reached the age of liability on 27 September 1946 with the honorary rank of Colonel. He retired to Portsmouth where he died in April 1972; sold together with copied research.…
The campaign group of four awarded to Captain D. J. R. Simson, Royal Navy, who was killed by a German sniper on 23 May 1940 while serving aboard H.M.S. Keith at Boulogne when the port was infiltrated by German troops; he also received a posthumous 'mention'Naval General Service 1915-62, 1 clasp, Palestine 1936-1939 (Capt. D. J. R. Simson. R.N.); 1939-1945 Star; Atlantic Star; War Medal 1939-45, with M.I.D. oak leaf, these in box of issue and with named Condolence slip, extremely fine (4)M.I.D. London Gazette 27 August 1940.David James Robert Simson was born on 7 September 1892, later studying at Osborne and then Dartmouth, taking the King's Medal. He was promoted Midshipman on 15 January 1910 and served aboard Russell and Lancaster in the Mediterranean and with Lion during her first commission. Later being further advanced Sub-Lieutenant on 15 April 1913, during the Great War he served on the destroyer Acasta and battleship King George V at the Battle of Jutland.From March 1918 he first held command on Usk. Simson was promoted to Lieutenant-Commander on 15 January 1923, Commander on 30 June 1928, and between 1929-30 was the Executive Officer at the boys' training establishment at Shotley. After this time he returned to serving aboard destroyers and commanded, among other vessels, Vanquisher in the Mediterranean, Valorous in the Home Fleet, and between 1934-35 the cruiser Cumberland in China. During the Naval Review in 1935 Simson commanded Thanet before commanding Vivien and Winchelsea and from May 1936 the new destroyer Grenville. He was promoted Captain on 30 June 1936 and was later placed in command of Codrington from 24 August 1939 until 26 November and was then in charge of Keith from 15 February 1940.On 10 May 1940, the Germans launched their invasion of France and the Low Countries. That day Keith and her sister Boreas escorted the light cruisers Arethusa and Galatea as they carried bullion from the Dutch port of Ijmuiden to the United Kingdom for safe keeping. On 12 May, she returned to the Hook of Holland in the Netherlands to evacuate Allied troops. After the destroyer Whitley had to be run aground on 19 May when she was damaged by German aircraft, she was scuttled by Keith. Keith was one of three destroyers on 21 May that evacuated 468 civilians from France. Two days later she was in Boulogne-sur-Mer, loading British troops at the Gare Maritime to be evacuated and was attacked by German troops who had infiltrated the port area. Simson was shot by a sniper and several crew members and a dozen soldiers were also killed.He is commemorated on the Chatham Naval Memorial. Keith sailed for the UK immediately afterwards and was later active during Operation Dynamo. She was sunk off Dunkirk by German air attacks on the morning of 31 May 1940.Brigadier W. A. Fox-Pitt, who served as commander of the 20th Guards Brigade to defend Boulogne and was subsequently awarded a D.S.O., wrote to Simson's brother, Lieutenant-Colonel A. M. Simson on 20 August 1946:'My only means of communication with England during the battle was through H.M. Ships so that if there was no destroyer in, I was completely out of touch. The last destroyers left Boulogne during the night of the 23/24th and I was out of touch with England until H.M.S. Keith came in about 3p.m. By this time I had ordered a withdrawal into a closer perimeter round the Harbour in order to prevent the Germans getting round my northerly flank and cutting us off.I went aboard the Keith and had a conference with Simson and discussed the situation and sent off certain signals explaining the progress of the battle. I also had a very welcome cup of tea and gave one of the officers a letter to post for me in England. We were both pretty certain then that it was a waste of life to continue to hold Boulogne as my casualties were mounting pretty rapidly.However, a signal arrived while I was on board from the Prime Minister saying "You will evacuate all non military personnel (Pioneer Corps etc), the 20th Guards Brigade will fight it out". I then left the Keith and went and saw my Battalion Commanders and gave further orders for holding the town. I was away about two hours and then returned to the Keith, for further orders. While on board I received the signal telling to evacuate. As it