Dolomieu’s manuscript notes on the essence of geological research –‘Errors experienced prevent the mind from dealing with new research: we think we know and this is the greatest obstacle to really knowing’ DOLOMIEU DEODAT GRATET DE: (1750-1801) French geologist after whom the mineral and the rock dolomite were named. A supporter of Napoleon Bonaparte during the French Revolution, Dolomieu was captured and held as a prisoner of war in Italy from 1799. Following Napoleon's successful invasion of Italy, one of the terms dictated by him in the peace treaty of Florence in March 1801 was the immediate release of Dolomieu. An extremely rare autograph manuscript signed, with his initials G D D, two pages, 12mo (6.5 x 9.5 cm), n.p., n.d., in French. Dolomieu's manuscript notes, comprising thirty-seven lines written in a small, although perfectly legible, hand is entitled 'Les Erreurs reconnues sont des verites acquises' (Translation: 'The errors recognised are the truths acquired') and states, in part, 'et leur decouverte est d'autant plus utile qu'elles ont été de nature à séduire beaucoup de gens. Les erreurs vécues empechent l'esprit de s'occuper de nouvelles recherches: on croit savoir et c'est le plus grand obstacle a savoir reellement…….La verite recherchee par les hommes est comme le feu qu'ils produisent avec des matieres combustibles; plus elle s'etend, plus elle a de tendance a s'etendre de nouveau. On fait un pas vers la decouverte de la cause d'un phenomene quelconque lorsque l'on trouve que les causes auxquelles on l´attribuait n'ont aucun rapport avec lui. Comme il n'y a point d'effets sans causes, lorsqu'on decouvre un plus grand nombre de faits qui, quoique contemporain d'un phenomene, n'ont point de rapports avec lui, on se rapproche de la connaissance de la cause qui pourra l'expliquer. Cette methode d'approche de la verite, qu'on peut dire negative et d'exclusion peut reussir finalement quoiqu'elle puisse etre longue. Mais elle est essentielle a employer surtout dans les recherches geologiques' (Translation: 'and their discovery is all the more useful in that they have been of a nature to seduce many people. Errors experienced prevent the mind from dealing with new research: we think we know and this is the greatest obstacle to really knowing…….The truth sought by men is like the fire they produce with combustible materials; the more it expands, the more it tends to expand again. One takes a step toward discovering the cause of any phenomenon when one finds that the causes to which it was attributed have no connection with it. As there are no effects without causes, when we discover a greater number of facts which, although contemporaneous with a phenomenon, have no connection with it, we come closer to knowing the cause that can explain it. This method of approaching the truth, which can be said to be negative and of exclusion, can ultimately succeed, although it may take a long time. But it is essential to use especially in geological research'). An interesting and important text. Some very light, minor foxing and age wear, otherwise VGThe text of Dolomieu’s manuscript originates from a scientific work published in 1778-79 by Jean-Andre Deluc (1727-1817) Swiss geologist, natural philosopher and meteorologist who devised measuring instruments. Deluc’s father was a supporter of Jean-Jacques Rousseau and Jean-Andre also wrote of conversations he had experienced with Voltaire and Rousseau in an essay on the General Principle of Mortality which he had published in 1798.
We found 1583 price guide item(s) matching your search
There are 1583 lots that match your search criteria. Subscribe now to get instant access to the full price guide service.
Click here to subscribe- List
- Grid
-
1583 item(s)/page
A collection of various small scientific instruments and measuring tools including a J Collark of Dresden pocket barometer with compass verso, another pocket barometer in plated case, an Accurist thickness measure, a gilt brass cased pocket compass (glass smashed), a Wynne's Infallible Exposure meter (x 2), a Zeiss Icon light meter, a French photometre by J Decoudun of Paris, a Gowlands "The Berwick" lens measure, a Gowlands light meter and a Holden's calculex patent circular slide rule
A RARE POCKET BAROGRAPH IN ORIGINAL MAHOGANY CASEJULES RICHARD, PARIS, FOR RETAIL BY LUTZ AND SHULTZ FLORIDA AND BUENES AIRES, CIRCA 1910The nickel plated mechanism with timepiece movement set to the upper right incorporating platform cylinder escapement regulated by sprung monometallic balance, driving via system of gears the upper of two rollers positioned beneath the movement to rotate a looped twelve-hour paper scale calibrated for altitude in feet 0-5000 and with further reverse scale annotated 42-76 spanning the same arc, the upper left with aneroid barometer mechanism incorporating twin vacuum capsules operating via a system of hinged levers a radially-pivoted recording pointer tensioned via a coil spring positioned beneath the primary rocking arm, the mechanism set beneath a nickel-plated cover with slider for setting the elevation of the recording arm labelled A, 1, B and shuttered aperture for escapement regulation access, over retailer's name LUTZ Y SCHULZ, FLORIDA 171, BUENOS AIRES followed by BREVETE S.G.D.G. oval above JR monogram for Jules Richard to lower margin, contained in a hinged rectangular cast metal case covered in faux tooled black Morocco and with glazed aperture for the chart, in original mahogany box incorporating lidded section containing a good quantity of spare charts, ink bottle and winding key.The instrument 12cm (4.75ins) high, 8.5cm (3.375ins) wide, 3.5cm (1.375ins) deep; the mahogany box 18cm (7ins) wide, 14cm (5ins) deep, 5cm (2ins) high. Jules Richard was born in 1848 and trained under his father before working with other scientific instrument and clock manufacturers. However he later diversified in the manufacturing of telegraph equipment and worked closely with the French scientist E.J. Marey on electrical and photographic recording techniques during the 1870's. Following the death of his father in 1876, Jules inherited the family business and in 1882, he formed a partnership with his brother Max under the name of Richard Freres. This partnership was dissolved in 1891 but the company was maintained with Jules taking sole control of the business until 1921 when it was listed as a public company.Lutz and Schulz were a leading firm of opticians and suppliers of surveying, optical and scientific instruments operating from Florida and Buenes Aires from around 1905. In 1912 they opened a flagship store at Rambla Bristol 117, Florida 240 and operated from Mar Del Plata, Buenos Aires from where they continued well into the 20th century. The fact that the current lot is marked FLORIDA 171 suggests that it pre-dates the opening of the Rambla Bristol store, hence can be confidently dated to between 1905-12. The present instrument belongs to a series produced by Jules Richard with differing ranges and durations to the papers. The nickel cover is stamped C which would appear to be the corresponding model designation for an instrument that has scale range of 0-5,000 feet and records for eight hours. Vavasseur Antiques are currently listing another, almost identical example, however theirs is designated a model 'F' with scale range of 0-7,000 feet and a recording duration of six hours.
A REGENCY TWELVE-INCH TERRESTRIAL LIBRARY TABLE GLOBEDRAWN BY W. AND T.M. BARDIN, SOLD BY J. WATKINS, LONDON, CIRCA 1805The sphere applied with twelve engraved gores now incomplete and with oval blood-red varnish incorporating circular panel to the North Pacific inscribed THE, NEW TWELVE-INCH, Terrestrial Globe, REPRESENTING THE, ACCURATE POSITIONS OF THE, PRINCIPAL, KNOWN PLACES OF THE EARTH, FROM THE DISCOVERIES, OF CAPTAIN COOK, AND SUBSEQUENT CIRCUMNAVIGATORS, TO THE PRESENT PERIOD, with curved overlay J Watkins Charing Cross LONDON over with additions to 1805 to lower margin, with evidence of having an extensively annotated and fully graduated equatorial calibrated in minutes and degrees, ecliptic and meridians, also just visible many explorers' tracks and numerous notes and dates, the continents with nation states showing cities, towns, rivers, mountains in pictorial relief, pivoted via the pole axis within brass meridian circle divided for degrees, set within a horizon ring now lacking papers, the tripod stand incorporating four quadrants supporting the meridian ring over reeded squat baluster upright and downcurved supports, vacant compass stretcher and terminating with tapered feet.61cm (24ins) high, 44cm (17.25ins) diameter overall. The text of the circular panel printed to the North pacific conforms to globes drawn by William and Thomas Marriot Bardin in 1803/05. William Bardin (1783-98) was a freeman of the Leatherseller's Company who starting making globes in around 1780. His first globes were 9 and 12 inch diameter published in collaboration with Gabriel Wright on 1st January 1782. Wright was a mathematical instrument maker who had previously worked for Benjamin Martin who, in turn, had acquired the plates of Senex's celebrated globes from James Ferguson. William's son, Thomas Marriott, is recorded in Clifton, Gloria Directory of Scientific Instrument Makers 1550-1851 as a globe maker apprenticed to his father, in 1783 with whom he went into partnership in 1790. Bardin and Son initially worked from 4 Hind Court, Fleet Street, London before moving to 16 Salisbury Square in 1975. William Bardin died in 1795 leaving the business in the hands of Thomas Marriott. The firm was taken-on by Thomas's daughter, Elizabeth Marriott, after his death in 1820 and then by her husband, S.S. Edkins. on their marriage in 1832. They took a son into partnership in 1848 and the business continued until shortly after S.S. Edkins's death in 1853. Jeremiah Watkins is recorded by Clifton as working from 5 Charing Cross, London 1798 until his death in 1810. In his earlier partnership with Walter Watkins he became one of the most prolific retailers of optical, scientific, mathematical and surveying instruments during the closing decade of the 18th century. At this time it was common practice for the vendors of globes to put their own trade label over that of the manufacturer.