was getting late I went ashore immediately to get my orders out and understood that the destroyers would put out and come back again after dark for the evacuation. I had only just left the ship when the air attack started and during the attack Simson was killed. The destroyers left the port as soon as they could and I continued with my arrangements for evacuation. I did not know that Simson had been killed until the destroyers came in later. Condor of the Whitshed, was then left in command of the Flotilla. Just before dark the destroyers came in again and I was told that I must evacuate immediately. This meant putting my plan in motion very quickly, but eventually all the troops were evacuated by about 2 a.m. on the 25th.My recollections of your brother are pretty vivid. I found him most helpful in concocting signals to England. He was at all times thoroughly calm and collected and very quick to grasp the situation on shore. He realised the importance of the destroyers as my only link with Dover, and I fear it may have been for this reason that he stayed in the port so long, as the destroyers were a very tempting target. I don't remember the Germans being within small arms range of the Keith at the time of the air attack, but the aircraft were machine gunning as well as dropping bombs. The real battle between the destroyers and the land targets took place later when the destroyers completely silenced the Germans for the rest of the night and I saw a German tank knocked out by one of their guns myself.'Sold together with the following archive comprising:i)The handwritten letter to Mrs Simson from Admiral Sir B. H. Ramsay, dated 25 May, written from Dover expressing his deepest sympathy upon his death.ii)Officer's bicorn hat, epaulettes and sword belt in named tin, together with Greatcoat Epaulettes.iii)Two sets of his pre-Second World War miniature medals, with riband bars.iv)Silver Oar rowing prize for the VIIIth Flotilla Officers Race 1925 H.M.S. Venturous, silver napkin ring and silver clothes brush.v)Letter to his wife and that to his brother from Fox-Pitt, besides photographs and assorted calling cards (5), newspaper cutting, Blue Lists (2), The List 1940, black armbands (2), besides a four leaf clover and lucky heather.…
'The C.O., Michael, and John had each destroyed an Me. 110, while Mac [McArthur] shot down two Junkers 87 dive-bombers. He would have got an Me. 110 also and got his sights on it, but nothing happened when he pressed his trigger. His ammunition was finished. So a very lucky Me. 110 lived to fight another day. Mac was very pleased about this fight, and certainly a bag of two for one's first action is very good. But it made him rather over-confident, and for the next few days he regarded the German Air Force rather as an organization which provided him with a little target practice and general harmless amusement. He soon learnt better!'One of numerous references to J. H. G. 'Butch' McArthur in David Crooks's wartime account of No. 609 Squadron in the Battle of Britain; Spitfire Pilot, refers.The outstanding Battle of Britain ace's immediate D.F.C. group of seven awarded to Wing Commander J. H. G. 'Butch' McArthur, Royal Canadian Air Force, late Royal Air ForceA superb airman, who had honed his flying skills in the Experimental Section of the Royal Aircraft Establishment in the lead up to hostilities, he claimed 8 confirmed 'kills' and 3 'probables' as a Flight Commander in Spitfires of No. 609 (West Riding) Squadron at the height of the Battle, on one occasion closing the range to just 10-20 yardsHis numerous combats, and those of his fellow pilots in 609 Squadron, are vividly recounted in the pages Flight Lieutenant D. M. Crook's famous wartime publication Spitfire PilotPost-war, and having served in the Royal Canadian Air Force at the time of the Korean conflict, his remarkable flying career ended in tragedy during a pleasure flight over Las Vegas in May 1961: both he and his passenger - a croupier from the famous Horseshoe Club - were killed when their aircraft inexplicably dived into the groundDistinguished Flying Cross, G.VI.R., the reverse officially dated '1940'; 1939-45 Star, clasp, Battle of Britain; Air Crew Europe Star; Defence and War Medals 1939-45; U.N. Korea 1950-54 (30386 McArthur J. H. G.), officially inscribed Canadian issue; Canadian Forces Decoration, G.VI.R., 2nd issue, the reverse of the suspension bar officially inscribed 'F/L J. H. G. McArthur', mounted