A MAHOGANY CASED BAROGRAPH INCORPORATING BAROMETER DIALNEGRETTI AND ZAMBRA, LONDON, LATE 19th CENTURYThe mechanism with eight segment aneroid chamber within gilt brass armature operating via a system of pivoted levers an inked pointer for recording the change in barometric pressure on the clockwork-driven paper-scale lined rotating drum, the front with open-centred circular silvered register calibrated in barometric inches, with the usual weather observations and signed NEGRETTI & ZAMBRA, LONDON to the lower margin within a brass bezel surround, the case with five panel bevel-glazed cover and ogee moulded base with frieze drawer containing spare charts over squab feet.21cm (8.25ins) high, 37cm (14.5ins) wide, 22.5cm (8.75ins) deep. Provenance:The present lot was almost certainly the property of the second Thomas Sopwith, born to the owner of the previous lot and father to the famous Aviation pioneer of the same name. Thomas Sopwith II followed in his father's footsteps becoming a civil engineer specialising in mining. He became the managing director of the Spanish Lead Mining Company (a British Company created to mine lead in in Linares, Jaen, Spain) in 1864, and died in 1898. The firm of Negretti & Zambra are recorded in Banfield, Edwin BAROMETER MAKERS AND RETAILERS 1660-1900 as being established in 1850 when a partnership between Enrico Negretti and Joseph Warren Zambra was formed. The firm became one of the most prolific makers of scientific instruments and continued trading well into the 20th century.Condition Report: The mechanism is in good original condition and appears fully-operational (responds to change in pressure - has been 'bag tested'). The pointer reading is reasonably accurate and the clockwork mechanism is working. The instrument retains its original lacquered brass finish with only minor spotting/discolouration in places. The case has noticeable sun-bleaching and degradation to the French polish finish hence would benefit from a re-polish by a cabinet maker otherwise is in sound original undamaged condition. The drawer contains a good quantity of spare charts together with an instruction leaflet. Condition Report Disclaimer
Y A VERY FINE PAIR OF REGENCY TWENTY-ONE INCH TERRESTRIAL AND CELESTIAL FLOOR-STANDING LIBRARY GLOBESJ. & W. CARY, LONDON, THE CELESTIAL DATED 1799, THE TERRESTRIAL DATED 1815/1823The terrestrial applied with eighteen hand-coloured engraved split half-gores incorporating circular cartouche inscribed CARY'S, NEW TERRESTRIAL GLOBE, EXHIBITING, The Tracks and Discoveries made by, CAPTAIN COOK: Also those of CAPTAIN VANCOUVER on the, NORTH WEST COAST OF AMERICA: And M. DE LA PEROUSE, on the COAST of TARTARY. TOGETHER, With every other Improvement collected from, Various Navigators to the present time. LONDON: and overlaid Made & Sold by J.& W. Cary, Strand, March 1st. 1815., with further inscription WITH ADDITIONS AND CORRECTIONS TO 1823 beneath, with fully graduated equatorial, ecliptic and four meridians, the Pacific ocean with an analemma, many explorers' tracks and numerous notes and dates, Antarctica with no land shown but Firm Fields and Vast Mountains of Ice 71.10 Highest South Lat of Capt. Cook and other notes, the continents with nation states faintly colour-outlined, showing cities depicted by a small building, towns, rivers, mountains in pictorial relief, marshland, caravan routes and African salt and copper mines, with numerous notes and Canada with no northern coastline; the celestial with conforming roundel inscribed CARY'S, New and Improved, CELESTIAL GLOBE, ON WHICH, Is carefully laid down the whole of the STARS and NEBULÆ, Contained in the ASTRONOMICAL CATALOGUE of the, REVD. Mr. WOLLASTON, F.R.S., Compiled from the Authorities of, FLAMSTEED, DE LA CAILLE, HEVELIUS, MAYER, BRADLEY, HERSCHEL, MASKELYNE &c. With an extensive number from the works of Miss Herschel, The whole adapted to the year 1800, and the, Limits of each Constellation determined, by a boundary line. London: Made & Sold by J.& W. Cary, No. 181 Strand Mar 1 1799, also made up of two sets of eighteen hand-coloured engraved split half-gores laid to the ecliptic poles, the axis through the celestial poles, with fully graduated equatorial, ecliptic with twilight zone and four colures, the constellations depicted by mythical beasts, figures and scientific instruments, with dotted boundaries, the stars shown to nine orders of magnitude with doubles, clusters and nebulæ and labelled with Greek and Roman characters and Arabic numerals denoting their source, with an explanation beneath the cartouche; each sphere pivoted via the polar axis within brass meridian circle divided for degrees and with brass hour circle to North pole, set within hand-coloured engraved paper horizon ring with compass points and degrees in both directions, Zodiac and calendar scales and wind directions, supported on a fine ebony line-strung satinwood stand with curved line-panelled frieze over three square section tapered legs united by three upward curved stretchers terminating with a baluster-turned upright supporting the globe via a brass clamp engaging with the meridian ring, the lower section with further turned stretchers supporting a glazed paper scale compass printed with elaborate thirty-two point rose within outer scale divided for degrees, over brass cup castors.Each 119cm (47ins) high, 69cm (27ins) diameter overall. Provenance:Purchased from Sally Turner Antiques, Hogarth House, High Street, Wendover, Bucks, 20th July 2002 for £95,000; thence by family descent. The celebrated Cary family business of scientific instrument and globe makers was established by John Cary at Johnson's Court, Fleet Street, London in 1782 moving to a new address at 'Corner of Arundel Square', Strand the following year. He was primarily an engraver of maps, charts and globes who moved again in 1783 to 188 Strand. By 1791 he had entered into what appeared to be a relatively casual partnership with his brother, William; this partnership lasted until circa 1816 by which time William and John Cary had moved again to 181 Strand before finally settling in 86 St. James in 1820. The following year he was succeeded by his sons, John (II) and George Cary, who continued from the firm's 181 Strand address until 1851/2 when the business was acquired by Henry Gould. Cary's 21-inch globes were the largest and most impressive produced during the George III and Regency period.Condition Report: Both globes are in very fine near retail clean condition. The celestial has some very slight filling and touching-in to address some cracking to the equinoctial affecting around a third of the circumference at that point. Otherwise faults are very much limited to a few very small historic scuff repairs and some very localised staining to the joints between some of the gores. The Terrestrial has a small (15 by 5mm) clean puncture just below Australia and a few very light surface scratching to the Southern regions. There is also a small filled scuff and staining adjacent to the bottom pivot. Sphere otherwise is in very fine condition with only or two small filled blemishes and light overall mottling. The brass fittings appear all-original and are in good condition with slightly mellowed lacquer finish. Both stands are in fine condition. The Horizon papers are in clean condition exhibiting only very minor browning. There are some light shrinkage cracking (from movement within the ring beneath) showing through the papers but no apparent losses or infilling. Both compasses are complete; the paper to the terrestrial has tears and rubbing but no losses, the celestial has losses and touching in to the paper, both have noticeable browning hence are now light beige in colour. The frames are in very good clean condition - the celestial has visible plugged fixings to the outer surfaces of the legs corresponding to the cabriole inner supports and compass stretcher; the terrestrial has similar visible plugs but for only for the compass stretcher. Faults are otherwise limited to light shrinkage and minor restorations to the ebony stringing. Condition Report Disclaimer
A GEORGE III EIGHTEEN-INCH CELESTIAL FLOOR-STANDING LIBRARY GLOBEW. AND T.M. BARDIN, SOLD BY J. AND W. WATKINS, LONDON, CIRCA 1800The sphere applied with two sets of twelve hand-coloured engraved split half-gores incorporating oval panel inscribed To the Rev., NEVIL MASKELYNE D.D. F.R.S., Astronomer Royal, This New British Celestial Globe, Containing the Positions of nearly 6000 Stars. Clusters, Nebulae, Planetary, Nebulae & c. Correctly computed & laid down for the year 1800; from the latest oservati,-ons and discoveries by Dr, Maskelyne, Dr. Herschel, The Rev'd. Mt. Wollaston &c &c, and with a further applied label Sold by J. & W. Watkins, Charing Cross London, with fully graduated equatorial and ecliptic with twilight zone, the constellations depicted by mythical beasts and figures with dotted boundaries, the stars shown to nine orders of magnitude with clusters and nebulæ, pivoted via the polar axis within brass meridian circle divided for degrees, set within a later facsimile printed paper horizon ring with compass points and degrees in both directions, Zodiac labelled in Latin, calendar scales and wind directions, in a stand with four down-curved quadrant supports cradling the globe baluster and ring-turned upright and three outswept supports each inlaid with diamond lozenge decoration and terminating with tapered feet.107cm (42ins) high, 61cm (24ins) diameter overall. William Bardin (1783-98) was a freeman of the Leatherseller's Company who starting making globes in around 1780. His first globes were 9 and 12 inch diameter published in collaboration with Gabriel Wright on 1st January 1782. Wright was a mathematical instrument maker who had previously worked for Benjamin Martin who, in turn, had acquired the plates of Senex's celebrated globes from James Ferguson. William's son, Thomas Marriott, is recorded in Clifton, Gloria Directory of Scientific Instrument Makers 1550-1851 as a globe maker apprenticed to his father, in 1783 with whom he went into partnership in 1790. Bardin and Son initially worked from 4 Hind Court, Fleet Street, London before moving to 16 Salisbury Square in 1975. William Bardin died in 1795 leaving the business in the hands of Thomas Marriott. The firm was taken-on by Thomas's daughter, Elizabeth Marriott, after his death in 1820 and then by her husband, S.S. Edkins. on their marriage in 1832. They took a son into partnership in 1848 and the business continued until shortly after S.S. Edkins's death in 1853. The partnership between Jeremiah and Walter Watkins is recorded in Clifton, Gloria Directory of British Scientific Instrument Makers 1550-1851 as working from 5 Charing Cross, London 1784-98. The business was continued by Jeremiah alone until his death in 1810. The partnership was one of the most prolific retailers of optical, scientific, mathematical and surveying instruments during the closing decade of the 18th century. At this time it was common practice for the vendors of globes to put their own trade label over that of the manufacturer.Condition Report: Globe has been cosmetically restored; has been gently cleaned and coat of fresh varnish applied. Both poles have evidence of slight movement but the globe is secure on its axis. The gores show evidence of historic rubbing and slight wear with a few small losses to the papers in places, slight opening of the joins between the papers, and there is overall greying beneath the relatively fresh varnish. The stand is in good restored condition; the horizon papers are unfortunately photographic replicas. The column has evidence of repaired vertical cracking but is in strong solid structural condition.Please note additional images are available which form an integral part of the condition report. Condition Report Disclaimer