as worn, good very fine (7)Provenance:Sotheby's, 6 March 1986 (Lot 628), when sold by the recipient's sister.D.F.C. London Gazette 22 October 1940:'This officer has led his flight and squadron with skill and determination. His brilliant leadership has been reflected in the high standard of morale in the flight. He has destroyed at least seven aircraft.'The original recommendation, for an immediate award which was approved by Dowding, states:'This officer has been a great asset to the Squadron since he joined it on 1 August 1940. His flying has been of the highest standard and he always leads his flight with skill and determination. On the occasions that he has led the Squadron he has displayed a sound sense of leadership and initiative. Individually he has always been keen and energetic in his desire to engage the enemy.To date he has destroyed 7 (confirmed) and 2 (unconfirmed) enemy aircraft and has severely damaged 2 others.'Covering remarks:'An outstanding fighter pilot who has now destroyed 8 enemy aircraft (confirmed) and 3 others probably, besides damaging a further 2.His brilliant and inspiring leadership has raised the morale of his flight to a very high standard since he took it over.'James Henry Gordon McArthur - or "Butch" to his friends and comrades - was born in Tynemouth on 12 February 1913 and was educated at West Jesmond Council School and Rutherford College, prior to attending the Marine School in South Shields. He subsequently found employment with the Marconi Company as a seagoing Radio Officer, in addition to obtaining certificates for Aircraft Radio Operation and Navigation.The latter qualifications led to his participation in the England to Australia 'MacRobertson Air Race' in 1934, when he flew with Captain Neville Stack, A.F.C., as his Radio-Navigator but their attempt ended in Athens - under controversial circumstances.On his return home, McArthur qualified for his Aero Certificate (No. 12614) at Redhill Aero Club in March 1935 and then teamed up with Captain T. Campbell-Black for an attempt on the London to Cape Town return record. Having flown non-stop from Hatfield to Cairo in their De Havilland Comet G-ADEF 'Boomerang', they took off for another refuelling stop in Kenya but, due to a problem with the aircraft, they were compelled to bale out north of Khartoum. Both landed safely in the desert and, on being rescued, gained membership of the famous Caterpillar Club, McArthur then being the youngest member.Brief employment as a First Officer in British Continental Airways having followed, McArthur was granted a short service commission in the Royal Air Force in May 1936. Confirmed in the rank of Pilot Officer after attending a course at R.A.F. Thornaby, he was posted to the Station Flight at Aldergrove and thence, in May 1938 to the Experimental Section at the Royal Aircraft Establishment at Farnborough as a Flying Officer and test pilot.McArthur was likewise employed on the outbreak of hostilities in September 1939 and, on being advanced to Flight Lieutenant, attended a refresher course at No. 7 O.T.U., Hawarden in July 1940. A subsequent posting to No. 238 Squadron was short-lived, however, for he was called back to Farnborough. But he continued to press for an operational posting.Battle of BritainThat wish was granted on 1 August 1940, when McArthur joined No. 609 (West Riding) Squadron, an Auxiliary Air Force unit, as a Flight Commander at Middle Wallop. Commanded by Squadron Leader H. S. Darley, D.S.O., 609 was largely manned by a pre-war class of weekend gentlemen fliers, among them Noel "Aggy" Agazarian and John Dundas; the latter's brother, Hugh, flew as wingman to Douglas Bader throughout the Battle.Over the coming weeks, on being 'scrambled' out of Middle Wallop and the satellite airfield at Warmwell, McArthur's 'brilliant leadership' of his flight - and on occasion the squadron - undoubtedly left its mark on such men. In writing to his mother in October 1940, John Dundas reported with pride that 609 was finally gaining recognition, listing McArthur's award of the D.F.C. as a case in point. He also noted that he had been given command of 'B' Flight, owing to McArthur being in hospital. More on that, later.Meanwhile, McArthur opened his operational account on 8 August 1940, when he destroyed a brace of Ju. 87s in a dogfight over the Isle of Wight-Weymouth sector. His combat report takes up the story:'…I dived on the outside of the Ju. 87 from just over 5,000 feet, fired a 7 second burst and saw him turn on his back and go into the sea. The formation then split up and I regained 4,000 feet very quickly. Height of Ju. was about 100 feet. I then dived again and gave a long burst of 10 seconds on another Ju. 87 which started to emit black smoke and dive into the sea. I then found the Me. 110. I climbed up a bit and was coming in at him from the port side and slightly above him. I turned quickly away from him and after a turn or two found myself quickly on his tail. I then found I had no more ammunition so pulled the override and hurried home … 'In Spitfire Pilot, David Crook recalls the squadron's 'bag' thus:'The C.O., Michael, and John had each destroyed an Me. 110, while Mac [McArthur] shot down two Junkers 87 dive-bombers. He would have got an Me. 110 also and got his sights on it, but nothing happened when he pressed his trigger. His ammunition was finished. So a very lucky Me. …
Three: Surgeon J. A. McMunn, Royal Horse Artillery, who latterly became Physician and Surgeon to the Royal Hospital Chelsea from 1862-96Crimea 1854-56, 1 clasp, Sebastopol (Asst. Surjn. J. M. McMunn. R. Arty.), contemporarily engraved naming; Indian Mutiny 1857-59, 2 copy clasps, Lucknow, Relief of Lucknow (Asst. Surgn. J, A, McMunn, F Tp. R. H. Arty.); Turkish Crimea 1855, Sardinian die, very fine (3)John Alexander McMunn was born on 30 October 1827 and was appointed an Assistant Surgeon in October 1853. He was present at Sebastopol in 1 Field Battery, No. 2 Captain Mercer's Company of the 8th Battalion, Royal Artillery (Medal & clasp) and thence served during the Indian Mutiny, his memorial at the Royal Hospital Chelsea stating '...with 'F' Troop R.H.A. at the Relief and Capture of Lucknow.'Returning home, he was Surgeon at the Royal Hospital from 1862 and appointed Physician and Surgeon on 4 November 1868, a position he held until 1896. McMunn died on 14 December 1899; sold together with copied research.…
A scarce 'Mohmand Operations' I.D.S.M. awarded to Subedar-Major M. Bakhsh, 3rd Battalion, 2nd Punjab Regiment, a long-served Indian officer who additionally received a 'mention' for the Loe-Agra Operations on the North-West FrontierIndian Distinguished Service Medal, G.V.R., 2nd 'Crowned Head' Type (Subdr. Maj. Maula Bakhsh, 3-2 Punjab R.), minor official correction to last initial of first name, good very fineJust 98 of this 'Crowned Head' G.V.R. type issued.I.D.S.M. G.G.O. 309 of 1936.M.I.D. G.G.O. 166 of 1936.Maula Bakhsh enlisted for service with the 3rd Battalion, 2nd Punjab Regiment on 24 May 1909 and rose steadily through the ranks during a career spanning some 27 years. He was made Jemadar in August 1918, Subedar in June 1923, and was finally promoted Subedar-Major on 12 June 1934 - this rank was the aspiration for any Indian soldier wanting to make a career out of the Army. The Subedar-Major was the most senior Indian rank in the Battalion.Bakhsh likely received his 'mention' for one of two events during the Loe-Agra Operations between 23 February-13 April 1935, either for his personal participation in a 'well arranged ambush of a sniping party' undertaken by two platoons of the 3rd Battalion, or an attack on a picquet. On the first instance, after an exceptionally detailed reconnaissance that afternoon, the same evening the troops involved (almost certainly with Subedar-Major Bakhsh) left camp to take up their positions. Official History takes up the story:'The party was in position by 2030 hours. Owing to the excessive darkness visibility was difficult beyond ten to fifteen yards.At 2245 hours a party of approximately twenty five enemy snipers came down the track immediately north of the Jindai Khwar from a westerly direction, and it transpired later that there was another party of ten following behind them. The section north of the Khwar opened fire on the leading party at a range of about five yards. This was immediately followed by rapid fire from the remainder of the ambush party. The enemy scattered and taking cover behind rocks and walls began a heavy but futile fire at close range on the ambush party. The firing ceased at 2330 hours, during which time, the enemy collected their casualties. They then moved off to the north west, making much noise and shouting abuse at each other and at the troops.The enemy losses in this successful affair were one killed and four wounded, of whome two died of their wounds. There were no casualties among the