A VICTORIAN LACQUERED BRASS PANTOGRAPHADIE, LONDON, CIRCA 1875The pivoted frame with circular dark green silk covered anchor-weight fitted to an adjustable slider against engraved ratio scale to one arm opposing fixed pencil holder to the other, the centre with subsidiary pivoted armature with further adjustable slider against a similar scale for the tracing stylus and signed Adie, London alongside 7393 over M.O.D. arrow device and W.D. to the opposing member, fitted with removable bone wheel castors to each junction/terminal, in original mahogany box with weighted pencil carrier, the inside of the lid with applied paper trade label inscribed ADIE, OPTICIAN, Mathematical & Philosophical, Instrument Maker, 15 Pall Mall, LONDON, FACTORY - 1 BROADWAY, WESTMINSTER S.W. and a later retailer's label W.F. STANLEY & Co. LTD, 286 HIGH HOLBORN, LONDON W.C.1.The box 84cm (33ins) long, 13.25cm (5.25ins) deep, 9cm (3.5ins) high. The Adie family of scientific, mathematical and philosophical instrument makers can be traced back to Alexander Adie who is recorded in Goodison, Nicholas English BAROMETERS 1680-1860 as born in Edinburgh 1774 and apprenticed to his uncle, the eminent Scottish instrument maker John Miller, in 1789. In 1804 his uncle took him into partnership under the name of Miller and Adie which continued until after Miller's death in 1815. Adie was particularly interested in meteorological instruments and is perhaps best known as the inventor of the Sympiesometer in 1818. In recognition of his work he was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society of Edinburgh in 1819. He was appointed optician to William IV and later Queen Victoria and took one of his sons, John, into partnership in 1835. Two of his other sons set up businesses; Robert in Liverpool and Patrick in London. Unfortunately John Adie was prone to 'fits of despondency' which resulted in him shooting himself in 1857, Alexander Adie died the following year - no doubt expediated by the stress of his son's demise. Patrick Adie worked from several addresses in London notably 385 Strand (1848-68), 15 Pall Mall (1869-1885), 29 Regent Street (1869-70), as well as Tothill Street in 1875. He died in 1886.Condition Report: The frame appears complete, undamaged and retains old lacquer finish. Both scales have significant discolouration and there appears to be no tracing stylus present. The box in in good original condition with minimal age related blemishes; there is no key present. Condition Report Disclaimer
° ° A selection of books on globes and scientific instruments to include; Decker, Elly and Van Der Krogt, Peter, Globes From The Western World, Trevor Philip & Sons Ltd, 1993; Wynter, Harriet and Turner, Anthony, Scientific Instruments, Studio Vista, 1975; Sumira, Sylvia, The Art and History of Globes, The British Library, 2014; together with others. Approx. 68 in total
Various Scientific Instruments, black-enamelled Watson & Sons 'Service I' microscope, with triple nosepiece and three objectives, Watson binocular dissection microscope, W Wilson spectroscope, Eumig P8 standard 8 projector, Agfa splicer, Ajax 10 x 50 binoculars and Opti laptop computer (a lot)
A Fulda porcelain coffee or hot chocolate cup and cover with stand, c.1785, blue crowned FF marks, impressed IK (?) marks, the cup with a channelled angular handle, the cup and saucer with rectangular faux-bois panels with a trompe loeil trophies including artists palettes, thermometers, books, musical and scientific instruments, sheet music and maps, the cup lower part and well of the saucer moulded with bands of acanthus leaves, gilt band rims, the saucer 15.6cm diameterProvenance: The Robert G. Vater Collection of European Ceramics. Condition Report: Some very, very slight wear to the gilding around the upper rim and three small flat chips to the edge of the handle; its cover and saucer in good order.
Apollo15 moonwalker Dave Scott and CMP Alfred Worden signed Space cover NASA Astronauts. 2001 30th Anniversary Apollo 15. postmarked cover. Superb illustration on front of scenes from the mission. Also illustrated on back with crew names and mission information. David Randolph Scott (born June 6, 1932) is an American retired test pilot and NASA astronaut who was the seventh person to walk on the Moon. Selected as part of the third group of astronauts in 1963, Scott flew to space three times and commanded Apollo 15, the fourth lunar landing; he is one of four surviving Moon walkers and the last surviving crew member of Apollo 15. Before becoming an astronaut, Scott graduated from the United States Military Academy at West Point and joined the Air Force. After serving as a fighter pilot in Europe, he graduated from the Air Force Experimental Test Pilot School (Class 62C) and the Aerospace Research Pilot School (Class IV). Scott retired from the Air Force in 1975 with the rank of colonel, and more than 5,600 hours of logged flying time. As an astronaut, Scott made his first flight into space as a pilot of the Gemini 8 mission, along with Neil Armstrong, in March 1966, spending just under eleven hours in low Earth orbit. He would have been the second American astronaut to walk in space had Gemini 8 not made an emergency abort. Scott then spent ten days in orbit in March 1969 as Command Module Pilot of Apollo 9, a mission that extensively tested the Apollo spacecraft, along with Commander James McDivitt and Lunar Module Pilot Rusty Schweickart. After backing up Apollo 12, Scott made his third and final flight into space as commander of the Apollo 15 mission, the fourth crewed lunar landing and the first J mission. Scott and James Irwin remained on the Moon for three days. Following their return to Earth, Scott and his crewmates fell from favour with NASA after it was disclosed that they had carried four hundred unauthorized postal covers to the Moon. After serving as director of NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in California, Scott retired from the agency in 1977. Since then, he has worked on a number of space-related projects and served as a consultant for several films about the space program, including Apollo 13. Alfred Merrill Worden (February 7, 1932 - March 18, 2020) was an American test pilot, engineer and NASA astronaut who was the command module pilot for the Apollo 15 lunar mission in 1971. One of only 24 people to have flown to the Moon, he orbited it 74 times in the command module (CM) Endeavour. Worden was born in Michigan in 1932; he spent his early years living on farms and attended the University of Michigan for one year, before securing an appointment to the United States Military Academy at West Point, New York. Graduating in 1955, he elected to be commissioned in the United States Air Force, though he had no piloting experience. He proved adept at flying fighter planes, and honed his skills, becoming a test pilot before his selection as a Group 5 astronaut in 1966. He served on the support crew for Apollo 9 and the backup crew for Apollo 12 before his selection for the Apollo 15 crew in 1970, with David Scott as commander and James Irwin as lunar module pilot. After Apollo 15 reached lunar orbit, and his crewmates departed to land on the Moon, Worden spent three days alone in the CM, becoming in the process the individual who travelled the farthest from any other human being, a distinction he still holds. He took many photographs of the Moon and operated a suite of scientific instruments that probed the Moon. During Apollo 15's return flight to Earth, Worden performed an extravehicular activity (EVA), or spacewalk, to retrieve film cassettes from cameras on the exterior of the spacecraft. It was the first deep space EVA in history, and as of 2022 remains the one that has taken place farthest from Earth. After their return, the crew became involved in a controversy over postal covers they had taken to the Moon; they were reprimanded by NASA and did not fly in space again. Worden remained at NASA until 1975 at the Ames Research Center, then entered the private sector. He engaged in a variety of business activities, and had a longtime involvement with the Astronaut Scholarship Foundation, serving as chair of its board of directors from 2005 until 2011. He made many public appearances, promoting a renewed space program and education in the sciences, before his death in 2020. Good condition. All autographs come with a Certificate of Authenticity. We combine postage on multiple winning lots and can ship worldwide. UK postage from £5.99, EU from £7.99, Rest of World from £9.99
Apollo15 moonwalker Dave Scott and CMP Alfred Worden signed Space cover NASA Astronauts. 