troops.' (Official History of Operations on the North-West Frontier of India 1920-1935, p. 177, refers).The second possible occasion is also worth noting in detail; the attack on Kila Hari has been described as 'one of the most ferocious and sustained attacks that was ever inflicted by tribesmen in the history of the North-West Frontier'. The night defence of the Kila Hari post in the Loe-Agra operations of the Nowshera Brigade in April 1935 by a party of the 72nd Punjabis (3/2nd Punjab Regt) is an epic - a small detachment was attacked by an unexpectedly-well-led tribal lashkar of some 1,000 Shamozais. The picquet was almost overwhelmed in the hand-to-hand fighting which involved revolvers, bayonets, stones and knives and lasted an incredible ten hours; this piquet consisted of one rifle company and a machine-gun platoon drawn from the 3/2nd Punjabis. An intelligence report, received during the afternoon of 5 April, stated that a large enemy lashkar had been sighted and was intending to launch an attack on Kila Hari Post from the east, but this report was considered unreliable and not given credence.The unexpected attack began about 7.30 p.m. when Shamozai swordsmen attempted to rush the machine-gun post. This resulted in severe hand-to-hand fighting but the tribesmen's attack, although pressed home with considerable ferocity, was beaten back. The enemy made further assaults at approximately 15-minute intervals until midnight, but all were repulsed. At about 9.30 p.m. the lower post on the ridge was heavily attacked, followed by other attacks against other posts which were also beaten off. The tribesmen surrounded the position and kept it under constant fire until just before dawn, when they withdrew. It was then confirmed that during this night attack 28 tribesmen had been killed and almost certainly a far larger number wounded.As for Bakhsh's I.D.S.M., the Official History makes no reference to any specific actions by the 3/2nd Battalion during the Mohmand operations, but it is worthy of note that this is a unique award to the Regiment for that campaign; sold together with copied service history extracts, Indian Army lists, Gazette entries, a compact disk of copied research, and official histories - also a copy of an article written by the recipient in 1936 for the Duke of Wellington's Regiment journal, 'Comrades in Arms: Friendship Between British and Indian Troops in Nowshera' (The Iron Duke, No. 35, October 1936, p. 217-218 refers).…
An outstanding posthumous Gold Al Valore Militare awarded to Commander P. Paiette, II Garibaldi Assault Brigade, a gallant Italian partisan who was Killed in Action with a German patrol in February 1944Italy, Republic, Al Valore Militare, Gold issue, silver-gilt, marked 'A-800' (Paietta Pietro (M) M. Carlo. (Vercelli) 24-2-944.), good very fineCitation states:'Organizer of the first partisan detachments in the Biella area. Commander of the Garibaldi Brigade, he bravely led his men in the bitter battles against an enemy superior in numbers and means. Always first in the fray, always present where the danger was greatest, an example and an incitement, he sustained numerous battles at the head of his unit, inflicting heavy losses on the enemy. During a reconnaissance he clashed with a German unit and although in inferior conditions he refused to surrender and with weapons in hand accepted the fight until he fell riddled with bullets. Heroic commander and passionate animator, he made his holocaust a warning and example to the people . – Monte Casto (Vercelli), 24 February 1944.'Pietro Paietta was born on 7 February 1914 in Taino. He attended middle school in Novara and found employment as an accountant in the local branch of the Stipel Company. Enlisted in 1935 in the 4th Bersaglieri Regiment of the Trento Motorized Division, mobilized for AO (East Africa) needs, he was in Libya from December 1935 until August 1936. Repatriated and discharged with the rank of Corporal Major eligible for the rank of Sergeant, he entered the Bank of Luino which he left the following year to enlist as a Volunteer in the Garibaldi International Brigade during the Civil War in Spain. Wounded and mutilated of an arm in the Battle of the Ebro on 18 March 1938, he moved to France.After the capitulation of the French army to Germany in the spring of 1941, he took part in the resistance movement as a commander of groups of francs tireurs. On 8 September 1943, having returned to Italy and taken refuge in the Biella area, he was the organiser of the first partisan groups that were later to form the II Garibaldi Assault Brigade, of which he held command. (https://www.combattentiliberazione.it/m-o-v-m-dall8-settembre-1943/paietta-pietro, refers)…
‘I am glad to learn that the Government has granted an increase of the pension allowed to ex-Lieut. Charles Jenkins, a native of Ventnor, of the Cape Mounted Rifles ... for distinguished conduct in the field during the Zulu War of 1879. Lieut. Jenkins daringly made the charge single-handed with revolver and sword upon a number of Zulus who were defending their own kraal, but were forced by him to retreat, seven of the enemy being left dead ... It was owing to the action of Lieut. Jenkins that an army of Zulus who were coming over the hill at the battle of Inyazana ... were successfully put to flight ... Lord Chelmsford afterwards recommended the soldier for promotion from Sergeant-Major to Lieutenant.’A newspaper extract refers.The outstanding campaign group of three awarded to Lieutenant C. Jenkins, Natal Native Contingent, late Royal Navy and Cape Mounted Rifles; he was the only man to earn a field commission from Lord Chelmsford during the Zulu War - that gallantry latter earned him a pension for 'for distinguished Conduct in the field'Baltic 1854-54 (C. J. Jenkins, Boy 2nd C. H.M.S. Ajax); South Africa 1877-79, 1 clasp, 1877-8-9 (Lieut. C. Jenkins, 4th Battn. N.N.C.), re-engraved naming; Cape of Good Hope General Service 1880-97, 1 clasp, Basutoland (Pte. C. Jenkins. C. M. Rif.), mounted on silver bar as worn, very fineCharles Jenkins was born at Brading, Isle of Wight in 1840 and served in the Royal Navy as a Boy 2nd Class in the Baltic operations (Medal), leaving home for a new life in South Africa in 1858. He joined the Cape Mounted Riflemen but returned home in 1868, being married on Christmas Day that year and taking work as a warder at Portsea. Little more needs to be said of his exploits during the Zulu campaign, but his record would appear to be a unique one.His final campaign would be in the Basuto Gun War of 1881, when serving with the Cape Mounted Rifles, although it took until 1903 for his Medal to reach him back on the Isle of Wight (Isle of Wight Mercury refers). Jenkins served in the Bechuanaland expedition as Interpreter to Sir Charles Warren and was 'disabled by accident on duty' in July 1885. This was further detailed in a 1904 letter from Major-General Sir F. Carrington:'I have much pleasure in testifying to the good services of Sgt. Major Charles Jenkins. He served under my command in the Basuto War in the Cape mounted Rifles and afterwards in the 2nd Mounted Rifles during Sir. C. Warren’s expedition in Bechuanaland where he was promoted to Sgt. Major for his efficiency and general good service. He unfortunately met with a severe accident when on duty by his horse backing into one of our wagons he was escorting – the horse being killed and Sgt. Major Jenkins having his collarbone and six ribs broken. He was taken to Mafeking Hospital where for some time he lay in a precarious state. He is in possession of the Baltic medal, Zulu War medal, Cape general Service medal and clasp for Basutoland. He is, I know, in most needy circumstances never having regained sufficient strength to do much work.'By April 1906 Major-General Hart Symot had taken up the case to assist in getting an increase in pension:'...I remember your gallant fighting in the critical action with the 2nd Zulu Army on the 22nd January at Inyazana, and your promotion from Non Commissioned Officer to Lieutenant in our NNC by Lord Chelmsford, upon my report.'The reply followed by letter from the Royal Hospital Chelsea in November 1906:'Sir,I am directed by the Lords and others, Commissioners of this hospital, to acquaint you that having taken into consideration all the circumstances of your case they have been pleased to increase your pension from nine pence to fifteen pence per diem. The additional 6d per day is awarded for ‘distinguished Conduct in the Field’.'The gallant old soldier died on 7 November 1919 and is buried at Ventnor.…