2001 30th Anniversary Apollo 15. postmarked cover. Superb illustration on front of scenes from the mission. Also illustrated on back with crew names and mission information. David Randolph Scott (born June 6, 1932) is an American retired test pilot and NASA astronaut who was the seventh person to walk on the Moon. Selected as part of the third group of astronauts in 1963, Scott flew to space three times and commanded Apollo 15, the fourth lunar landing; he is one of four surviving Moon walkers and the last surviving crew member of Apollo 15. Before becoming an astronaut, Scott graduated from the United States Military Academy at West Point and joined the Air Force. After serving as a fighter pilot in Europe, he graduated from the Air Force Experimental Test Pilot School (Class 62C) and the Aerospace Research Pilot School (Class IV). Scott retired from the Air Force in 1975 with the rank of colonel, and more than 5,600 hours of logged flying time. As an astronaut, Scott made his first flight into space as a pilot of the Gemini 8 mission, along with Neil Armstrong, in March 1966, spending just under eleven hours in low Earth orbit. He would have been the second American astronaut to walk in space had Gemini 8 not made an emergency abort. Scott then spent ten days in orbit in March 1969 as Command Module Pilot of Apollo 9, a mission that extensively tested the Apollo spacecraft, along with Commander James McDivitt and Lunar Module Pilot Rusty Schweickart. After backing up Apollo 12, Scott made his third and final flight into space as commander of the Apollo 15 mission, the fourth crewed lunar landing and the first J mission. Scott and James Irwin remained on the Moon for three days. Following their return to Earth, Scott and his crewmates fell from favour with NASA after it was disclosed that they had carried four hundred unauthorized postal covers to the Moon. After serving as director of NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in California, Scott retired from the agency in 1977. Since then, he has worked on a number of space-related projects and served as a consultant for several films about the space program, including Apollo 13. Alfred Merrill Worden (February 7, 1932 - March 18, 2020) was an American test pilot, engineer and NASA astronaut who was the command module pilot for the Apollo 15 lunar mission in 1971. One of only 24 people to have flown to the Moon, he orbited it 74 times in the command module (CM) Endeavour. Worden was born in Michigan in 1932; he spent his early years living on farms and attended the University of Michigan for one year, before securing an appointment to the United States Military Academy at West Point, New York. Graduating in 1955, he elected to be commissioned in the United States Air Force, though he had no piloting experience. He proved adept at flying fighter planes, and honed his skills, becoming a test pilot before his selection as a Group 5 astronaut in 1966. He served on the support crew for Apollo 9 and the backup crew for Apollo 12 before his selection for the Apollo 15 crew in 1970, with David Scott as commander and James Irwin as lunar module pilot. After Apollo 15 reached lunar orbit, and his crewmates departed to land on the Moon, Worden spent three days alone in the CM, becoming in the process the individual who travelled the farthest from any other human being, a distinction he still holds. He took many photographs of the Moon and operated a suite of scientific instruments that probed the Moon. During Apollo 15's return flight to Earth, Worden performed an extravehicular activity (EVA), or spacewalk, to retrieve film cassettes from cameras on the exterior of the spacecraft. It was the first deep space EVA in history, and as of 2022 remains the one that has taken place farthest from Earth. After their return, the crew became involved in a controversy over postal covers they had taken to the Moon; they were reprimanded by NASA and did not fly in space again. Worden remained at NASA until 1975 at the Ames Research Center, then entered the private sector. He engaged in a variety of business activities, and had a longtime involvement with the Astronaut Scholarship Foundation, serving as chair of its board of directors from 2005 until 2011. He made many public appearances, promoting a renewed space program and education in the sciences, before his death in 2020. Good condition. All autographs come with a Certificate of Authenticity. We combine postage on multiple winning lots and can ship worldwide. UK postage from £5.99, EU from £7.99, Rest of World from £9.99
A GROUP OF SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENTS, comprising two brass sextants, a Sestrel Seafix hand held nautical compass and electronic navigation device, a Sestrel brass cased liquid-damped compass, a handheld brass compass by Stanley of London, and a modern mounted clock and barometer set marked 'Classic' (6) (Condition Report: fair condition, sd and missing parts, untested)
A John Dovaston Signpost/Angle Barometer, English, Dated 1786,signed John Dovaston fecit 1786, the mahogany baseboard with turned wood cistern cover, mercury thermometer with silver scale and sliding pointer, weather silvered scale with slide and pointer, 33in (84cm) high Footnotes:Provenance:Property from the Stephen Edell Collection.John Dovaston (1740-1808) was a scientific instrument maker known to have produced barometers as well as table globes, among other instruments. For a full description see 'An 18th Century Yeoman-polymath and a Pair of Manuscript Globes, 'intended for the wife of his son'', Bulletin of the Science Instrument Society, No. 65, by Stephen Edell.For further information on this lot please visit Bonhams.com
A Pair of J. & W. Cary 15-inch Terrestrial and Celestial Floor Standing Globes, English, circa 1820,the 15-diameter terrestrial sphere with hand coloured gores and cartouche printed CARY'S NEW TERRESTRIAL GLOBE, Drawn from the most recent GEOGRAPHICAL WORKS, showing the whole of the New Discoveries with the TRACKS of the PRINCIPAL NAVIGATORS and every improvement in Geography to the present Time. London, Published by J&W. Cary 181 Strand Apri.2.1819,the 15-diameter celestial sphere with hand coloured gores and cartouche printed Celestial cartouche reading CARY'S NEW CELESTIAL GLOBE, ON WHICH are carefully laid down the whole of the SARS AND NEBULAE continued in the catalogues of Wollaston, Herschel, Bode, Piazzi, Zach & c. calculated to the Year 1820,each globe mounted in brass meridian with engraved circle of degrees, within horizon ring applied with printed calendar and zodiac scales, raised on mahogany stand with a turned knop and curved legs, stretcher and compass, 40 1/2in (103cm) high each Footnotes:The Cary family of globe makers was founded in the late 18th century by John Cary (1755-1835). Cary's began with the engraving and selling of maps from the early 1780s, having previously been apprenticed to William Palmer, and became a freeman in 1778.The first globes by Cary were advertised in the January 1791 edition of Traveller's Companion, which offered 3 1/2-inch, 9-inch, 12-inch and 21-inch diameter terrestrial and celestial globes. The address of the company at this time was 181, Strand, London, and the company was commonly known as J & W Cary, to recognise the contribution of John's brother William (1759-1825). It is from this address that the present pair of globes were produced. While John and William Cary had a joint enterprise for globes, the brothers operated as separate business entities when producing other maps or scientific instruments. William Cary was primarily an optician and nautical instrument maker, having been apprenticed to Jesse Ramsden whose workshop was also located on the Strand.This lot is subject to the following lot symbols: TPTP For auctions held in Scotland: Lots will be moved to an offsite storage location (Constantine, Constantine House, North Caldeen Road, Coatbridge ML5 4EF, Scotland, UK) and will only be available for collection from this location at the date stated in the catalogue. Please refer to the catalogue for further information.For all other auctions: Lots will be moved to an offsite storage location (Cadogan Tate, Auction House Services, 241 Acton Lane, London NW10 7NP, UK) and will only be available for collection from this location at the date stated in the catalogue. Please note transfer and storage charges will apply to any lots not collected after 14 calendar days from the auction date.For further information on this lot please visit Bonhams.com
Brian Sanders (British, B. 1937) "Deep Sea Fishing -- Great Britain" Original Watercolor painting on Illustration Board. Provenance: Collection of James A. Helzer (1946-2008), Founder of Unicover Corporation. This painting was originally published on the Fleetwood First Day Cover for the Great Britain Fishing Boats set of 4 stamps issue of September 23, 1981. From the primitive spears used by yesterday's fishermen, fishing has become a huge commercial industry equipped with some amazing scientific instruments. Today's commercial fisherman uses fishing aids not even dreamed of a hundred years ago. His boat may be fitted with echo sounders that permit him to locate and track fish from thousands of feet away, or his craft may bear electrical devices that actually force fish to swim into his nets. The painting tells the story of modern day fishing in Great Britain. In the center of the painting is pictured a Cornish crab and lobster potter, typical of the area. At the lower left a fisherman is shown hauling in a traditional herring drift net. With the advent of modern herring fishing methods, man has seriously depleted the stock along the coast of Britain. Today, protective measures guard the herring and they are gradually making a recovery. Featured in the upper left of the painting is the crew of a trawler, sorting and gutting their cod catch. At the right of the painting is pictured a typical trawler, multi-rigged for side and stern trawling. While the men haul in one net, another can be shot and set. Thus, the men make the most of their time at sea. In many ways, fishing has changed in all industrial countries in recent decades, but despite modern inventions, the excitement of the seafaring life endures for the men who make their living in the world's great oceans. Image Size: 12 x 14.25 in. Overall Size: 16 x 22.25 in. Unframed. (B06852)
Apollo15 moonwalker Dave Scott and CMP Alfred Worden signed Space cover NASA Astronauts. 2001 30th Anniversary Apollo 15. postmarked cover. Superb illustration on front of scenes from the mission. Also illustrated on back with crew names and mission information. David Randolph Scott (born June 6, 1932) is an American retired test pilot and NASA astronaut who was the seventh person to walk on the Moon. Selected as part of the third group of astronauts in 1963, Scott flew to space three times and commanded Apollo 15, the fourth lunar landing; he is one of four surviving Moon walkers and the last surviving crew member of Apollo 15. Before becoming an astronaut, Scott graduated from the United States Military Academy at West Point and joined the Air Force. After serving as a fighter pilot in Europe, he graduated from the Air Force Experimental Test Pilot School (Class 62C) and the Aerospace Research Pilot School (Class IV). Scott retired from the Air Force in 1975 with the rank of colonel, and more than 5,600 hours of logged flying time. As an astronaut, Scott made his first flight into space as a pilot of the Gemini 8 mission, along with Neil Armstrong, in March 1966, spending just under eleven hours in low Earth orbit. He would have been the second American astronaut to walk in space had Gemini 8 not made an emergency abort. Scott then spent ten days in orbit in March 1969 as Command Module Pilot of Apollo 9, a mission that extensively tested the Apollo spacecraft, along with Commander James McDivitt and Lunar Module Pilot Rusty Schweickart. After backing up Apollo 12, Scott made his third and final flight into space as commander of the Apollo 15 mission, the fourth crewed lunar landing and the first J mission. Scott and James Irwin remained on the Moon for three days. Following their return to Earth, Scott and his crewmates fell from favour with NASA after it was disclosed that they had carried four hundred unauthorized postal covers to the Moon. After serving as director of NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in California, Scott retired from the agency in 1977. Since then, he has worked on a number of space-related projects and served as a consultant