The Second World War D.S.M. group of nine awarded to Chief Petty Officer Cook A. V. E. Smithurst, Royal Navy who won his award serving on H.M.S. LondonLondon was the flagship for the escort force that failed to safeguard convoy PQ17 resulting in the loss of two thirds of the convoys vesselsDistinguished Service Medal, G.VI.R. (C.P.O. Cook (S) A Van Eck Smithurst. C/M. 33903); British War and Victory Medals (33903 A.V.E. Smithurst. CK.R.N.); Naval General Service 1915-62, 1 clasp, Palestine 1936-1939 (MX.33903 A.V.E. Smithurst. C.P.O. CK.R.N.); 1939-45 Star; Atlantic Star; Burma Star; War Medal 1939-45; Royal Navy L.S. & G.C., G.V.R. (M 33903 A.V.E. Smithurst C.P.O. CK. H.M.S. Enterprise), contact marks, good very fine (9)D.S.M. London Gazette 14 June 1945.Allan Van Eck Smithurst was born on 7 September 1900 at Grantham, Lincolnshire, the son of Percy Smithurst. A baker, Smithurst enlisted in the Royal Navy on 10 September 1918, he was shore based for the duration of the Great War. Remaining in service after the war he served variously on Calypso, Ceres, and Cumberland in 1927 by which time he had been promoted to Leading Cook. On 24 November 1930 he was promoted to Petty Officer Cook and on 22 October 1933 whilst serving on Enterprise he was awarded his L.S. & G.C. Promoted to Chief Petty Officer Cook on 7 November 1934 he was posted to Sussex for service in the Mediterranean qualifying for his Naval General Service Medal.Shore based at the beginning of the Second World War he was posted to London on 7 February 1941 and served aboard her for the duration of the war.London was involved in the pursuit of the German battleship Bismarck in May 1941. During this time at sea, many cracks appeared in her upper deck and hull, due to the weight of the new superstructure causing stresses. She entered a commercial shipyard on the River Tyne in October 1941 and was under repair until February 1942. London then spent March-November 1942 in the North Atlantic on convoy protection duties in the company of several US Navy warships.Convoy PQ 17On 27 July 1942, convoy PQ-17 departed Iceland for the Soviet Union. Out of 34 merchant ships, only 11 would make it to port. At first, things seemed to be going well for the convoy as they beat off multiple German air attacks with relative ease. But, on 4 July, everything went wrong. An order arrived from Admiral Sir Dudley Pound, the First Sea Lord himself, reading 'Convoy is to scatter'. Fearing an imminent attack from German surface ships like Tirpitz the escort ships fled west while the merchant ships made for the Soviet Union.But the Tirpitz was nowhere near the convoy, in fact, it was still at its moorings in northern Norway. Instead of saving the convoy from disaster, Admiral Pound's order had doomed PQ-17 to destruction. Over the following week, two thirds of the convoy were sunk by German aircraft and U-Boats. It was the biggest loss to a British convoy of the Second World War.This period of operations in the heavy North Atlantic seas caused hull cracks and popped rivets in her lower hull, necessitating the ship again going into the dry-dock in December 1942 for strengthening of the hull and for the fitting of newer and more refined radar, and of more light anti-aircraft guns. This refit rectified her hull and was completed in May 1943, with the ship ready for sea in July. After sea trials and loading of ammunition, she was assigned to operate off the South African coast and then to the Eastern Fleet for the rest of the war.The story of H.M.S. London is the subject of a book written by Iain Ballantyne, ' From Fighting Sail to The Arctic Convoys & Tomorrow's War.', which relates the following about PQ17, stating:'Relentless air attacks by bombers flying from German airbases in northern Norway, coupled with incendiary attacks by submarines operating in Wolf packs, began to take a heavy toll on the merchant ships with losses increasing daily. On 4 July the First Sea Lord Admiral Pound, expecting a German surface attack in superior strength on the close support group, ordered the cruisers and escort destroyers to turn back to the west and instructed the convoy to scatter. Between 4 and 6 July, 18 freighters were sunk by surface ships, submarines and land-based aircraft. On 7 July three further ships were torpedoed by submarines. On 10 July three ships were bombed and sunk by aircraft. Only when the surviving ships of the convoy began to straggle onto Archangel did it become apparent that the convoy had suffered catastrophic loses. Nine ships of 56,611 tons were sunk by U-Boats; eight ships of 40,376 tons were sunk by the Luftwaffe; and eight ships which were damaged during air attacks were finished off by U-Boats. A total of 24 ships totalling 143,977 tons were lost, along with 3,350 military vehicles, 430 tanks, 210 aircraft and 99,316 tons of war supplies.'Smithurst was shore pensioned on 1 August 1945. He died at Hastings, Sussex in 1974; sold together with copied research.…