for several films about the space program, including Apollo 13. Alfred Merrill Worden (February 7, 1932 - March 18, 2020) was an American test pilot, engineer and NASA astronaut who was the command module pilot for the Apollo 15 lunar mission in 1971. One of only 24 people to have flown to the Moon, he orbited it 74 times in the command module (CM) Endeavour. Worden was born in Michigan in 1932; he spent his early years living on farms and attended the University of Michigan for one year, before securing an appointment to the United States Military Academy at West Point, New York. Graduating in 1955, he elected to be commissioned in the United States Air Force, though he had no piloting experience. He proved adept at flying fighter planes, and honed his skills, becoming a test pilot before his selection as a Group 5 astronaut in 1966. He served on the support crew for Apollo 9 and the backup crew for Apollo 12 before his selection for the Apollo 15 crew in 1970, with David Scott as commander and James Irwin as lunar module pilot. After Apollo 15 reached lunar orbit, and his crewmates departed to land on the Moon, Worden spent three days alone in the CM, becoming in the process the individual who travelled the farthest from any other human being, a distinction he still holds. He took many photographs of the Moon and operated a suite of scientific instruments that probed the Moon. During Apollo 15's return flight to Earth, Worden performed an extravehicular activity (EVA), or spacewalk, to retrieve film cassettes from cameras on the exterior of the spacecraft. It was the first deep space EVA in history, and as of 2022 remains the one that has taken place farthest from Earth. After their return, the crew became involved in a controversy over postal covers they had taken to the Moon; they were reprimanded by NASA and did not fly in space again. Worden remained at NASA until 1975 at the Ames Research Center, then entered the private sector. He engaged in a variety of business activities and had a longtime involvement with the Astronaut Scholarship Foundation, serving as chair of its board of directors from 2005 until 2011. He made many public appearances, promoting a renewed space program and education in the sciences, before his death in 2020. All autographs come with a Certificate of Authenticity. We combine postage on multiple winning lots and can ship worldwide. UK postage from £5.99, EU from £7.99, Rest of World from £9.99
A World War I German Naval ship Anschutz & Co gyrocompass, with bronze chapter ring and glass dial, grey painted case, 29.4x19cm.By repute salvaged form a German ship at Scapa Flow by Royal Naval Midshipman S.F.G.Tuke. The German Imperial Naval battleships destroyed or through over board all scientific instruments before the ships were scuttled. The gyrocompass was an important invention for nautical navigation because it allowed accurate determination of a vessel’s location at all times regardless of the vessel’s motion, the weather and the amount of steel used in the construction of the ship.
NO RESERVE Horology.- Dubois (Pierre) Historie de L'Horlogerie, colour and plain plates, illustrations, book-label, Paris, contemporary calf, spine gilt, morocco spine labels renewed, joints cracking but firm, wear to spine ends, 1849 § Derham (F.R.S.L.) Traité d'Horlogerie piur les Montres et les Pendules, 7 folding engraved plates and tables, pp. 65-68 with small tear at top edge and tape repairs, browning and foxing, later calf, spine gilt, Paris, Gregoire Depuis, 1731; and 15 others horology and scientific instruments, v.s. (17)
Science and the Enlightenment - Wright (Gabriel), The Description and Use of both the Globes, The Armillary Sphere, and Orrery, Exemplified In a large Variety of Problems in Astronomy, Geography, Dialling, &c. Carefully selected from the late Messrs. Martin and Ferguson, and other Eminent Men [...], To which is added, A Short Account of the Solar System by G. Wright [...], first and ?sole edition thus, London: s.n., [1783], folding engraved frontispiece with scientific instruments, the other plates lacking or defective, contemporary calf gilt, 8vo in 4s. Provenance: Maria Anne & Sophia Caroline Berens, contemporary ink manuscript ownership inscription.
Apollo 15 moonwalker Dave Scott Alfred Worden signed Space cover NASA Astronauts. 2001 30th Anniversary Apollo 15. postmarked cover. Superb illustration on front of scenes from the mission. Also illustrated on back with crew names and mission information. David Randolph Scott (born June 6, 1932) is an American retired test pilot and NASA astronaut who was the seventh person to walk on the Moon. Selected as part of the third group of astronauts in 1963, Scott flew to space three times and commanded Apollo 15, the fourth lunar landing; he is one of four surviving Moon walkers and the last surviving crew member of Apollo 15. Before becoming an astronaut, Scott graduated from the United States Military Academy at West Point and joined the Air Force. After serving as a fighter pilot in Europe, he graduated from the Air Force Experimental Test Pilot School (Class 62C) and the Aerospace Research Pilot School (Class IV). Scott retired from the Air Force in 1975 with the rank of colonel, and more than 5,600 hours of logged flying time. As an astronaut, Scott made his first flight into space as a pilot of the Gemini 8 mission, along with Neil Armstrong, in March 1966, spending just under eleven hours in low Earth orbit. He would have been the second American astronaut to walk in space had Gemini 8 not made an emergency abort. Scott then spent ten days in orbit in March 1969 as Command Module Pilot of Apollo 9, a mission that extensively tested the Apollo spacecraft, along with Commander James McDivitt and Lunar Module Pilot Rusty Schweickart. After backing up Apollo 12, Scott made his third and final flight into space as commander of the Apollo 15 mission, the fourth crewed lunar landing and the first J mission. Scott and James Irwin remained on the Moon for three days. Following their return to Earth, Scott and his crewmates fell from favour with NASA after it was disclosed that they had carried four hundred unauthorized postal covers to the Moon. After serving as director of NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in California, Scott retired from the agency in 1977. Since then, he has worked on a number of space-related projects and served as a consultant for several films about the space program, including Apollo 13. Alfred Merrill Worden (February 7, 1932 - March 18, 2020) was an American test pilot, engineer and NASA astronaut who was the command module pilot for the Apollo 15 lunar mission in 1971. One of only 24 people to have flown to the Moon, he orbited it 74 times in the command module (CM) Endeavour. Worden was born in Michigan in 1932; he spent his early years living on farms and attended the University of Michigan for one year, before securing an appointment to the United States Military Academy at West Point, New York. Graduating in 1955, he elected to be commissioned in the United States Air Force, though he had no piloting experience. He proved adept at flying fighter planes, and honed his skills, becoming a test pilot before his selection as a Group 5 astronaut in 1966. He served on the support crew for Apollo 9 and the backup crew for Apollo 12 before his selection for the Apollo 15 crew in 1970, with David Scott as commander and James Irwin as lunar module pilot. After Apollo 15 reached lunar orbit, and his crewmates departed to land on the Moon, Worden spent three days alone in the CM, becoming in the process the individual who travelled the farthest from any other human being, a distinction he still holds. He took many photographs of the Moon and operated a suite of scientific instruments that probed the Moon. During Apollo 15's return flight to Earth, Worden performed an extravehicular activity (EVA), or spacewalk, to retrieve film cassettes from cameras on the exterior of the spacecraft. It was the first "deep space" EVA in history, and as of 2022 remains the one that has taken place farthest from Earth. After their return, the crew became involved in a controversy over postal covers they had taken to the Moon; they were reprimanded by NASA and did not fly in space again. Worden remained at NASA until 1975 at the Ames Research Center, then entered the private sector. He engaged in a variety of business activities and had a longtime involvement with the Astronaut Scholarship Foundation, serving as chair of its board of directors from 2005 until 2011. He made many public appearances, promoting a renewed space program and education in the sciences, before his death in 2020. Good Condition. All autographs come with a Certificate of Authenticity. We combine postage on multiple winning lots and can ship worldwide. UK postage from £5.99, EU from £7.99, Rest of World from £9.99
Apollo15 moonwalker Dave Scott and CMP Alfred Worden signed Space cover NASA Astronauts. 2001 30th Anniversary Apollo 15. postmarked cover. Superb illustration on front of scenes from the mission. Also illustrated on back with crew names and mission information. David Randolph Scott (born June 6, 1932) is an American retired test pilot and NASA astronaut who was the seventh person to walk on the Moon. Selected as part of the third group of astronauts in 1963, Scott flew to space three times and commanded Apollo 15, the fourth lunar landing; he is one of four surviving Moon walkers and the last surviving crew member of Apollo 15. Before becoming an astronaut, Scott graduated from the United States Military Academy at West Point and joined the Air Force. After serving as a fighter pilot in Europe, he graduated from the Air Force Experimental Test Pilot School (Class 62C) and the Aerospace Research Pilot School (Class IV). Scott retired from the Air Force in 1975 with the rank of colonel, and more than 5,600 hours of logged flying time. As an astronaut, Scott made his first flight into space as a pilot of the Gemini 8 mission, along with Neil Armstrong, in March 1966, spending just under eleven hours in low Earth orbit. He would have been the second American astronaut to walk in space had Gemini 8 not made an emergency abort. Scott then spent ten days in orbit in March 1969 as Command Module Pilot of Apollo 9, a mission that extensively tested the Apollo spacecraft, along with Commander James McDivitt and Lunar Module Pilot Rusty Schweickart. After backing up Apollo 12, Scott made his third and final flight into space as commander of the Apollo 15 mission, the fourth crewed lunar landing and the first J mission. Scott and James Irwin remained on the Moon for three days. Following their return to Earth, Scott and his crewmates fell from favour with NASA after it was disclosed that they had carried four hundred unauthorized postal covers to the Moon. After serving as director of NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in California, Scott retired from the agency in 1977. Since then, he has