The Africa General Service Medal awarded to District Commissioner H. M. Douglas, Aro Frontier Force, whose long service in Africa saw him thanked by the Secretary of State for his actions during the Ngor Rising and a brace of 'mentions' for fine services in NigeriaAfrica General Service 1902-56, 4 clasps, Aro 1901-1902, S. Nigeria 1902, S. Nigeria 1904, S. Nigeria 1905-06 (Dis: Comr. H. M. Douglas, Aro F.F.), extremely fineM.I.D. London Gazette 23 February & 18 September 1906.Harold Mordey Douglas was born at Sunderland in January 1875, the son of Mordey and Emma Douglas. Joining the Colonial Service in 1894 he served initially as consular agent for Puerto de la Luz, Canary Islands. He was appointed Assistant District Commissioner with the Niger Coast Protectorate in 1897 - the start of a long career in Africa. Whilst in the Protectorate he became involved in organising transport for a cross river-expedition which occurred in 1900.The outbreak of the Anglo-Aro War in 1901 saw Douglas appointed Political Officer with No. 2 column, Aro Field Force. The fighting was surprisingly fierce given the disparity in forces with the city of Arochukwu falling after four days of fighting. The war ended not long after the fall of Bende in the Spring of 1902.Appointed District Commissioner for South Nigeria in 1902, Douglas received the thanks of the Secretary of State for his prompt actions taken in suppressing the Ngor rising in June 1902, earning his South Nigeria 1902 clasp in the process. Again appointed Political Officer to the Imo River expedition, Southern Nigeria in March 1904 he served under the command of then Major Hugh Trenchard.Joining the Bende-Onitsha Hinterland expedition, again as Political Officer, he was 'mentioned' for this service as well as earning the 1905-1906 clasp. The London Gazette on 23 February 1906 states the following of his work there:'After the withdrawal of the Ouitsha Hinterland patrol from the Owerri District, the inhabitants of a small district to the east of Owerri, which had not been visited, refused to allow passage along their roads, and fired on a military escort travelling over one of them. The District Commissioner, Mr. H. M. Douglas, and a small force under Lieutenant Halfpenny, with 86 rank and file, visited the country and met with constant resistance, four soldiers being killed and three wounded before this thickly-populated district submitted.'After the expedition Douglas was appointed Senior District Commissioner in 1906 before transferring to Central Province as Acting Provincial Secretary in 1908-09. His final role was as Acting Assistant Provincial Commissioner and Provincial Secretary of Central Province in 1910-13. Douglas was still living at Warri Province in 1914, he died on 24 May 1926 at the Kapara Estate, Fort Jameson, North-East Rhodesia; sold together with copied extracts from medal rolls, London Gazette entries and other research.Note further information on Douglas can be found in an Article in the O.M.R.S. journal of March 2019 entitled 'Black Douglas'.…
Bowker's RoversRaised in Graaff-Reinet and Somerset East districts by Commandant B. E. Bowker for the Ninth War of 1877.85 Medals issued to this unit, 47 of which with the '1877-8' clasp. The unit also earned some 34 of a total of all the 167 rare '1877' clasps - for the operations from September 1877.South Africa 1877-79, 1 clasp, 1877-8 (Tpr. C. Mattig. Bowkers Rovers.), very fineAlso served alongside a relative, Trooper M. Mattig.…
The 1945 B.E.M. awarded to Miss M. Jacomb, Manageress of the Corner Club & Hostel, CairoBritish Empire Medal, G.VI.R., Civil Division (Miss Mary Jacomb), mounted as worn on bow and tails riband, good very fineB.E.M. London Gazette 23 January 1945.Mary Jacomb was decorated for her fine work as the Manageress of the Corner Club & Hostel, Cairo, also known as Talbot House TOC H. Corner Club Heliopolis Services Club.…
-
375892 item(s)/page









































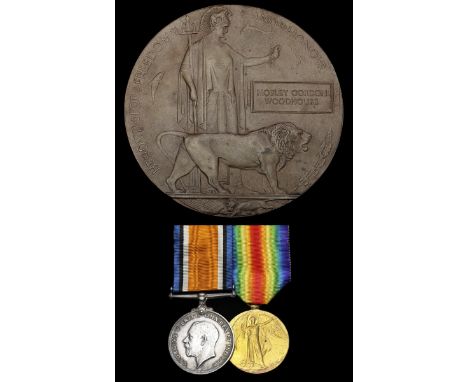




!['The C.O., Michael, and John had each destroyed an Me. 110, while Mac [McArthur] shot down two Junkers 87 dive-bombers. He wo](https://cdn.globalauctionplatform.com/5d973dee-439b-4cad-a633-b2b500cc4fbb/4792aa89-82b0-47d2-ad06-b2b500d55c86/468x382.jpg)