worked on a number of space-related projects and served as a consultant for several films about the space program, including Apollo 13. Alfred Merrill Worden (February 7, 1932 - March 18, 2020) was an American test pilot, engineer and NASA astronaut who was the command module pilot for the Apollo 15 lunar mission in 1971. One of only 24 people to have flown to the Moon, he orbited it 74 times in the command module (CM) Endeavour. Worden was born in Michigan in 1932; he spent his early years living on farms and attended the University of Michigan for one year, before securing an appointment to the United States Military Academy at West Point, New York. Graduating in 1955, he elected to be commissioned in the United States Air Force, though he had no piloting experience. He proved adept at flying fighter planes, and honed his skills, becoming a test pilot before his selection as a Group 5 astronaut in 1966. He served on the support crew for Apollo 9 and the backup crew for Apollo 12 before his selection for the Apollo 15 crew in 1970, with David Scott as commander and James Irwin as lunar module pilot. After Apollo 15 reached lunar orbit, and his crewmates departed to land on the Moon, Worden spent three days alone in the CM, becoming in the process the individual who travelled the farthest from any other human being, a distinction he still holds. He took many photographs of the Moon and operated a suite of scientific instruments that probed the Moon. During Apollo 15's return flight to Earth, Worden performed an extravehicular activity (EVA), or spacewalk, to retrieve film cassettes from cameras on the exterior of the spacecraft. It was the first "deep space" EVA in history, and as of 2022 remains the one that has taken place farthest from Earth. After their return, the crew became involved in a controversy over postal covers they had taken to the Moon; they were reprimanded by NASA and did not fly in space again. Worden remained at NASA until 1975 at the Ames Research Center, then entered the private sector. He engaged in a variety of business activities and had a longtime involvement with the Astronaut Scholarship Foundation, serving as chair of its board of directors from 2005 until 2011. He made many public appearances, promoting a renewed space program and education in the sciences, before his death in 2020. Good condition. All autographs come with a Certificate of Authenticity. We combine postage on multiple winning lots and can ship worldwide. UK postage from £5.99, EU from £7.99, Rest of World from £9.99
Apollo15 moonwalker Dave Scott and CMP Alfred Worden signed Space cover NASA Astronauts. 2001 30th Anniversary Apollo 15. postmarked cover. Superb illustration on front of scenes from the mission. Also illustrated on back with crew names and mission information. David Randolph Scott (born June 6, 1932) is an American retired test pilot and NASA astronaut who was the seventh person to walk on the Moon. Selected as part of the third group of astronauts in 1963, Scott flew to space three times and commanded Apollo 15, the fourth lunar landing; he is one of four surviving Moon walkers and the last surviving crew member of Apollo 15. Before becoming an astronaut, Scott graduated from the United States Military Academy at West Point and joined the Air Force. After serving as a fighter pilot in Europe, he graduated from the Air Force Experimental Test Pilot School (Class 62C) and the Aerospace Research Pilot School (Class IV). Scott retired from the Air Force in 1975 with the rank of colonel, and more than 5,600 hours of logged flying time. As an astronaut, Scott made his first flight into space as a pilot of the Gemini 8 mission, along with Neil Armstrong, in March 1966, spending just under eleven hours in low Earth orbit. He would have been the second American astronaut to walk in space had Gemini 8 not made an emergency abort. Scott then spent ten days in orbit in March 1969 as Command Module Pilot of Apollo 9, a mission that extensively tested the Apollo spacecraft, along with Commander James McDivitt and Lunar Module Pilot Rusty Schweickart. After backing up Apollo 12, Scott made his third and final flight into space as commander of the Apollo 15 mission, the fourth crewed lunar landing and the first J mission. Scott and James Irwin remained on the Moon for three days. Following their return to Earth, Scott and his crewmates fell from favour with NASA after it was disclosed that they had carried four hundred unauthorized postal covers to the Moon. After serving as director of NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in California, Scott retired from the agency in 1977. Since then, he has worked on a number of space-related projects and served as a consultant for several films about the space program, including Apollo 13. Alfred Merrill Worden (February 7, 1932 - March 18, 2020) was an American test pilot, engineer and NASA astronaut who was the command module pilot for the Apollo 15 lunar mission in 1971. One of only 24 people to have flown to the Moon, he orbited it 74 times in the command module (CM) Endeavour. Worden was born in Michigan in 1932; he spent his early years living on farms and attended the University of Michigan for one year, before securing an appointment to the United States Military Academy at West Point, New York. Graduating in 1955, he elected to be commissioned in the United States Air Force, though he had no piloting experience. He proved adept at flying fighter planes, and honed his skills, becoming a test pilot before his selection as a Group 5 astronaut in 1966. He served on the support crew for Apollo 9 and the backup crew for Apollo 12 before his selection for the Apollo 15 crew in 1970, with David Scott as commander and James Irwin as lunar module pilot. After Apollo 15 reached lunar orbit, and his crewmates departed to land on the Moon, Worden spent three days alone in the CM, becoming in the process the individual who travelled the farthest from any other human being, a distinction he still holds. He took many photographs of the Moon and operated a suite of scientific instruments that probed the Moon. During Apollo 15's return flight to Earth, Worden performed an extravehicular activity (EVA), or spacewalk, to retrieve film cassettes from cameras on the exterior of the spacecraft. It was the first "deep space" EVA in history, and as of 2022 remains the one that has taken place farthest from Earth. After their return, the crew became involved in a controversy over postal covers they had taken to the Moon; they were reprimanded by NASA and did not fly in space again. Worden remained at NASA until 1975 at the Ames Research Center, then entered the private sector. He engaged in a variety of business activities and had a longtime involvement with the Astronaut Scholarship Foundation, serving as chair of its board of directors from 2005 until 2011. He made many public appearances, promoting a renewed space program and education in the sciences, before his death in 2020. Good condition. All autographs come with a Certificate of Authenticity. We combine postage on multiple winning lots and can ship worldwide. UK postage from £5.99, EU from £7.99, Rest of World from £9.99
A collection of scientific instruments and equipment, including a WWII brass telescope, inscribed 'W. Ottway & Co Ltd, Ealing, London, 1941, Patt. No. G 2020' and with broad arrow below, in original wooden case, 38 by 9 by 9cm, a Britannic adding machine, cased, 36 by 19 by 18cm, a reproduction brass sextant, and a cased set of medical instruments of graduating size, possibly for female patients. (8)
Physik - Astronomie - Scholastik - - Cursus philosophicus ad usum scola benedictina accomodatus. Manuskript mit 1 gestoch. Frontispiz (Paris, Crespy) u. zahlr., z.T. gefalt. Baumdiagrammen, Tabellen und Tuschezeichnungen. 1740-41. 166, 126, 173 S. Gr.-8°. Restaurierter Ldr. d. Zt. (etwas berieben). Das allegorische Frontispiz stellt den heiligen Benedikt dar, der vor der Heiligen Schrift kniet und von der Sphäre des Wissens erleuchtet wird. - Manuskript auf Papier für den Gebrauch in einer benediktinischen Institution, verfasst in Latein. Die zahlreichen Illustrationen sind im Text beschriftet und erläutert und die Akribie, mit der die Figuren gezeichnet und beschrieben wurden, legt die These eines für Publikationszwecke vorbereiteten Manuskripts nahe. - Dieses wichtige Werk besteht aus drei Teilen: Scholastik, Metaphysik, Physik. Der physikalische Teil ist mit wunderbaren Federzeichnungen illustriert, die wissenschaftliche Instrumente, verschiedene Experimente (Vakuum, Flüssigkeitsdynamik, etc.), Armillarsphären, Beschreibung meteorologischer Phänomene, Baumzucht und verschiedene kosmologische Systeme darstellen. Dieser Teil weist ein offensichtliches wissenschaftliches Interesse auf, wie die Tafel 7 auf Seite 92 zeigt, die den Fortschritt der Erkenntnisse über die physikalische Natur des Vakuums sowie die Experimente von Boyle, Toriccelli und Huyghens über die Schwerkraft der Luftmasse beschreibt. - Vereinzelte gelöste Blätter bzw. Montierungen. Stellenweise wurmgängig. Ein Blatt eingerissen. Am Ende etwas wasserrandig u. mit etwas sporfleckig. Nur stellenweise mit Randläsuren. - Hervorragendes Dokument der wissenschaftlichen und philosophischen Bildung im 18. Jahrhundert. Physics - Astronomy - Scholasticism - Manuscript with 1 engr. frontispiece (Paris, Crespy) and many, partly folded tree diagrams, tables and pen-and-ink drawings. - The allegorical frontispiece depicts St. Benedict kneeling before the Holy Scriptures, illuminated by the sphere of knowledge. - Manuscript course on paper for the use of a Benedictine institution, written in an intelligent and regular ink handwriting, in Latin. Illustrated with numerous tree diagrams, tables, some of them folding, and pen-and-ink drawings, captioned and explained in the text. This important (professorial?) work consists of three parts: scholasticism, metaphysics, physics, the physical part being illustrated with interesting pen drawings representing scientific instruments, various experiments (vacuum, fluid dynamics, etc.), cosmological systems. The meticulousness with which the figures have been drawn and described suggests the possibility of a manuscript prepared for publishing purposes. The last part, physics, particularly illustrated (armillary spheres, various cosmological systems, scientific instruments, description of meteorological phenomena, arboriculture) offers an obvious scientific interest, witness plate 7 on page 92 describing the progress of knowledge concerning the physical nature of the vacuum as well as the experiments of Boyle, Toriccelli and Huyghens on the gravity of the mass of the air. - In a contemporary, restored binding in full basane. Isolated detached leaves or mounted pieces of paper. Some worming in places. One leaf with tear. At the end somewhat waterstained and with some mould stains. Some marginal tears. - Extraordinary document of the scientific and philosophical education in the 18th century.
NO RESERVE Scientific Instruments.- Goodison (Nicholas) English Barometers 1680-1860, 1969 § Lennox-Boyd (Mark) Sundials: History, Art, People, Science, 2005 § Cleempoel (Koenraad van) Astrolabes at Greenwich: A Catalogue of the Astrolabes in the National Maritime Museum, Greenwich, Oxford, 2005 § Philip & Sons Ltd. (Trevor) Globes and the Mechanical Universe, 2010 § Bennett (J.A.) The Divided Circle: A History of Instruments for Astronomy, Navigation and Surveying, Oxford, 1987 § Hambley (Maya) Drawing Instruments 1580-1980, 1998, illustrations, original cloth or boards with dust-jackets, the first rubbed and frayed; and 12 others on scientific instruments, 4to & 8vo (18)
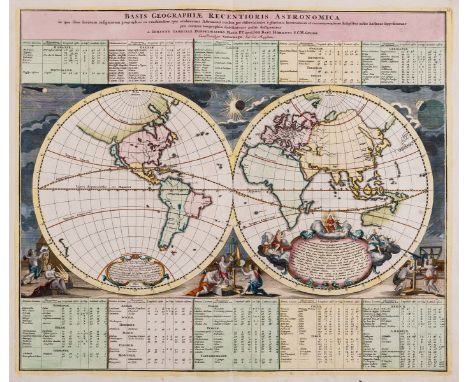
World.- Doppelmayr (Johann Gabriel) Basis Geographiae Recentioris Astronomica in qua Situs Locorum Insigniorum Geographici ea Exactitudine, qua Celeberrimi Astronomi Eosdem per Observationes..., double hemisphere world map showing the continents without political divisions, with California as an island, and only the western and northern coastlines of Australia shown, the surrounds are decorated with vignettes of putto with scientific instruments, and with solar events occurring in the sky, engraving with vibrant hand-colouring, on laid paper with indistinct text-based watermark, platemark 490 x 580 mm (19 1/4 x 22 3/4 in), sheet 530 x 615 mm (20 3/4 x 24 1/4 in), central vertical fold, minor handling creases, scattered surface dirt, unframed, Johann Baptist Homann, [circa 1742]
Apollo 15 Astronauts Dave Scott, Jim Irwin and Col Al Worden signed on two Space covers. Apollo 15 (July 26 - August 7, 1971) was the ninth crewed mission in the United States' Apollo program and the fourth to land on the Moon. It was the first J mission, with a longer stay on the Moon and a greater focus on science than earlier landings. Apollo 15 saw the first use of the Lunar Roving Vehicle. The mission began on July 26 and ended on August 7, with the lunar surface exploration taking place between July 30 and August 2. Commander David Scott and Lunar Module Pilot James Irwin landed near Hadley Rille and explored the local area using the rover, allowing them to travel further from the lunar module than had been possible on previous missions. They spent 181?2 hours on the Moon's surface on four extravehicular activities (EVA) and collected 170 pounds (77 kg) of surface material. At the same time, Command Module Pilot Alfred Worden orbited the Moon, operating the sensors in the scientific instrument module (SIM) bay of the service module. This suite of instruments collected data on the Moon and its environment using a panoramic camera, a gamma-ray spectrometer, a mapping camera, a laser altimeter, a mass spectrometer, and a lunar subsatellite deployed at the end of the moonwalks. The lunar module returned safely to the command module and, at the end of Apollo 15's 74th lunar orbit, the engine was fired for the journey home. During the return trip, Worden performed the first spacewalk in deep space. The Apollo 15 mission splashed down safely on August 7 despite the loss of one of its three parachutes. Good condition. All autographs come with a Certificate of Authenticity. We combine postage on multiple winning lots and can ship worldwide. UK postage from £5.99, EU from £7.99, Rest of World from £9.99
A good late 18th century mahogany quarter chiming longcase clockJames Allen, LondonThe pagoda top with ball and spire finials sitting on ribbed mouldings, the centre with shaped apron over silk backed sound frets mounted on brass stop-fluted Doric columns over a long door with flame veneer flanked by matching quarter columns on a doubled stepped plinth with applied moulded panel. The 12 inch arched brass dial with strike/silent over a Roman and Arabic chapter ring and scroll spandrels framing the matted centre with recessed seconds and applied arched signature riband. The movement with heavy plates united by five large knopped pillars, the going train with anchor escapement, the original pendulum with brass strip and lenticular bob suspended from a substantial back cock on the backplate, striking the hours on a bell and chiming the quarters on eight bells and hammers. Together with three brass-cased weights 2.55m (8ft 5ins) high. Footnotes:James Allan, also spelt Allen, was born in Forres, Scotland likely around 1739. He seems to have been initially apprenticed to a blacksmith in Forres, and after completing his apprenticeship he moved to London. By chance, he shared a house with a sextant maker, and apparently Allan would assist the sextant maker in the evenings. Allan must have preferred instrument making to blacksmithing, as by 1786 he was making Borda circles, likely with Jesse Ramsden, whom he appears to have remained close to throughout his life. In 1790, he was listed as working at 76 New Gravel Lane, before moving to 12 Blewit's Buildings, Fetter Lane around 1800, where he would remain for the rest of his career. In 1809, he is listed in the trade directories at this address as a 'divider of mathematical instruments'. In 1816, he published his own method for making highly accurate screws and was subsequently awarded a silver medal for his screw making, by the Society for the Encouragement of Arts, Manufacturers and Commerce. This same organisation gave him several awards throughout the years: two gold medals, one for his self-correcting dividing engine (1810) and another for a theodolite of his own manufacture (1815), as well as another silver medal for a new Reflecting Repeating circle (1811). On 3 February 1820, he received another award, of £100, this time from the Board of Longitude for his 'Self-Correcting Dividing Engine' used for the manufacturing of theodolites, sextants, etc. This engine is now in the Science Museum in London. It seems that shortly after this he moved back to Forres, where he died a year later, on 7 September 1821, his obituary being published in the Inverness Courier. James Allan would later be mentioned by Thomas Reid, in his Treatise on Clock and Watch Making: Theoretical and Practical, as a late watchmaker of London and a 'master in the art of dividing mathematical and astronomical instruments'.One of his sons, also James, served an apprenticeship to the well-known instrument maker Charles Fairbone, then worked in Ramsden's shop between 1813-1816, before transferring to Matthew Berge's shop located at 196 Piccadilly. In 1819, he and Nathaniel Worthington, a former apprentice to both Berge and Allan (Snr.) inherited the business on Berge's death, setting up the partnership of Worthington and Allan. Interestingly, James Allan, of 196 Piccadilly, was enrolled at the London Mechanics Institute between June 1825 to March 1826. The partnership between Worthington and Allan continued until 1835, after which point Worthington assumed full control, until his death in 1851. Whether Allan died in 1835, or the partners simply had a falling out, remains unknown.Another son, John, seems to have worked with his father between 1790-1794, before he established himself as a marine instrument maker in Baltimore, having left the UK in 1807. His adverts boasted that all the instruments were made using his father's improved dividing engine.Reid, T (1832) Treatise on Clock and Watch Making: Theoretical and Practical. Philadelphia: Carey & Lea.McConnell, A. (2016) Jesse Ramsden (1735–1800): London's Leading Scientific Instrument Maker. Abingdon-on-Thames: Routledge.de Clercq, P. R. (1985) 'Nineteenth-Century Scientific Instruments and their Makers: Papers presented' Fourth Scientific Instrument Symposium. October 1984.The British Antique Dealers' Association (2022). Worthington & Allan-London. Available at: https://www.bada.org/object/worthington-allan-london-outstanding-flat-wall-bow-front-mahogany-stick-barometer-circa-1820Public Ledger and Daily Advertiser. Friday 25 February 1820Inverness Courier.Thursday 13 September 1821Grace's Guide (2020) James Allan (London). Available at: https://www.gracesguide.co.uk/James_Allan_(London)#cite_note-3 This lot is subject to the following lot symbols: TPTP Lot will be moved to an offsite storage location (Cadogan Tate, Auction House Services, 241 Acton Lane, London NW10 7NP, UK) and will only be available for collection from this location at the date stated in the catalogue. Please note transfer and storage charges will apply to any lots not collected after 14 calendar days from the auction date.For further information on this lot please visit Bonhams.com
A unique and extremely interesting late 18th century ebonised longcase timepiece with additional counting featureWright, PoultryThe hood with serpentine arched cresting supported on freestanding brass-mounted Doric columns, with gilt-heightened gothic-arched glazed side doors over an elaborately stepped and moulded throat section, the long arched door with gilt-heightened raised moulding over a conforming stepped moulded section to the plain base on shaped apron. The 12-inch one-piece silvered arched dial centred by a Roman chapter ring with matching pierced blued steel hands, wound at VI, surmounted by a series of four subsidiary dials - the furthest to the right-hand side set with two hands simply giving running seconds and the hour in a 24-hour day. The remaining three are directly geared and mark the passing of each individual hour, their dials marked as 100; 1000 and 20,000.The large weight driven movement with plates measuring 21.5cms x 18cms (8.25ins x 7ins) united by four substantial knopped pillars, the large diameter barrel driving a four wheel train terminating in an anchor escapement set to the top right hand side of the plates, directly behind the subsidiary seconds dial, the plain pendulum suspended from a centrally-mounted cock, thereby necessitating a pivotted right-angled linkage to the crutch. Together with the pendulum with steel rectangular-section rod terminating in a brass bob, later crank winder, case key and brass-clad weight. 2.07m (6ft 10ins) highFootnotes:Thomas Wright was born around 1744 and was made Free of the Clockmakers Company in 1770, establishing himself in the Poultry likely at number 13, and moving later to number 6. At some point between 1770 and 1781, he was appointed watch and clockmaker to the King, though how he obtained this distinction is unknown. Around 1781, Thomas Earnshaw approached Wright to finance his patent for a detached spring chronometer escapement, the former having previously had a falling out with his previous financer. After much discussion, it was decided that Wright would file the patent on Earnshaw's behalf, and Earnshaw would recompensate Wright the 100-guinea patent fee, by charging an additional guinea for each of the first 100 chronometers sold. The patent, 1354, was filed by Wright in 1783. It has been claimed, by Earnshaw, that Wright insisted these first 100 chronometers bear the stamp Wright's Patent on the movement. One such chronometer is known which carries this stamp, though the others seem to use T. W. Pt. 34, with the T.W. presumably standing for Thomas Wright. In 1784, Earnshaw developed a bimetallic compensation balance, and the first watch this was used on was signed Thomas Wright in the Poultry, London, No. 2228. Thomas Earnshaw was not the only famous colleague Wright had, as he also worked with Matthew Boulton, of Lunar Society fame, beginning around 1770. Boulton and Wright produced a clock for King George III in 1771; Boulton supplied the gilt bronze and Blue John case, while Wright supplied the movement. It is possible that this is how Wright received his Royal warrant, though why Boulton contacted Wright in the first place is not clear. Although the clock was made for the King, the design was used by Bolton to manufacture at least six other 'King's clocks'. The escapement was originally verge but was replaced with a pin wheel in the 1820's by Benjamin Vulliamy. Wright is known to have had at least one child, George William, who was apprenticed to his father in 1785. Unfortunately, Wright died in 1792 on a visit to Birmingham, possibly to meet with Boulton, and his son does not appear to have been made free. There also does not seem to be a record of a 'George William Wright clockmaker' and it is possible he pursued a different career after his father's death. There is some indication that Wright's shop was taken over by a horologist named Thorp and the shop name became 'Wright & Thorp', though this hasn't been confirmed. Watches from Wright seem to be more prolific than his clocks, though some of Wright's work can be found at the Palace Museum in Peking.There was also a Thomas Wright of Fleet Street working between 1718-1748 as a scientific instrument maker. This Thomas Wright was also Mathematical Instrument Maker to His Royal Highness, George, Prince of Wales and famed as one of the best instrument makers of the day. Whether this was a relation of Thomas', possibly his father, remains unknown.Weaving, A. H. (1991) 'Clocks for the Emperor', Antiquarian Horolgy, Vol. 19 (4), pg. 389.Randall, A. G. (1984) 'An Early Pocket Chronometer by Tomas Earnshaw, signed Robert Tomlin', Antiquarian Horolgy, Vol. 14 (6), pgs. 609-615.Crisford, A. (1976) 'Thomas Wright in the Poultry London No. 2228', Antiquarian Horolgy, Vol. 9 (7), pgs. 785-788.Science Museum Group (2022) Thomas Wright. Available at: https://collection.sciencemuseumgroup.org.uk/people/cp38979/thomas-wrightSotheby's (2005) An important English ormolu musical and quarter chiming table clock, Thomas Wright and, Matthew Boulton, London and Birmingham, circa 1772. Available at: https://www.sothebys.com/en/auctions/ecatalogue/2005/fine-clocks-watches-barometers-mechanical-music-scientific-instruments-l05881/lot.77.htmlHobbins, J. H. (1912) 'The Chronometer: Its History and Use in Navigation', The Horological Journal, Vol. 55 (4), pgs. 57-65.The British Museum (2022) Thomas Wright. Available at: https://www.britishmuseum.org/collection/term/BIOG81737Atkins, C. E. (1931) The Company of Clockmakers: Register of Apprentices 1631-1931, London: The Clockmakers Company.Royal Collection Trust (2022) Mantel Clock. Available at: https://www.rct.uk/collection/30028/mantel-clockThis lot is subject to the following lot symbols: TPTP Lot will be moved to an offsite storage location (Cadogan Tate, Auction House Services, 241 Acton Lane, London NW10 7NP, UK) and will only be available for collection from this location at the date stated in the catalogue. Please note transfer and storage charges will apply to any lots not collected after 14 calendar days from the auction date.For further information on this lot please visit Bonhams.com
Breitling. A titanium multifunction flyback chronograph, perpetual calendar wristwatch with digital display, Cockpit, B50, EB5010, circa 2015. Movement: cal. B50 SuperQuartz. Dial: blue, luminescent Arabic numerals, applied Arabic numerals, digital displays for split chronograph, alarms, lap function, countdown timer, calendar, UTC worldtime. Case: titanium, screw-down back, no. 1702876, titanium bracelet. Signed: case, dial, movement and bracelet. Dimensions: diameter 47mm, bracelet circumference approximately 180mm. Accessories: International Warranty, Attestation De Chronomètre, instructions, spare links, presentation case and charger. £1,700-£2,000 --- Breitling was founded in the Swiss Jura in 1884 by Léon Breitling, creating scientific chronographs and timers. In 1934 Breitling patented the breakthrough chronograph with a second pusher at 4 o’clock which resets the chronograph to zero, this innovation would lead to the development of chronograph wristwatch we know today. The brand became extremely popular with aviators and large orders from the British Airforce were to follow, supplying chronograph instruments for airplane dashboards. The brand has become synonymous with revolutionary technology to conquer the skies.
Joseph Furttenbach Mechanische ReißLaden, das ist ein gar geschmeidige, bey sich verborgen tragende Laden, die aber solcher gestalt, dass .. alle fünffzehen Recreationen .. dem Menschen begnadeten Ingenieurkunst .. exercirt werden. Augsburg, J. Schultes 1644. Erste Ausgabe dieser Beschreibung einer vielseitig einsetzbaren Instrumenten-Sammlung. Erste Ausgabe. - 'A remarkable collection of scientific Instruments, carefully described and depicted, applied to Mathematics, Surveying, Astronomy, Navigation, Fireworks, Gunnery, and Civil, Military, and Naval Architecture' (Sotheran). EINBAND: Halbpergamentband des 19. Jahrhunderts mit marmorierten Bezugspapieren. 16 : 20,5 cm. - ILLUSTRATION: Mit gestochenem doppelblattgr. Frontispiz und 4 gefalteten Kupfertafeln von Raphael Custos. - KOLLATION: 5 Bll., 104 S., 5 Bll. LITERATUR: Ornamentstich-Slg. Bln. 1727. - Sotheran I, 8189. - Lotz S. 30. First edition. With double-page engraved frontispiece and 4 folded engraved plates. Half vellum of 19th century with marbled boards. - 2 plates with small tears in the margin. - Fine copy. Dieses Objekt wird regel- oder differenzbesteuert angeboten.
comprising of: Collection Nachet, Instruments Scientifiques et Livres Anciens, Notice Sur L'Invention Du Microscope Et Son Evolution Par Albert Nachet, 1929 1st edition, grey paper cover, Condition: spine string perished, cover loose, pages good; A bound copy of three early 20th century French scientific instrument sales including a Drouot Catalogue from 1911, A Drouot cataloge from 1935, a catalogue of instruments from the collection of J. A. Billmier, a catalogue from Drouot dated 1956 with handwritten list of results. Two German catalogues of scientific instruments from 1923 with early Sotheby & Co bookplate and another from 1924 (4)
* Zoetrope. A Victorian zoetrope, c. 1890s, comprising a circular tin drum with 13 slots, black exterior and white interior, supported on a spindle on a turned wooden base, the drum 28 cm diameter and 20 cm high, together with 2 contemporary geometric zoetrope discs and 24 colour lithographic zoetrope strips on paper, mostly with 13 images and showing horses, animals, scientific instruments, dancing, spinning tops and humorous scenes, strips 8 x 85 cmQTY: (27)
Scientific instruments. An English brass level, Watson & Son 313 High Holborn London, No 618, c1900, the telescope surmounted by a bubble level, a compass below with floating circle of degrees, on staff head mount, 38cm l, fitted teak case with leather strap and a folding tripod (2) Good condition
-
1583 item(s)/page